1 CHAPTER 15. BIOCHEMISTRY: THE CHEMISTRY OF OUR
... molecule, linked together as shown in Fig. 15-2; such a sugar polymer is also called a polysaccharide. They are found mainly in the seeds of plants, where they serve as a reserve food supply for the newly sprouted plant. Tubers, like potatoes, which form on the roots of some plants, serve a similar ...
... molecule, linked together as shown in Fig. 15-2; such a sugar polymer is also called a polysaccharide. They are found mainly in the seeds of plants, where they serve as a reserve food supply for the newly sprouted plant. Tubers, like potatoes, which form on the roots of some plants, serve a similar ...
Biology Revision
... Cell Theory Cells were first described by Robert Hooke in 1665. In the 1830s two German scientists, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden, using light microscopes, suggested the cell theory: 1. All organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular (one celled) or multicellular (many celled). ...
... Cell Theory Cells were first described by Robert Hooke in 1665. In the 1830s two German scientists, Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden, using light microscopes, suggested the cell theory: 1. All organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular (one celled) or multicellular (many celled). ...
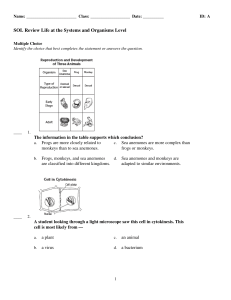
ExamView - SOL Review Life at the Systems and
... Fewer sugars stored in roots and stems would diffuse into the soil. ...
... Fewer sugars stored in roots and stems would diffuse into the soil. ...
Cnidarians and worms have different body plans.
... are so small and flat that they move with cilia, not muscles. These flatworms absorb nutrients directly through the skin. Many flatworms live as parasites, feeding off other organisms. For example, tapeworms are flatworms that infect humans and other animals. The tapeworm has no need for a digestive ...
... are so small and flat that they move with cilia, not muscles. These flatworms absorb nutrients directly through the skin. Many flatworms live as parasites, feeding off other organisms. For example, tapeworms are flatworms that infect humans and other animals. The tapeworm has no need for a digestive ...
Biology XI Support Material 2016
... -Organism viz. Planaria reproduce by regeneration in which a fragment of body forms whole organism. -Fungi, filamentousalgae, protonema of moss reproduce by fragmentation also. -In unicellular organisms growth & reproduction are synonymous. - Certain organisms do not reproduce viz. mule ,worker bees ...
... -Organism viz. Planaria reproduce by regeneration in which a fragment of body forms whole organism. -Fungi, filamentousalgae, protonema of moss reproduce by fragmentation also. -In unicellular organisms growth & reproduction are synonymous. - Certain organisms do not reproduce viz. mule ,worker bees ...
Human Systems and Homeostasis
... contrast, neurons develop extensions that transmit and receive messages from other neurons. Humans, like almost all multicellular organisms, are collections of specialized cells that work together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which is formed by the union of an egg and sperm. ...
... contrast, neurons develop extensions that transmit and receive messages from other neurons. Humans, like almost all multicellular organisms, are collections of specialized cells that work together. These cells arise from a single cell, the zygote, which is formed by the union of an egg and sperm. ...
Jeopardy - bussebio
... $400 Question from Evolution Over thousands of years a river forms in the middle of a forest. The river separates a population of squirrel. As time goes on the squirrel population evolve into 2 new species. What type of isolation is being described? ...
... $400 Question from Evolution Over thousands of years a river forms in the middle of a forest. The river separates a population of squirrel. As time goes on the squirrel population evolve into 2 new species. What type of isolation is being described? ...
Invertebrates
... blood vessels that act as pumps to force the blood along. The closed circulatory system of a few mollusks and other invertebrates( for example earthworms) is a much more efficient system. Here blood is pumped through a closed system of arteries, veins, and capillaries, much like us humans ...
... blood vessels that act as pumps to force the blood along. The closed circulatory system of a few mollusks and other invertebrates( for example earthworms) is a much more efficient system. Here blood is pumped through a closed system of arteries, veins, and capillaries, much like us humans ...
