Body Systems Working Together
... • Food/nutrients are brought into the body through the digestive system where it is broken down into very small molecules • The Circulatory system carries these nutrient molecules around the body to the cells • Endocrine: produces substances, like insulin, which aid in the absorption of the nutrient ...
... • Food/nutrients are brought into the body through the digestive system where it is broken down into very small molecules • The Circulatory system carries these nutrient molecules around the body to the cells • Endocrine: produces substances, like insulin, which aid in the absorption of the nutrient ...
NSS 211 - National Open University of Nigeria
... which also has Greek origin, is the study of how organisms perform their vital functions. An example is the study of how a muscle contracts or what kind of forces contracting muscles exert on the skeleton. ...
... which also has Greek origin, is the study of how organisms perform their vital functions. An example is the study of how a muscle contracts or what kind of forces contracting muscles exert on the skeleton. ...
Characteristics ~
... – Ectoderm, a layer of cells on the outer surface of the gastrula, grows and divides developing into skin and nervous tissue. – Endoderm, a layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula, develops into the lining of the animal’s digestive tract. – Mesoderm, made up of two layers of cells ly ...
... – Ectoderm, a layer of cells on the outer surface of the gastrula, grows and divides developing into skin and nervous tissue. – Endoderm, a layer of cells lining the inner surface of the gastrula, develops into the lining of the animal’s digestive tract. – Mesoderm, made up of two layers of cells ly ...
Associate Program Faculty Notes (Standard)
... It is the “aerobic harvesting of chemical energy from organic fuel molecules” (Simon, Reece, & Dickey, 2010, p. 94). The three stages are glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and electron transport. Refer to p. 96 of the text. What is the role of glycolysis? Include the reactants and the products. Where d ...
... It is the “aerobic harvesting of chemical energy from organic fuel molecules” (Simon, Reece, & Dickey, 2010, p. 94). The three stages are glycolysis, citric acid cycle, and electron transport. Refer to p. 96 of the text. What is the role of glycolysis? Include the reactants and the products. Where d ...
Name Notes Page ______ 1 Bacteria Objectives
... o Methanogens take their name from methane, the natural gas they produce. These Archaea die if they are exposed to oxygen. They may live in the dense mud of swamps and marshes, and in the guts of animals such as cows and termites. o Halophiles live in very salty lakes and ponds. Some halophiles die ...
... o Methanogens take their name from methane, the natural gas they produce. These Archaea die if they are exposed to oxygen. They may live in the dense mud of swamps and marshes, and in the guts of animals such as cows and termites. o Halophiles live in very salty lakes and ponds. Some halophiles die ...
Study Guide Human Anatomy 231
... you are a more typical student, you may have more than 1,600 - 1,800 new terms to learn in this class. That comes out to more than 100 new terms per week for a full-length semester! While there are many hundreds of new terms for you to learn in this class, that is not as onerous as it seems. The par ...
... you are a more typical student, you may have more than 1,600 - 1,800 new terms to learn in this class. That comes out to more than 100 new terms per week for a full-length semester! While there are many hundreds of new terms for you to learn in this class, that is not as onerous as it seems. The par ...
Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Question
... 1. Define Tissue. Answer: It is the group of similar cells along with intercellular substances Performing specific functioin. 2. What is organ system? Answer: When two or more organs perform a common function by their physical and/or chemical interaction they together form organ system. 3. Which tis ...
... 1. Define Tissue. Answer: It is the group of similar cells along with intercellular substances Performing specific functioin. 2. What is organ system? Answer: When two or more organs perform a common function by their physical and/or chemical interaction they together form organ system. 3. Which tis ...
HISTOLOGY— THE STUDY OF TISSUES
... understanding, the biologists of past generations were not discouraged by this complexity, but discovered patterns that made it more understandable. One pattern is the fact that these trillions of cells belong to only 200 different types or so, and these cells are organized into tissues that fall in ...
... understanding, the biologists of past generations were not discouraged by this complexity, but discovered patterns that made it more understandable. One pattern is the fact that these trillions of cells belong to only 200 different types or so, and these cells are organized into tissues that fall in ...
The Human Body—An Orientation Anatomy—Levels of Study The
... o Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors o Responds to internal and external change o Sends messages via nerve impulses to central nervous system o Central nervous system activates effectors (muscles and glands) ...
... o Consists of brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sensory receptors o Responds to internal and external change o Sends messages via nerve impulses to central nervous system o Central nervous system activates effectors (muscles and glands) ...
Movement In and Out of Cells
... Water molecules diffuse across the membrane from the weak sugar solution into the strong sugar solution. This continues until the concentration is the same on both sides of the membrane. 37 of 44 ...
... Water molecules diffuse across the membrane from the weak sugar solution into the strong sugar solution. This continues until the concentration is the same on both sides of the membrane. 37 of 44 ...
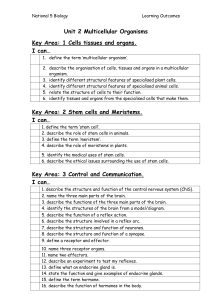
Unit 2 Key areas
... 12. describe an experiment to test my reflexes. 13. define what an endocrine gland is. 14. state the function and give examples of endocrine glands. 15. define the term hormone. 16. describe the function of hormones in the body. ...
