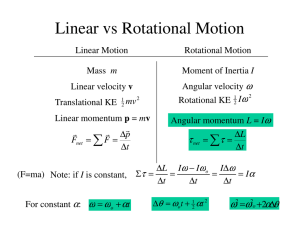
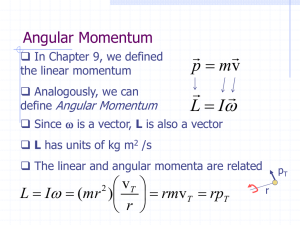
Rotational Motion
... Two parts to torque: Lever arm To get the most effect, effort force should be exerted as far from the axis of rotation as possible (why doorknobs are at the edge of a door) L = r, if the force is exerted perpendicular to the axis of rotation ...
... Two parts to torque: Lever arm To get the most effect, effort force should be exerted as far from the axis of rotation as possible (why doorknobs are at the edge of a door) L = r, if the force is exerted perpendicular to the axis of rotation ...
Centripetal Force
... • The easiest way to think of torque is to consider a door. • When you open a door, where do you push? • If you exert a force at the hinge, the door will not move • If exert a force on the side of the door opposite the hinge, and to push or pull with a force perpendicular to the door. ...
... • The easiest way to think of torque is to consider a door. • When you open a door, where do you push? • If you exert a force at the hinge, the door will not move • If exert a force on the side of the door opposite the hinge, and to push or pull with a force perpendicular to the door. ...
Section 8-2 Center of Mass
... ii. Shorter lever arm = smaller torque 3. Torque depends on the angle between force and the lever arm a. Changing the angle will change the ease that the object will move with b. Torque = () = Greek letter Tau c. SI unit = N • m d. Torque is (+) or (-) depending on direction of the rotation i. (+) ...
... ii. Shorter lever arm = smaller torque 3. Torque depends on the angle between force and the lever arm a. Changing the angle will change the ease that the object will move with b. Torque = () = Greek letter Tau c. SI unit = N • m d. Torque is (+) or (-) depending on direction of the rotation i. (+) ...