Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 3: Producing new cells
... o The 2 copies are called chromatids and they line up on the equator of the cell. o Spindle fibres pull the chromatids apart to opposite poles. o The cytoplasm divides and the nuclear membrane reforms. o 2 separate identical cells are formed. o Cell culture allows the growing of cells in a dish in a ...
... o The 2 copies are called chromatids and they line up on the equator of the cell. o Spindle fibres pull the chromatids apart to opposite poles. o The cytoplasm divides and the nuclear membrane reforms. o 2 separate identical cells are formed. o Cell culture allows the growing of cells in a dish in a ...
Evolution of bilateral symmetry
... Pseudocoelomates: Nematoda and Rotifera • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
... Pseudocoelomates: Nematoda and Rotifera • All pseudocoelomates lack a defined circulatory system, but most have a oneway digestive tract (meaning mouth and anus now) • In all pseudocoelomates, the pseudocoel serves as a hydrostatic skeleton ...
Jeoparday_Final
... The laws of probability apply to the allele that each parent will pass to its offspring through the sperm or the egg. Using the laws of probability we can determine the chances of offspring receiving a certain allele from the mother or the father. Depending on the allele that the offspring will get, ...
... The laws of probability apply to the allele that each parent will pass to its offspring through the sperm or the egg. Using the laws of probability we can determine the chances of offspring receiving a certain allele from the mother or the father. Depending on the allele that the offspring will get, ...
Press Release
... Heidelberg, 29 June 2007 - Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distribute ...
... Heidelberg, 29 June 2007 - Hormones control growth, metabolism, reproduction and many other important biological processes. In humans, and all other vertebrates, the chemical signals are produced by specialised brain centres such as the hypothalamus and secreted into the blood stream that distribute ...
INSIDE LIVING THINGS
... What part of the orange plant is this? Why does an orange tree grow fruit? What does an orange look like inside? Put students in groups. Have them discuss the parts they think are inside an orange. Then give each group an orange, a plate, and a plastic knife. Instruct students to use their knife to ...
... What part of the orange plant is this? Why does an orange tree grow fruit? What does an orange look like inside? Put students in groups. Have them discuss the parts they think are inside an orange. Then give each group an orange, a plate, and a plastic knife. Instruct students to use their knife to ...
Human Body Booklet
... 3. Describe the interactions with other systems in the human body. 4. Include a picture of the system or an individual organ in the system (some illustrations will be provided for you, some you will have to find on your own). 5. Include information regarding the rubric category you created on your o ...
... 3. Describe the interactions with other systems in the human body. 4. Include a picture of the system or an individual organ in the system (some illustrations will be provided for you, some you will have to find on your own). 5. Include information regarding the rubric category you created on your o ...
06/Simple Marine Animals
... Marine creatures can be found living anywhere from the ocean’s surface to its bottom. You learned that plankton are usually found near the surface. Zooplankton such as forams and radiolarians are both members of the larger group of unicellular animal-like organisms called protozoa. Thousands of spec ...
... Marine creatures can be found living anywhere from the ocean’s surface to its bottom. You learned that plankton are usually found near the surface. Zooplankton such as forams and radiolarians are both members of the larger group of unicellular animal-like organisms called protozoa. Thousands of spec ...
Drosophila
... equivalence - that is, they all have the same genes. • In many plants, whole new organisms can develop from differentiated somatic cells. •The fact that a mature plant cell can dedifferentiate (reverse its function) and then give rise to all the different kinds of specialized cells of a new plant ...
... equivalence - that is, they all have the same genes. • In many plants, whole new organisms can develop from differentiated somatic cells. •The fact that a mature plant cell can dedifferentiate (reverse its function) and then give rise to all the different kinds of specialized cells of a new plant ...
Biology Review Activity Booklet - Student 2014-15
... Using the forceps, remove the potato core from Beaker A (blue liquid) and pat it dry with a paper towel. With the metric ruler, measure the length of the potato core to the nearest millimeter. Record the results in the “after submersion” row of Table 1. Then use the metric balance to determine the m ...
... Using the forceps, remove the potato core from Beaker A (blue liquid) and pat it dry with a paper towel. With the metric ruler, measure the length of the potato core to the nearest millimeter. Record the results in the “after submersion” row of Table 1. Then use the metric balance to determine the m ...
lect 4
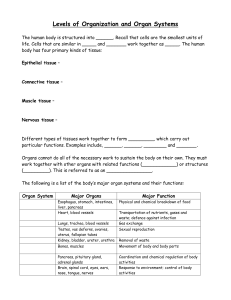
... A cell is the structural, functional, and biological unit of organisms. (1, 5, 6. 7, 8) “When two or more similar cells join together we get a tissue. Two or more similar tissue fuse to form a organ. Different organs function together to make a organ system.“ (8) ...
... A cell is the structural, functional, and biological unit of organisms. (1, 5, 6. 7, 8) “When two or more similar cells join together we get a tissue. Two or more similar tissue fuse to form a organ. Different organs function together to make a organ system.“ (8) ...
