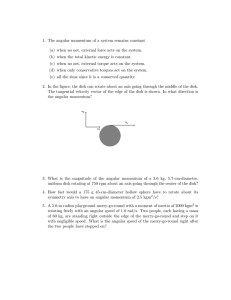
1. The angular momentum of a system remains constant (a) when no
... (a) when no net, external force acts on the system. (b) when the total kinetic energy is constant. (c) when no net, external torque acts on the system. (d) when only conservative torques act on the system. (e) all the time since it is a conserved quantity. 2. In the figure, the disk can rotate about ...
... (a) when no net, external force acts on the system. (b) when the total kinetic energy is constant. (c) when no net, external torque acts on the system. (d) when only conservative torques act on the system. (e) all the time since it is a conserved quantity. 2. In the figure, the disk can rotate about ...
Cross Product
... Torque Example T= R x F = RFsin() is the angle between the location of the applied force and the point where the radius meets this force. In this case, = 90, which means that the torque is just the product of the radius and the applied force because sin(90) = ...
... Torque Example T= R x F = RFsin() is the angle between the location of the applied force and the point where the radius meets this force. In this case, = 90, which means that the torque is just the product of the radius and the applied force because sin(90) = ...
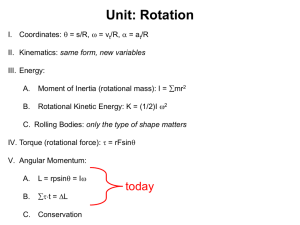
AP Physics Chapter 11-12 Key Equations and Ideas Rotation s = qr
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
... the body. If a body is forced to rotate about an axis that does not pass through the center of mass, use the Parallel Axis Theorem to calculate its rotational inertia. ...
PHY 101 ... ______________________ Take home exam #1 Solution Key
... Name ___Solution Key______________________ ...
... Name ___Solution Key______________________ ...
Describing Rotational Motion
... an angular equation for force. • F t (torque, Nm) • m I (moment of inertia, kgm2) • a a (angular acceleration, rad/s2) ...
... an angular equation for force. • F t (torque, Nm) • m I (moment of inertia, kgm2) • a a (angular acceleration, rad/s2) ...
Torque 1
... 3. The moment arm of the biceps brachii muscle about the elbow joint is largest when the angle at the elbow joint is approximately a. 180° (fully extended) b. 150° c. 120° d. 90° e. The angle of the elbow joint doesn't affect the moment arm of the biceps brachii muscle. 4. A weightlifter is attempti ...
... 3. The moment arm of the biceps brachii muscle about the elbow joint is largest when the angle at the elbow joint is approximately a. 180° (fully extended) b. 150° c. 120° d. 90° e. The angle of the elbow joint doesn't affect the moment arm of the biceps brachii muscle. 4. A weightlifter is attempti ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 12
... • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) • Units are Newton-meters Door Demo ...
... • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) • Units are Newton-meters Door Demo ...
Physics Web Search: Torque
... 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must be the centripetal force that keeps the lady bug moving in a circle? _______ ...
... 6. From Newton’s second law, a force will cause an __________________________ 7. When considering angular motion, a torque will cause an ___________________ ____________________ (consider both torque equations) 8. What must be the centripetal force that keeps the lady bug moving in a circle? _______ ...
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics
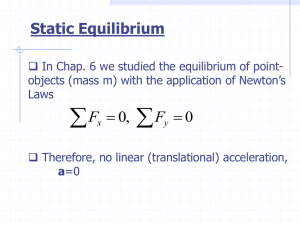
... Static Equilibrium In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...
... Static Equilibrium In Chap. 6 we studied the equilibrium of pointobjects (mass m) with the application of Newton’s Laws ...