Points to take note for Biology - Learning Made Simple Singapore
... - Water is used for transport of various substances in animals (dissolved food substances and waste such as urea in blood) and plants (to carry dissolved mineral salts), heat regulation (water evaporates as sweat from skin in animals and transpiration in leaves help to cool down temperature), chemi ...
... - Water is used for transport of various substances in animals (dissolved food substances and waste such as urea in blood) and plants (to carry dissolved mineral salts), heat regulation (water evaporates as sweat from skin in animals and transpiration in leaves help to cool down temperature), chemi ...
Living Systems - Alaska K-12 Science Curricular Initiative (AKSCI)
... mammals; vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical and have an internal skeleton of bone or cartilage, a nervous system along the back that is divided into brain and spinal cord, and not more than two pairs of limbs ...
... mammals; vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical and have an internal skeleton of bone or cartilage, a nervous system along the back that is divided into brain and spinal cord, and not more than two pairs of limbs ...
Sec 1.4 Worms
... female individuals. --Other species have one individual with both male & female organs. -Some reproduce asexually by breaking into pieces. ...
... female individuals. --Other species have one individual with both male & female organs. -Some reproduce asexually by breaking into pieces. ...
GCSE Biology Textbook sample
... The size of sub-cellular structures is important. Mitochondria and chloroplasts vary in size and shape. The complexity of a mitochondrion indicates how active a cell is. Chloroplast size varies from one species to another. Scientists sometimes investigate the ratio of the area of the cytoplasm t ...
... The size of sub-cellular structures is important. Mitochondria and chloroplasts vary in size and shape. The complexity of a mitochondrion indicates how active a cell is. Chloroplast size varies from one species to another. Scientists sometimes investigate the ratio of the area of the cytoplasm t ...
Macmillan Science Library - Animal Sciences Vol..
... or as members of groups, or how they share resources within an ecosystem, to give just a few examples. Finally, Animal Sciences surveys the connection between animals and humans. Humans are unique in the animal kingdom because of their ability to alter environments significantly. Agriculture, which ...
... or as members of groups, or how they share resources within an ecosystem, to give just a few examples. Finally, Animal Sciences surveys the connection between animals and humans. Humans are unique in the animal kingdom because of their ability to alter environments significantly. Agriculture, which ...
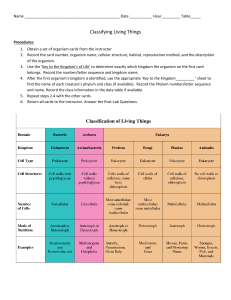
Classifying Living Things
... 1. a. Organism’s body usually small in size; no plant organs, roots, stems, leaves; no special structures for transporting food and water (non- vascular plants)……………………………………………………..………………..Phylum BRYOPHYTA (mosses) b. Organism’s body usually macroscopic; has well-defined organs—roots, stems, leaves ...
... 1. a. Organism’s body usually small in size; no plant organs, roots, stems, leaves; no special structures for transporting food and water (non- vascular plants)……………………………………………………..………………..Phylum BRYOPHYTA (mosses) b. Organism’s body usually macroscopic; has well-defined organs—roots, stems, leaves ...
functions
... • The glandular epithelia that line the lumen of the digestive and respiratory tracts form a mucous membrane that secretes a slimy solution called mucus that lubricates the surface and keeps it moist. • The free epithelial surfaces of some mucous membranes have beating cilia that move the film of mu ...
... • The glandular epithelia that line the lumen of the digestive and respiratory tracts form a mucous membrane that secretes a slimy solution called mucus that lubricates the surface and keeps it moist. • The free epithelial surfaces of some mucous membranes have beating cilia that move the film of mu ...
Solutions for all Natural Sciences Grade 9 Learner`s Book
... organised according to topics and each topic is structured in the same way: Topic opener page: The topic starts with a full-colour photograph of something that is related to the content of the topic. ‘What you will learn about in this topic’ lists the content to be covered in the topic. There is als ...
... organised according to topics and each topic is structured in the same way: Topic opener page: The topic starts with a full-colour photograph of something that is related to the content of the topic. ‘What you will learn about in this topic’ lists the content to be covered in the topic. There is als ...
