Regulating the Internal Environment
... Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal AP Biology ...
... Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal AP Biology ...
Lab 1
... Additional Directions: Whenever you see “sig. _____” this means to put your initials after you completely read the following section. Introduction: 1. Name the three stages of the cell cycle: ...
... Additional Directions: Whenever you see “sig. _____” this means to put your initials after you completely read the following section. Introduction: 1. Name the three stages of the cell cycle: ...
Blog resource: http://tinyurl
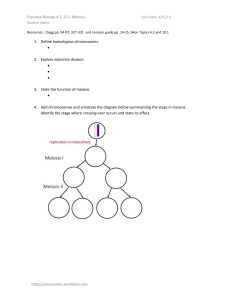
... Remember: Meiosis is the key to success in Biology. If we understand how meiosis works and gives rise to genetic variation, we can understand how life has evolved and adapted. Make sure you can explain all of the ways in which meiosis leads to variation amongst a population. ...
... Remember: Meiosis is the key to success in Biology. If we understand how meiosis works and gives rise to genetic variation, we can understand how life has evolved and adapted. Make sure you can explain all of the ways in which meiosis leads to variation amongst a population. ...
Amphibians Notes
... oxygen. The second loop sends blood from the heart to the ____________ and back. ...
... oxygen. The second loop sends blood from the heart to the ____________ and back. ...
Chapter 1 - Maintaining Life
... • Too low – chemical reactions stop • Too high – chemical reactions occur too fast and proteins lose shape and stop working. ...
... • Too low – chemical reactions stop • Too high – chemical reactions occur too fast and proteins lose shape and stop working. ...
UNIT
... FLORIDA SCIENCE BENCHMARKS SC.6.L.14.1 (AA): Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to molecules and cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to organisms. SC.6.L.14.5 (AA): Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the ...
... FLORIDA SCIENCE BENCHMARKS SC.6.L.14.1 (AA): Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to molecules and cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to organisms. SC.6.L.14.5 (AA): Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the ...
Drosophila
... 2. Researchers study development in model organisms to identify general principles • The criteria for choosing a model organism: readily observable embryos, short generation times, relatively small genomes, and preexisting knowledge about the organism and its genes. ...
... 2. Researchers study development in model organisms to identify general principles • The criteria for choosing a model organism: readily observable embryos, short generation times, relatively small genomes, and preexisting knowledge about the organism and its genes. ...
BIOL0601 Module 4 Assignment 4 (M4A)
... undergoes clonal expansion. Its clones go on to destroy cells carrying this foreign protein. This would include virus infected cells and cancer cells. They also form memory T cells that are ready to spring into action in response to a re-occurrence. The cells which destroy other cells are called cyt ...
... undergoes clonal expansion. Its clones go on to destroy cells carrying this foreign protein. This would include virus infected cells and cancer cells. They also form memory T cells that are ready to spring into action in response to a re-occurrence. The cells which destroy other cells are called cyt ...
Study Guide
... 4. Describe the locomotion of a leech on land. ____________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 5. Critical Thinking Some parasitic leeches are attracted by warmth. What type of host would you ...
... 4. Describe the locomotion of a leech on land. ____________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 5. Critical Thinking Some parasitic leeches are attracted by warmth. What type of host would you ...
YEAR 10 IGCSE BIOLOGY REVISION GUIDE DBGS DIGESTION
... Carbohydrate (stimulus): Pancreas (receptor) -> stimulated and secretes hormone insulin -> insulin decreases glucose levels to normal Insulin causes body cells to absorb more glucose and change it into glycogen o Diabetes: when pancreas doesn’t create insulin. Diabetics take insulin shots. It ...
... Carbohydrate (stimulus): Pancreas (receptor) -> stimulated and secretes hormone insulin -> insulin decreases glucose levels to normal Insulin causes body cells to absorb more glucose and change it into glycogen o Diabetes: when pancreas doesn’t create insulin. Diabetics take insulin shots. It ...
Xenotransplants: Using Animal Organs To Save Human Lives by
... large litters, and they grow quickly to maturity. They can be raised in sterile environments, which would reduce the likelihood of transmission of at least some pig diseases to humans. Many researchers, however, still worry about viruses that are unknown or that have become part of the animals' geno ...
... large litters, and they grow quickly to maturity. They can be raised in sterile environments, which would reduce the likelihood of transmission of at least some pig diseases to humans. Many researchers, however, still worry about viruses that are unknown or that have become part of the animals' geno ...
lect 4
... An organ system is a group of organs that work together and complete a particular task such as the respiratory systems job is to carry oxygen to your lungs and other parts of your body then dispose of carbon dioxide. A cell is the structural, functional, and biological unit of organisms. (1, 5, ...
... An organ system is a group of organs that work together and complete a particular task such as the respiratory systems job is to carry oxygen to your lungs and other parts of your body then dispose of carbon dioxide. A cell is the structural, functional, and biological unit of organisms. (1, 5, ...
as a PDF
... notochord and notochord-dependent structures for feeding and growth), then the functional burden on structures dependent on the notochord decreased in the ascidians when they evolved a sessile habit during the feeding stages, with consequent loss of the tail at metamorphosis. If a population of fish ...
