equilibrium
... pivoting about an axis under influence of two forces of equal magnitude act in opposite directions along parallel lines of action (a couple) ...
... pivoting about an axis under influence of two forces of equal magnitude act in opposite directions along parallel lines of action (a couple) ...
Chapter 8: Rotational motion
... the least, so will reach the bottom first. The shape which has most of its mass closest to the center has least rotational inertia, i.e. first is ball, second is cylinder, and last is the ring. ...
... the least, so will reach the bottom first. The shape which has most of its mass closest to the center has least rotational inertia, i.e. first is ball, second is cylinder, and last is the ring. ...
Chapter 8- Rotational Motion
... It is clear that to make an object start rotating, a force is needed; Unlike in linear motion, the position and direction of the applied force matter as well. In the figure, the applied force will be more effective in opening the door than force assuming they both have the same magnitude. The angula ...
... It is clear that to make an object start rotating, a force is needed; Unlike in linear motion, the position and direction of the applied force matter as well. In the figure, the applied force will be more effective in opening the door than force assuming they both have the same magnitude. The angula ...
Agenda
... causes of linear motion – Forces are vector quantities • A vector is a geometric object with magnitude and a direction • Magnitude and a direction must be specified ...
... causes of linear motion – Forces are vector quantities • A vector is a geometric object with magnitude and a direction • Magnitude and a direction must be specified ...
Chapter 13 - AJRomanello
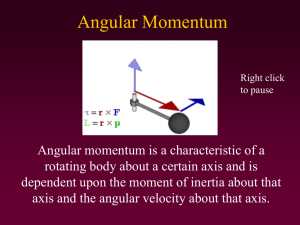
... FΔt = mΔV In an angular system the change in angular momentum is given by: FrΔt = IΔω or ΤΔt = IΔω ...
... FΔt = mΔV In an angular system the change in angular momentum is given by: FrΔt = IΔω or ΤΔt = IΔω ...
Quiz
... moment of inertia is 12.00 kg.m2? (Ignore the vertical force.) a) –16.67 rad/s2 b) –2400 rad/s2 c) –190.0 rad/s2 d) –15.83 rad/s2 ...
... moment of inertia is 12.00 kg.m2? (Ignore the vertical force.) a) –16.67 rad/s2 b) –2400 rad/s2 c) –190.0 rad/s2 d) –15.83 rad/s2 ...
Physics 140 HOMEWORK Chapter 10B Q7. Figure 10
... exceed g if the chimney remained intact. Meanwhile, the radial acceleration at points in the upper part of the chimney would increase to the point that the chimney is under tension, not compression. In actual collapses, the chimney frequently breaks maybe 70% of the way up while falling, and the low ...
... exceed g if the chimney remained intact. Meanwhile, the radial acceleration at points in the upper part of the chimney would increase to the point that the chimney is under tension, not compression. In actual collapses, the chimney frequently breaks maybe 70% of the way up while falling, and the low ...
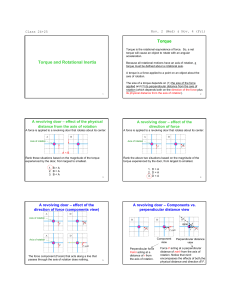
Chapter 9: Torque and Rotation
... Torque is usually represented by the lower case Greek letter “tau,” t. When calculating torque, if the line of action passes through the center of rotation, the lever arm is zero, and so is the torque, no matter how large a force is applied. ...
... Torque is usually represented by the lower case Greek letter “tau,” t. When calculating torque, if the line of action passes through the center of rotation, the lever arm is zero, and so is the torque, no matter how large a force is applied. ...
Rotation
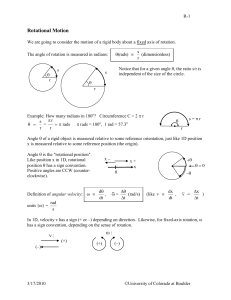
... Translation: body’s movement described by x(t). Rotation: body’s movement given by θ(t) = angular position of the body’s reference line as function of time. Angular displacement: body’s rotation about its axis changing the angular position from θ1 to θ2. ...
... Translation: body’s movement described by x(t). Rotation: body’s movement given by θ(t) = angular position of the body’s reference line as function of time. Angular displacement: body’s rotation about its axis changing the angular position from θ1 to θ2. ...