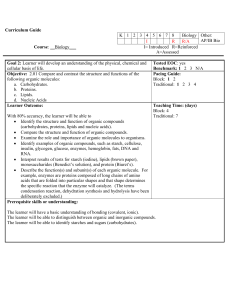
Curriculum Guide Template DRAFT
... parts of the cell, demonstrate knowledge of the parts of a cell in reference to cell functions and apply their knowledge of the cell and the cell parts to a real world situation. Writing: 15. Students will define essential vocabulary using a three part definition (term, classification, distinguishin ...
... parts of the cell, demonstrate knowledge of the parts of a cell in reference to cell functions and apply their knowledge of the cell and the cell parts to a real world situation. Writing: 15. Students will define essential vocabulary using a three part definition (term, classification, distinguishin ...
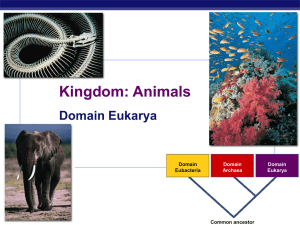
Common Ancestry
... Cells can create more complex molecules from simpler molecules. An example of this is protein synthesis where proteins are created by joining amino acids together during RNA translation. Amino Acid ...
... Cells can create more complex molecules from simpler molecules. An example of this is protein synthesis where proteins are created by joining amino acids together during RNA translation. Amino Acid ...
Directions for Use HistoChoice® MB (Molecular Biology) Tissue
... specially formulated to preserve antigenic sites (for antibody probes) and nucleic acid sites (for in situ hybridizations) in their native state, rendering pre-digestion or other recovery procedures for these important sites unnecessary. Primary antibodies can often be diluted several-fold due to th ...
... specially formulated to preserve antigenic sites (for antibody probes) and nucleic acid sites (for in situ hybridizations) in their native state, rendering pre-digestion or other recovery procedures for these important sites unnecessary. Primary antibodies can often be diluted several-fold due to th ...
Living Enviroment - William H. Maxwell HS
... organism within an ecosystem. Ecological Succession, ...
... organism within an ecosystem. Ecological Succession, ...
Life

Life is a characteristic distinguishing physical entities having biological processes (such as signaling and self-sustaining processes) from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased (death), or because they lack such functions and are classified as inanimate. Various forms of life exist such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. The criteria can at times be ambiguous and may or may not define viruses, viroids or potential artificial life as living. Biology is the primary science concerned with the study of life, although many other sciences are involved.The smallest contiguous unit of life is called an organism. Organisms are composed of one or more cells, undergo metabolism, maintain homeostasis, can grow, respond to stimuli, reproduce (either sexually or asexually) and, through evolution, adapt to their environment in successive generations. A diverse array of living organisms can be found in the biosphere of Earth, and the properties common to these organisms—plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria—are a carbon- and water-based cellular form with complex organization and heritable genetic information.Abiogenesis is the natural process of life arising from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years. The earliest life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era when sufficient crust had solidified following the molten Hadean Eon. The earliest physical evidence of life on Earth is biogenic graphite from 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks found in Western Greenland and microbial mat fossils in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone found in Western Australia. Some theories, such as the Late Heavy Bombardment theory, suggest that life on Earth may have started even earlier, and may have begun as early as 4.25 billion years ago according to one study, and even earlier yet, 4.4 billion years ago, according to another. The mechanism by which life began on Earth is unknown, although many hypotheses have been formulated. Since emerging, life has evolved into a variety of forms, which have been classified into a hierarchy of taxa. Life can survive and thrive in a wide range of conditions. Nonetheless, more than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.The chemistry leading to life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. Though life is confirmed only on the Earth, many think that extraterrestrial life is not only plausible, but probable or inevitable. Other planets and moons in the Solar System and other planetary systems are being examined for evidence of having once supported simple life, and projects such as SETI are trying to detect radio transmissions from possible alien civilizations.The meaning of life—its significance, origin, purpose, and ultimate fate—is a central concept and question in philosophy and religion. Both philosophy and religion have offered interpretations as to how life relates to existence and consciousness, and on related issues such as life stance, purpose, conception of a god or gods, a soul or an afterlife. Different cultures throughout history have had widely varying approaches to these issues.