... notochord and notochord-dependent structures for feeding and growth), then the functional burden on structures dependent on the notochord decreased in the ascidians when they evolved a sessile habit during the feeding stages, with consequent loss of the tail at metamorphosis. If a population of fish ...
Anatomical Terminology
... Divison of Labor A cell is made up of many parts with different functions that work together. Similarly, the parts of a factory or a machine work together to carry out different functions and come up with a ...
... Divison of Labor A cell is made up of many parts with different functions that work together. Similarly, the parts of a factory or a machine work together to carry out different functions and come up with a ...
Chapter 1 Outline
... Chapter 1 introduces and establishes the framework upon which all the other chapters are built. This chapter provides the necessary terminology so that instructor and students are all “speaking the same language.” Marieb begins by defining the key terms anatomy and physiology, and then continues to ...
... Chapter 1 introduces and establishes the framework upon which all the other chapters are built. This chapter provides the necessary terminology so that instructor and students are all “speaking the same language.” Marieb begins by defining the key terms anatomy and physiology, and then continues to ...
Kidney Excretion PPT Notes - Bremen High School District 228
... Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life aa ...
... Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life aa ...
Characteristics of Living Things
... use energy • All living things need energy. • Plants get energy from the sun (photosynthesis) and animals get energy from eating plants and other animals. • Animals and plants use energy to ...
... use energy • All living things need energy. • Plants get energy from the sun (photosynthesis) and animals get energy from eating plants and other animals. • Animals and plants use energy to ...
Unit 1 - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... ● How do we determine when a group of cells can be called a tissue or when a group of tissues can be called an organ? ● How do the systems of the body work together to sustain life? ● To what extent can we infer the functional role of a cell, tissue or organ from its structural characteristics? Cont ...
... ● How do we determine when a group of cells can be called a tissue or when a group of tissues can be called an organ? ● How do the systems of the body work together to sustain life? ● To what extent can we infer the functional role of a cell, tissue or organ from its structural characteristics? Cont ...
Biological Concepts: Diversity (Pillsbury)
... This four credit-hour course will examine the diversity of life on Earth. We will cover all major organismal groups including bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. A central theme in the class is evolution as a force driving diversity. Particular emphasis will be placed on how these organi ...
... This four credit-hour course will examine the diversity of life on Earth. We will cover all major organismal groups including bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals. A central theme in the class is evolution as a force driving diversity. Particular emphasis will be placed on how these organi ...
Multicellularity
... P granules, then, are an example of an autonomous signal, which is present only in cells that can trace their lineage back to the P4 cell. The P4 cell was generated by a series of asymmetric cell divisions in which the P granules were only inherited by one of the two daughter cells. Again, you do n ...
... P granules, then, are an example of an autonomous signal, which is present only in cells that can trace their lineage back to the P4 cell. The P4 cell was generated by a series of asymmetric cell divisions in which the P granules were only inherited by one of the two daughter cells. Again, you do n ...
Great Barrier Reef
... Of the 20 metazoan phyla with extensive fossil records, at least 11 first appeared in the Cambrian. Of the remainder, 1 is known to Precambrian and the other 8 first appear more recently (Collins 1994). An additional 12 soft-bodied phyla have ...
... Of the 20 metazoan phyla with extensive fossil records, at least 11 first appeared in the Cambrian. Of the remainder, 1 is known to Precambrian and the other 8 first appear more recently (Collins 1994). An additional 12 soft-bodied phyla have ...
MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER TWO EXAMIN
... b. Regulator c. Promoter d. Operator e. Repressor 1 mark ...
... b. Regulator c. Promoter d. Operator e. Repressor 1 mark ...
Student Book
... world health and disease. A disease is any breakdown in the structure or function of an organism. Scientists who study a particular disease gather information about how that disease affects the organism. They look at all levels of the organism, from molecules and cells to organs and the whole organi ...
... world health and disease. A disease is any breakdown in the structure or function of an organism. Scientists who study a particular disease gather information about how that disease affects the organism. They look at all levels of the organism, from molecules and cells to organs and the whole organi ...
Biology

Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Modern biology is a vast and eclectic field, composed of many branches and subdisciplines. However, despite the broad scope of biology, there are certain general and unifying concepts within it that govern all study and research, consolidating it into single, coherent fields. In general, biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the synthesis and creation of new species. It is also understood today that all organisms survive by consuming and transforming energy and by regulating their internal environment to maintain a stable and vital condition.Subdisciplines of biology are defined by the scale at which organisms are studied, the kinds of organisms studied, and the methods used to study them: biochemistry examines the rudimentary chemistry of life; molecular biology studies the complex interactions among biological molecules; botany studies the biology of plants; cellular biology examines the basic building-block of all life, the cell; physiology examines the physical and chemical functions of tissues, organs, and organ systems of an organism; evolutionary biology examines the processes that produced the diversity of life; and ecology examines how organisms interact in their environment.