Click here for printer-friendly sample test questions
... 8. Use the following diagram to answer the following. ...
... 8. Use the following diagram to answer the following. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... a) superior (cranial) - towards the head b) inferior (caudal) - towards the feet c) anterior (ventral) - towards the front d) posterior (dorsal) - towards the back e) medial - towards the midline f) lateral - away from the midline g) proximal - nearest the point of attachment h) distal - farthest fr ...
... a) superior (cranial) - towards the head b) inferior (caudal) - towards the feet c) anterior (ventral) - towards the front d) posterior (dorsal) - towards the back e) medial - towards the midline f) lateral - away from the midline g) proximal - nearest the point of attachment h) distal - farthest fr ...
Life Science: Cells
... 1. Review with the class the parts of a cell and the jobs carried out by each part. The Cells Alive! Web site (www.cellsalive.com) can be very helpful for the review. There you can see interactive diagrams featuring the parts of both plant and animal cells and watch animations of cell division. 2. B ...
... 1. Review with the class the parts of a cell and the jobs carried out by each part. The Cells Alive! Web site (www.cellsalive.com) can be very helpful for the review. There you can see interactive diagrams featuring the parts of both plant and animal cells and watch animations of cell division. 2. B ...
1.3.2 Chemical Elements
... The Chemicals of Life All things (matter), both living and nonliving things are made up of chemicals. **It was once thought that living things were different ...
... The Chemicals of Life All things (matter), both living and nonliving things are made up of chemicals. **It was once thought that living things were different ...
doc - AState.edu
... A. Gross Anatomy-large body structures 1. includes regional (all parts of an area-leg) 2. systemic anatomy (systems-cardiovascular) B. Microscopic Anatomy-too small to be seen without a microscope 1. Cytology-study of cells 2. Histology-study of tissues C. Developmental anatomy-changes that occur as ...
... A. Gross Anatomy-large body structures 1. includes regional (all parts of an area-leg) 2. systemic anatomy (systems-cardiovascular) B. Microscopic Anatomy-too small to be seen without a microscope 1. Cytology-study of cells 2. Histology-study of tissues C. Developmental anatomy-changes that occur as ...
Levels of Organization - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
TOPICS FOR EXAMINATION II – Biology 1406
... What are the basic characteristics shown by chordates? What is the order of evolution of the major groups of vertebrates, including birds, amphibians, fish, and reptiles? What is an amniotic egg and why is it important? How is it postulated that vertebrate jaws evolved? What are the most important c ...
... What are the basic characteristics shown by chordates? What is the order of evolution of the major groups of vertebrates, including birds, amphibians, fish, and reptiles? What is an amniotic egg and why is it important? How is it postulated that vertebrate jaws evolved? What are the most important c ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... The elaboration of the replicon model was obviously a first step in this direction. As mentioned above, the hypothesis of a link between DNA (the replicator) and the cell membrane is an important part of the replicon model. But it was not immediately conceived. Before the conference at Cold Spring H ...
... The elaboration of the replicon model was obviously a first step in this direction. As mentioned above, the hypothesis of a link between DNA (the replicator) and the cell membrane is an important part of the replicon model. But it was not immediately conceived. Before the conference at Cold Spring H ...
the origin of species
... young, they were home to many plants and animals known nowhere else in the world. – Darwin thought it unlikely that all of these species could have been among the original colonists of the islands. ...
... young, they were home to many plants and animals known nowhere else in the world. – Darwin thought it unlikely that all of these species could have been among the original colonists of the islands. ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... A kingdom made up of complex, multicellular organisms that are usually green, have cell walls made of cellulose, cannot move around, and use the sun's energy to make sugar by photosynthesis. The location of an object. The energy that an object has because of the position, shape, or condition of the ...
... A kingdom made up of complex, multicellular organisms that are usually green, have cell walls made of cellulose, cannot move around, and use the sun's energy to make sugar by photosynthesis. The location of an object. The energy that an object has because of the position, shape, or condition of the ...
Chapter 7 Notes - cloudfront.net
... occur in great quantities both in salt and fresh water. When the plant dies, the shell sinks to the bottom. Over time, large quantities of these shells accumulate. They can be collected and used as diatomaceous earth in swimming pool filters. The shells allow water to pass through but trap any small ...
... occur in great quantities both in salt and fresh water. When the plant dies, the shell sinks to the bottom. Over time, large quantities of these shells accumulate. They can be collected and used as diatomaceous earth in swimming pool filters. The shells allow water to pass through but trap any small ...
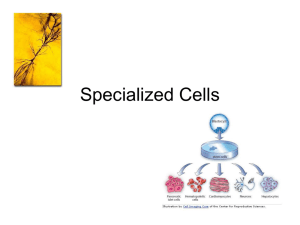
Specialized Cells
... work together to perform complex tasks. *exs. All plant’s leaves make up an organ system that provides energy for the plant. ...
