A sweet trick for fighting infection
... “tremendous success” but notes there could be room to improve further too. In some cases where the native bacterial structure can’t be used a synthetic structure produced in a chemistry lab is an attractive alternative. And it’s not just bacteria he has in his sights: he is also looking at how cleve ...
... “tremendous success” but notes there could be room to improve further too. In some cases where the native bacterial structure can’t be used a synthetic structure produced in a chemistry lab is an attractive alternative. And it’s not just bacteria he has in his sights: he is also looking at how cleve ...
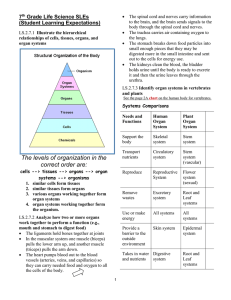
Human Body Introduction - Living Environment H: 8(A,C)
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
Electrons - davis.k12.ut.us
... Most atoms have too many or too few electrons in their outermost energy level which is not complete. Valance is the number of extra or deficient electrons in outermost orbital. Anions - extra electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net negative charge. Cation - deficient electrons in outermos ...
... Most atoms have too many or too few electrons in their outermost energy level which is not complete. Valance is the number of extra or deficient electrons in outermost orbital. Anions - extra electrons in outermost orbital which creates a net negative charge. Cation - deficient electrons in outermos ...
Lecture 1 (1/14/08) "King Kong and Evolution"
... Given distance to each of our solar system’s planets, calculation whether water-based life could exist. ...
... Given distance to each of our solar system’s planets, calculation whether water-based life could exist. ...
Lecture 1 (1/14/08) "King Kong and Evolution"
... Given distance to each of our solar system’s planets, calculation whether water-based life could exist. ...
... Given distance to each of our solar system’s planets, calculation whether water-based life could exist. ...
PART I CHAPTER <^ STUDY GUIDE NA?1E 1. Animals without
... What materials are spicules made:of?? Fibrous network of tough, flexible material-sthat-rmake.nup certain sponges ••'••*•-•?!>'' • • :~ •: y^-'\?r- -srl? ac. * :.-\--• ..- \- . 37. .Term which means a sponge is permanently:attached ^tp--something by'its base •_ ...
... What materials are spicules made:of?? Fibrous network of tough, flexible material-sthat-rmake.nup certain sponges ••'••*•-•?!>'' • • :~ •: y^-'\?r- -srl? ac. * :.-\--• ..- \- . 37. .Term which means a sponge is permanently:attached ^tp--something by'its base •_ ...
3584 the biology of flagellates and amoebas
... Chilomonas has two flagella. It absorbs nutrients directly from decomposing vegetation, as does Astasia, an “instant species” derived from a Euglena that has lost its chloroplasts. Colonial flagellates suggest a possible evolutionary bridge between single cells and simple multicellular plants. Volv ...
... Chilomonas has two flagella. It absorbs nutrients directly from decomposing vegetation, as does Astasia, an “instant species” derived from a Euglena that has lost its chloroplasts. Colonial flagellates suggest a possible evolutionary bridge between single cells and simple multicellular plants. Volv ...
Cells and Systems Quiz – Section 1 and 2 – Study Guide
... chemical digestion, peristalsis, villi, alveoli, trachea, ureter, urethra, nephron, sweat glands, peripheral nervous system, central nervous system Be Able to Explain ...
... chemical digestion, peristalsis, villi, alveoli, trachea, ureter, urethra, nephron, sweat glands, peripheral nervous system, central nervous system Be Able to Explain ...
DIVERSITY INL IVINGO RGANISMS
... for thousands of years while insects like mosquitoes die within a few days. Life also ranges from colourless or even transparent worms to brightly coloured birds and flowers. This bewildering variety of life around us has evolved on the earth over millions of years. However, we do not have more than ...
... for thousands of years while insects like mosquitoes die within a few days. Life also ranges from colourless or even transparent worms to brightly coloured birds and flowers. This bewildering variety of life around us has evolved on the earth over millions of years. However, we do not have more than ...
Document
... Zygote: A single sperm penetrates the mother's egg cell, and the resulting cell is called a zygote. The zygote is a single cell. The zygote contains all of the genetic information (DNA) necessary to become a child. Half of the genetic information comes from the mother' s egg (23 chromosomes) and hal ...
... Zygote: A single sperm penetrates the mother's egg cell, and the resulting cell is called a zygote. The zygote is a single cell. The zygote contains all of the genetic information (DNA) necessary to become a child. Half of the genetic information comes from the mother' s egg (23 chromosomes) and hal ...
Student Packet 16 Plant Animal Cells L.14.3
... Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 as amended - prohibits discrimination in employment on the basis of race, color, religion, gender, or national origin. Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 - prohibits discrimination on the basis of gender. Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 196 ...
... Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 as amended - prohibits discrimination in employment on the basis of race, color, religion, gender, or national origin. Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 - prohibits discrimination on the basis of gender. Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 196 ...
Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi
... obtaining food and energy An organism that cannot manufacture its own food and instead obtains its food and energy by taking in organic substances, usually plant or animal matter. All animals, protozoans, fungi, and most bacteria are HETEROTROPHS. An organism that manufactures its own food from inor ...
... obtaining food and energy An organism that cannot manufacture its own food and instead obtains its food and energy by taking in organic substances, usually plant or animal matter. All animals, protozoans, fungi, and most bacteria are HETEROTROPHS. An organism that manufactures its own food from inor ...
Cell Biology Unit
... 1.2f - Cells have particular structures that perform specific jobs. These structures perform the actual work of the cell. Just as systems are coordinated and work together, cell parts must also be coordinated and work together. 1.2g - Each cell is covered by a membrane that performs a number of impo ...
... 1.2f - Cells have particular structures that perform specific jobs. These structures perform the actual work of the cell. Just as systems are coordinated and work together, cell parts must also be coordinated and work together. 1.2g - Each cell is covered by a membrane that performs a number of impo ...
UNIT 1
... dead organism? Fill in the blanks using these words: alive (2), reproduce, time, dies , cells, environment. Nonliving organisms have never been………… They have never done the three basic functions of organisms: Feed, interact with the …………… and ………………… Nonliving things are not made up with …………. A dea ...
... dead organism? Fill in the blanks using these words: alive (2), reproduce, time, dies , cells, environment. Nonliving organisms have never been………… They have never done the three basic functions of organisms: Feed, interact with the …………… and ………………… Nonliving things are not made up with …………. A dea ...
ch1_objectives
... research developments that have advanced systems biology. Explain the importance of regulatory mechanisms in living things. Distinguish between positive and negative feedback. Evolution, Unity, and Diversity ...
... research developments that have advanced systems biology. Explain the importance of regulatory mechanisms in living things. Distinguish between positive and negative feedback. Evolution, Unity, and Diversity ...
Ch. 14.1 Notes
... DNA. • The fluid a between the cell membrane and the nucleus is the cytoplasm. ...
... DNA. • The fluid a between the cell membrane and the nucleus is the cytoplasm. ...
Note 9.1 - Maintaining Internal Balance
... a) Take in nutrients and other required chemicals from the environment, process and transported throughout the body, along with the removal of metabolic wastes. b) Synthesize proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other molecules essential for life. c) Sense and respond to changes in the external environ ...
... a) Take in nutrients and other required chemicals from the environment, process and transported throughout the body, along with the removal of metabolic wastes. b) Synthesize proteins, fats, carbohydrates and other molecules essential for life. c) Sense and respond to changes in the external environ ...
2017 RC 4 Student Notes PPT
... In humans, body temperature is controlled through various feedback mechanisms. On a warm day, physical activity of the muscular and skeletal system causes the endocrine system to signal the integumentary system to perspire until body temperature returns to normal. Animals obtain nutrients and energy ...
... In humans, body temperature is controlled through various feedback mechanisms. On a warm day, physical activity of the muscular and skeletal system causes the endocrine system to signal the integumentary system to perspire until body temperature returns to normal. Animals obtain nutrients and energy ...
Simple Sugars
... Starch and glycogen are both made from many glucose molecules, so how do the differ? ...
... Starch and glycogen are both made from many glucose molecules, so how do the differ? ...
TOPICS FOR EXAMINATION II – Biology 1406
... important? How is it postulated that vertebrate jaws evolved? What are the most important characteristics that define the birds and the mammals? ...
... important? How is it postulated that vertebrate jaws evolved? What are the most important characteristics that define the birds and the mammals? ...
Zoology – Cells
... a. Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. b. They help digest foreign material or engulfed bacteria by fusing with a food vacuole produced by phagocytosis. c. They destroy injured or diseased cells. E. ________________________________ (the Powerhouses of the cell) 1. T ...
... a. Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. b. They help digest foreign material or engulfed bacteria by fusing with a food vacuole produced by phagocytosis. c. They destroy injured or diseased cells. E. ________________________________ (the Powerhouses of the cell) 1. T ...
cell membrane - School
... 1. Label and identify the major structures that make up a typical animal cell. 2. Describe what these structures do. 3. Name and describe how 2 specialised animal cells are adapted for their job. ...
... 1. Label and identify the major structures that make up a typical animal cell. 2. Describe what these structures do. 3. Name and describe how 2 specialised animal cells are adapted for their job. ...
ANATOMY GIANT REVIEW PACKET Unit 1: Intro to Anatomy
... • Energy of motion • Energy being used right now ...
... • Energy of motion • Energy being used right now ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.