Nine Week Review Notes. Everything you need to know about cells
... All living things have six characteristics. If you don’t have all six you are not considered to be a living thing. Cells Chemicals of life Use energy Grow and develop Respond to surroundings Reproduce. Cellular Organization Cells are basic unit of structure all things are made of cells Unicellular A ...
... All living things have six characteristics. If you don’t have all six you are not considered to be a living thing. Cells Chemicals of life Use energy Grow and develop Respond to surroundings Reproduce. Cellular Organization Cells are basic unit of structure all things are made of cells Unicellular A ...
Chapter 9 Booklet
... specialized. For example nerve cells are long to allow them to transmit signals over a distance. Also each system in an animal or plant works to keep it alive by performing a specific life function. For example, plant roots are adapted to take in food and water, just as a human’s mouth and teeth all ...
... specialized. For example nerve cells are long to allow them to transmit signals over a distance. Also each system in an animal or plant works to keep it alive by performing a specific life function. For example, plant roots are adapted to take in food and water, just as a human’s mouth and teeth all ...
Science Demos, Labs
... digestive, circulatory, and respiratory systems in humans, and how these systems interact. ...
... digestive, circulatory, and respiratory systems in humans, and how these systems interact. ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... Their foods or nutrients are largely made up of pre-formed organic matter. These organic nutrients come from plant or animal sources. Heterotrophs may be classified differently depending on the ways in which they obtain their nutrients. Herbivores include those organisms whose main food sources ar ...
... Their foods or nutrients are largely made up of pre-formed organic matter. These organic nutrients come from plant or animal sources. Heterotrophs may be classified differently depending on the ways in which they obtain their nutrients. Herbivores include those organisms whose main food sources ar ...
SEMIOTICA VOLUME 127 NUMBER 1
... 15. Semiotics of the artificial: The ‘self’ of self-reproducing systems in cellular automata* Arantza Etxeberria and Jesus Ibanez ...
... 15. Semiotics of the artificial: The ‘self’ of self-reproducing systems in cellular automata* Arantza Etxeberria and Jesus Ibanez ...
Document
... Overview: Inquiring About Life • An organism’s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution – For example, the ghost plant is adapted to conserving water; this helps it to survive in the crevices of rock walls ...
... Overview: Inquiring About Life • An organism’s adaptations to its environment are the result of evolution – For example, the ghost plant is adapted to conserving water; this helps it to survive in the crevices of rock walls ...
here - Sensavis
... Precipitation........................................................................................................................................ 13 Vegetation......................................................................................................................................... ...
... Precipitation........................................................................................................................................ 13 Vegetation......................................................................................................................................... ...
General Microbiology 11:680:390 Description: General Microbiology
... 3. Laboratory grades (25%) will be assessed on a range of written reports, quizzes and a practical examination. Refer to your lab manual for lab grade breakdown. NOTE: A student must satisfactorily complete the laboratory section in order to pass the class. Overall Learning Goal: Students are expect ...
... 3. Laboratory grades (25%) will be assessed on a range of written reports, quizzes and a practical examination. Refer to your lab manual for lab grade breakdown. NOTE: A student must satisfactorily complete the laboratory section in order to pass the class. Overall Learning Goal: Students are expect ...
1 PRE-TEST
... This gives you a rough idea of the speed of diffusion of vinegar molecules through air. Inside and outside cells, water will diffuse from higher to lower concentration until it reaches equilibrium. This is called osmosis. The cytoplasm of a cell has many materials dissolved in it. When the cell is p ...
... This gives you a rough idea of the speed of diffusion of vinegar molecules through air. Inside and outside cells, water will diffuse from higher to lower concentration until it reaches equilibrium. This is called osmosis. The cytoplasm of a cell has many materials dissolved in it. When the cell is p ...
13 - Joe Griffin Media Ministries
... efficacious through the power of the Holy Spirit in accomplishing supernatural results. ...
... efficacious through the power of the Holy Spirit in accomplishing supernatural results. ...
1 mark - kcse
... State a factor that denatures enzymes Name the features that increase the surface area of small intestines ...
... State a factor that denatures enzymes Name the features that increase the surface area of small intestines ...
Spring Final Review Guide
... community, population energy flow in heterotrophic cells (eukaryotic cells) starts with food, then ATP then cell work Chemosynthesis ATP, ADP structure and function ...
... community, population energy flow in heterotrophic cells (eukaryotic cells) starts with food, then ATP then cell work Chemosynthesis ATP, ADP structure and function ...
Viruses - Ms. Keener
... • Bacteria can reproduce asexually (one parent) by means of binary fission: one cell divides into two identical cells. or • Bacteria can reproduce sexually (two parents) by means of conjunction: one bacteria transfers some genetic material to another bacteria though a thread like bridge. ...
... • Bacteria can reproduce asexually (one parent) by means of binary fission: one cell divides into two identical cells. or • Bacteria can reproduce sexually (two parents) by means of conjunction: one bacteria transfers some genetic material to another bacteria though a thread like bridge. ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.