Chapter 21: Optical Properties
... n = index of refraction v (velocity of light in medium) -- Adding large ions (e.g., lead) to glass decreases the speed of light in the glass. -- Light can be “bent” as it passes through a transparent prism ...
... n = index of refraction v (velocity of light in medium) -- Adding large ions (e.g., lead) to glass decreases the speed of light in the glass. -- Light can be “bent” as it passes through a transparent prism ...
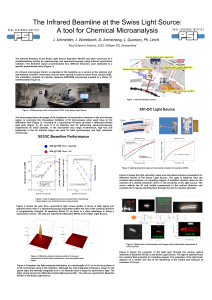
IR Workshop Poster - Beamline Presentation
... The microscope takes advantage of the brightness of synchrotron emission in the mid infrared region to overcome the throughput limitation of IR microscopes when used close to the diffraction limit (Figure 3). Focusing of a synchrotron IR beam provides a diffraction-limited light spot (Figure 4). As ...
... The microscope takes advantage of the brightness of synchrotron emission in the mid infrared region to overcome the throughput limitation of IR microscopes when used close to the diffraction limit (Figure 3). Focusing of a synchrotron IR beam provides a diffraction-limited light spot (Figure 4). As ...
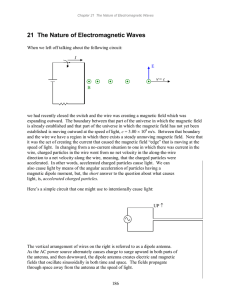
2-21 The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
... radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, X rays, and gamma rays. They are all the same thing— electric and magnetic fields that are oscillating in time and space. I am using the word light in a generic sense. It refers to waves of any one of these various frequencies of oscillations of electric ...
... radiation, visible light, ultraviolet light, X rays, and gamma rays. They are all the same thing— electric and magnetic fields that are oscillating in time and space. I am using the word light in a generic sense. It refers to waves of any one of these various frequencies of oscillations of electric ...
Blackbody Radiation - High Point University
... The horizontal axis represents the wavelength of light in units of micrometers (µm). Bands of colors (the rainbow on the graph) show where the wavelengths of visible light are. Wavelengths just shorter than purple are ultraviolet light, and wavelengths just longer than red are infrared light. The sm ...
... The horizontal axis represents the wavelength of light in units of micrometers (µm). Bands of colors (the rainbow on the graph) show where the wavelengths of visible light are. Wavelengths just shorter than purple are ultraviolet light, and wavelengths just longer than red are infrared light. The sm ...
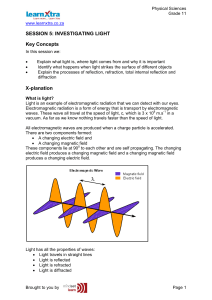
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts X
... When a beam of light strikes the surface at an angle of incidence between 0 0 and 900 (00 < θ i <900) you can see the effect of the change in speed of light. The because the beam of light changes direction. When it is slowing down it moves towards the normal (angle of refraction θr is less than the ...
... When a beam of light strikes the surface at an angle of incidence between 0 0 and 900 (00 < θ i <900) you can see the effect of the change in speed of light. The because the beam of light changes direction. When it is slowing down it moves towards the normal (angle of refraction θr is less than the ...
Optical Mineralogy
... will travel along the interface If angle of incidence is > CA, then total internal reflection CA can be derived from Snell’s law ...
... will travel along the interface If angle of incidence is > CA, then total internal reflection CA can be derived from Snell’s law ...
Atomic Emission Spectra
... A Tesla coil produces high-voltage, low-current electricity at a very high frequency. The electric shock produced by the Tesla coil is minimal. However, presenters or students with medical conditions (e.g., heart conditions) that may be affected by high voltage electricity should not operate or touc ...
... A Tesla coil produces high-voltage, low-current electricity at a very high frequency. The electric shock produced by the Tesla coil is minimal. However, presenters or students with medical conditions (e.g., heart conditions) that may be affected by high voltage electricity should not operate or touc ...
Waves Review (Key)
... perception of color. One receptor is sensitive to the color green, another to the color blue and a third to the color red. These three colors can then be combined to form any visible color in the spectrum. 30. How does a color filter work? A filter blocks all wavelengths except the one representing ...
... perception of color. One receptor is sensitive to the color green, another to the color blue and a third to the color red. These three colors can then be combined to form any visible color in the spectrum. 30. How does a color filter work? A filter blocks all wavelengths except the one representing ...
Light
... • Refraction is the bending of light rays. Light usually travels in straight lines and at a constant speed unless it changes from one medium to another. • A lens is a transparent material that refracts light. Lenses usually have one or more curved surfaces. There are two kinds of lenses: convex and ...
... • Refraction is the bending of light rays. Light usually travels in straight lines and at a constant speed unless it changes from one medium to another. • A lens is a transparent material that refracts light. Lenses usually have one or more curved surfaces. There are two kinds of lenses: convex and ...
Light
... • Refraction is the bending of light rays. Light usually travels in straight lines and at a constant speed unless it changes from one medium to another. • A lens is a transparent material that refracts light. Lenses usually have one or more curved surfaces. There are two kinds of lenses: convex and ...
... • Refraction is the bending of light rays. Light usually travels in straight lines and at a constant speed unless it changes from one medium to another. • A lens is a transparent material that refracts light. Lenses usually have one or more curved surfaces. There are two kinds of lenses: convex and ...
Architectural lighting design

""The Sun never knew how great it was until it hit the side of a building."" Louis KahnArchitectural lighting design is a field within architecture, interior design and electrical engineering that is concerned with the design of lighting systems, including natural light, electric light, or both, to serve human needs.The design process takes account of: the kind of human activity for which lighting is to be provided. the amount of light required. the colour of the light as it may affect the views of particular objects and the environment as a whole. the distribution of light within the space to be lighted, whether indoor or outdoor. the effect of the lightened system itself on the user.It is important to appreciate that the ultimate criterion of success in lighting is the human response, that is. whether what is to be seen clearly, easily and without discomfort."" Lighting designers are often specialists who must understand the physics of light production and distribution, the physiology and psychology of light perception by humans, the anatomy of the human eye, and the response of the rods and cones to light.