... 12. describe an experiment to test my reflexes. 13. define what an endocrine gland is. 14. state the function and give examples of endocrine glands. 15. define the term hormone. 16. describe the function of hormones in the body. ...
Biology
... the antelope. The antelope eats grass. The grass uses the nutrients from the dead lion to grow.) • Structure and function: (Xylem is a hallow tube. In plants xylem is used to transport water from the roots of plants to all ends of the plant.) • Stability and change: (Bacteria will reproduce using mi ...
... the antelope. The antelope eats grass. The grass uses the nutrients from the dead lion to grow.) • Structure and function: (Xylem is a hallow tube. In plants xylem is used to transport water from the roots of plants to all ends of the plant.) • Stability and change: (Bacteria will reproduce using mi ...
Nancy Caroline`s Emergency Care in the Streets, Seventh Edition
... help them understand and apply concepts of pathophysiology in subsequent lessons. It is also the foundation for determining possible consequences of the mechanism of injury and nature of illness as they assess patients in the field. Nearly every chapter has extensive relevance to a thorough foundati ...
... help them understand and apply concepts of pathophysiology in subsequent lessons. It is also the foundation for determining possible consequences of the mechanism of injury and nature of illness as they assess patients in the field. Nearly every chapter has extensive relevance to a thorough foundati ...
Interstitial fluid and the lymph
... • The clear, watery blood plasma -- containing the oxygen, proteins, glucose and white blood cells -- "leaks" out through the capillary walls and flows around all the cells. • The pores in the capillaries are too small to let red blood cells through, however All of the cells in your body are therefo ...
... • The clear, watery blood plasma -- containing the oxygen, proteins, glucose and white blood cells -- "leaks" out through the capillary walls and flows around all the cells. • The pores in the capillaries are too small to let red blood cells through, however All of the cells in your body are therefo ...
Missouri State Standards (Biology I End of Course Exam) Biology
... I. There is a fundamental unity underlying the diversity of all living organisms 1. Recognize cells both increase in number and differentiate, becoming specialized in structure and function, during and after embryonic development. DOK: 1 2. Describe the structure of cell parts (e.g., cell wall, cell ...
... I. There is a fundamental unity underlying the diversity of all living organisms 1. Recognize cells both increase in number and differentiate, becoming specialized in structure and function, during and after embryonic development. DOK: 1 2. Describe the structure of cell parts (e.g., cell wall, cell ...
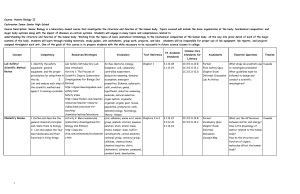
Concept Competency Resources/Strategies Vocabulary Text
... Course Description: Senior Biology is a laboratory-based course that investigates the structure and function of the human body. Topics covered will include the basic organization of the body; biochemical composition; and major body systems along with the impact of diseases on certain systems. Studen ...
... Course Description: Senior Biology is a laboratory-based course that investigates the structure and function of the human body. Topics covered will include the basic organization of the body; biochemical composition; and major body systems along with the impact of diseases on certain systems. Studen ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Cellular Physiology: Membrane Transport Membrane Transport – movement of substance into and out of the cell ...
... Cellular Physiology: Membrane Transport Membrane Transport – movement of substance into and out of the cell ...
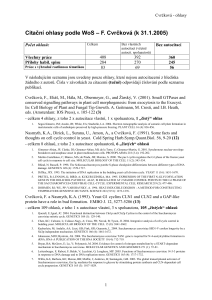
Citační ohlasy podle WoS – F. Cvrčková (k 31.1.2005)
... 40. Bouquin, N; Johnson, AL; Morgan, BA; Johnston, LH. 1999. Association of the cell cycle transcription factor Mbp1 with the Skn7 response regulator in budding yeast. MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF THE CELL 10 (10): 3389-3400. 41. Levine, K; Kiang, L; Jacobson, MD; Fisher, RP; Cross, FR. 1999. Directed evolu ...
... 40. Bouquin, N; Johnson, AL; Morgan, BA; Johnston, LH. 1999. Association of the cell cycle transcription factor Mbp1 with the Skn7 response regulator in budding yeast. MOLECULAR BIOLOGY OF THE CELL 10 (10): 3389-3400. 41. Levine, K; Kiang, L; Jacobson, MD; Fisher, RP; Cross, FR. 1999. Directed evolu ...
Section 1 - WordPress.com
... similar to and different from each other? How are living things similar to and different from non-living things? Why are levels of organization for structures and function important? ...
... similar to and different from each other? How are living things similar to and different from non-living things? Why are levels of organization for structures and function important? ...
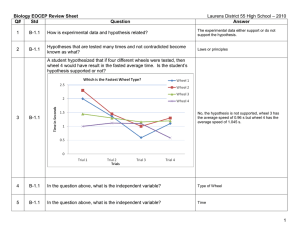
BIOL 218 F 2011 MTX 1 Q 110912.3
... Illustration of Body Cavities See Column II for Choices 63. Name this body region ILLUSTRATION ...
... Illustration of Body Cavities See Column II for Choices 63. Name this body region ILLUSTRATION ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.