... work together to perform complex tasks. *exs. All plant’s leaves make up an organ system that provides energy for the plant. ...
Waves - members.iinet.com.au
... react quickly with oxygen in the air and vigorously with water. They are unusual for metals as they are very soft and light and they have low melting and boiling points. Going across the groups the reactivity decreases while the metallic properties increase until the non-metals. The transition metal ...
... react quickly with oxygen in the air and vigorously with water. They are unusual for metals as they are very soft and light and they have low melting and boiling points. Going across the groups the reactivity decreases while the metallic properties increase until the non-metals. The transition metal ...
Chapter 1 honors review questions
... Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most members of a species have the same adaptations to their D)environment. E)Evolution can be used ...
... Members of a population with advantageous variations tend to survive and have B)more offspring. Each successive generation will include more members with the new advantageous C)variations. In the end, most members of a species have the same adaptations to their D)environment. E)Evolution can be used ...
Unit 2 Workbook 0910
... http://www.sciencenet.org.uk/database/Biology/Cell_Biology/b00308c.html Cells and Organelles http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cells.htm Animal Cell Organelles http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cells.htm Plant Cell Organelles http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/plntcell.htm Difference Betw ...
... http://www.sciencenet.org.uk/database/Biology/Cell_Biology/b00308c.html Cells and Organelles http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cells.htm Animal Cell Organelles http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cells.htm Plant Cell Organelles http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/plntcell.htm Difference Betw ...
Variation - Plantsbrook Science
... same genes, although they could have different alleles. Alleles coding for the same characteristic will be found at the same locus (place) on each chromosome in a homologous pair. Mutations are changes in the base sequence of an organism’s DNA. Thus mutations can produce new alleles of genes. A gene ...
... same genes, although they could have different alleles. Alleles coding for the same characteristic will be found at the same locus (place) on each chromosome in a homologous pair. Mutations are changes in the base sequence of an organism’s DNA. Thus mutations can produce new alleles of genes. A gene ...
Molecular Genetics
... understanding of the structure of graphite and other carbon compounds even before her appointment to King's College. Unfortunately, her reputation did not precede her. James Watson's unflattering portrayal of Franklin in his account of the discovery of DNA's structure, entitled "The Double Helix," d ...
... understanding of the structure of graphite and other carbon compounds even before her appointment to King's College. Unfortunately, her reputation did not precede her. James Watson's unflattering portrayal of Franklin in his account of the discovery of DNA's structure, entitled "The Double Helix," d ...
Classification y9 key ppt plus worksheet
... Living things need energy to carry out the functions that keep them alive. ...
... Living things need energy to carry out the functions that keep them alive. ...
Living things
... Nutrition consists of specialized organ systems through which material or substances are processed to obtain matter and energy for human activities. The respiratory system supplies the oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body and remove the carbon dioxide. It consists ...
... Nutrition consists of specialized organ systems through which material or substances are processed to obtain matter and energy for human activities. The respiratory system supplies the oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body and remove the carbon dioxide. It consists ...
C. transcription - Partners4results
... D. A genetic mutation occurs in one of the parent gametes and is passed to the offspring. ______8. Which of the following encodes the genetic information for the earlobe trait? A. ATP B. DNA C. amino acids D. carbohydrates ______9. In some pea plant experiments, Mendel studied the inheritance patter ...
... D. A genetic mutation occurs in one of the parent gametes and is passed to the offspring. ______8. Which of the following encodes the genetic information for the earlobe trait? A. ATP B. DNA C. amino acids D. carbohydrates ______9. In some pea plant experiments, Mendel studied the inheritance patter ...
Test Review – Ch
... AKA fermentation, occurs without presence of oxygen 19. Fermentation happens under (aerobic / anaerobic) conditions. Anaerobic 20. Which process occurs in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration? (Glycolysis, Krebs, ETC) Glycolysis 21. What are the two kinds of fermentation? What kind happens in our ...
... AKA fermentation, occurs without presence of oxygen 19. Fermentation happens under (aerobic / anaerobic) conditions. Anaerobic 20. Which process occurs in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration? (Glycolysis, Krebs, ETC) Glycolysis 21. What are the two kinds of fermentation? What kind happens in our ...
CellUnitWrapUpNotes
... Example: The Ted Talk guy who lost his feet used prosthetic feet Implants: A device that is placed inside the body to help it do something better or something that was not possible before. Example: Pace-maker (heart), Breast Implants (more appealing), Subcutaneous (under the skin) communication devi ...
... Example: The Ted Talk guy who lost his feet used prosthetic feet Implants: A device that is placed inside the body to help it do something better or something that was not possible before. Example: Pace-maker (heart), Breast Implants (more appealing), Subcutaneous (under the skin) communication devi ...
LKB1 and Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
... Other features of the protein suggest mechanisms of localization and regulation ...
... Other features of the protein suggest mechanisms of localization and regulation ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.