RLC Resonant Circuit - John A. Goree
... components. Therefore, in AC circuits the rules for combining these reactances must take into account both magnitudes and phase angles. The equivalent AC resistance (the quantity relating voltage and current) of a circuit containing reactances and resistances is called impedance (Z). Let’s compare t ...
... components. Therefore, in AC circuits the rules for combining these reactances must take into account both magnitudes and phase angles. The equivalent AC resistance (the quantity relating voltage and current) of a circuit containing reactances and resistances is called impedance (Z). Let’s compare t ...
Understanding Transducer Specifications
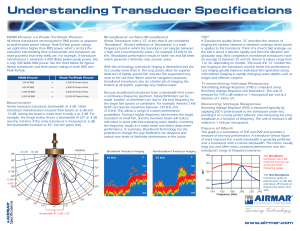
... The easiest way to understand how a transducer functions is to think of it as a speaker and a microphone built into one unit. A transducer receives sequences of high voltage electrical pulses called transmit pulses from the echosounder. Just like the stereo speakers at home, the transducer then conv ...
... The easiest way to understand how a transducer functions is to think of it as a speaker and a microphone built into one unit. A transducer receives sequences of high voltage electrical pulses called transmit pulses from the echosounder. Just like the stereo speakers at home, the transducer then conv ...
No Slide Title
... After we know how to convert RLC components from time to phasor domain, we can transform a time domain circuit into a phasor/frequency domain circuit. Hence, we can apply the KCL laws and other theorems to directly set up phasor equations involving our target variable(s) for solving. Next we f ...
... After we know how to convert RLC components from time to phasor domain, we can transform a time domain circuit into a phasor/frequency domain circuit. Hence, we can apply the KCL laws and other theorems to directly set up phasor equations involving our target variable(s) for solving. Next we f ...
XP-BD Manual
... Start Signal (Y): Close PID control when Y is 0, open PID control when Y is 1 Death Bound (Death):Compare the current PID output value with the preceding PID output value. If their difference is less than the set death bound, the module will abandon the current PID output value, still transfer the p ...
... Start Signal (Y): Close PID control when Y is 0, open PID control when Y is 1 Death Bound (Death):Compare the current PID output value with the preceding PID output value. If their difference is less than the set death bound, the module will abandon the current PID output value, still transfer the p ...
CSPEMI201A 数据资料DataSheet下载
... pi−style filters (C−R−C) that reduce EMI/RFI emissions while at the same time providing ESD protection. This part is custom−designed to interface with a speaker port on a cellular telephone or similar device. Each high quality filter provides more than 35 dB attenuation in the 800−2700 MHz range. Th ...
... pi−style filters (C−R−C) that reduce EMI/RFI emissions while at the same time providing ESD protection. This part is custom−designed to interface with a speaker port on a cellular telephone or similar device. Each high quality filter provides more than 35 dB attenuation in the 800−2700 MHz range. Th ...
Ultrasonic, TOFD and phased array flaw detectors and thickness
... various measuring modes (NORM, MEMORY, A-SCAN) can be selected. Robustness: The Zonotip features a very robust and shock-proof housing which allows the instrument to be used in the most demanding environments. Multi-language: Like all Proceq products, the Zonotip can be operated in eight different l ...
... various measuring modes (NORM, MEMORY, A-SCAN) can be selected. Robustness: The Zonotip features a very robust and shock-proof housing which allows the instrument to be used in the most demanding environments. Multi-language: Like all Proceq products, the Zonotip can be operated in eight different l ...
Implementation of a Digital Signal Processor
... significantly from a sinusoidal waveform and this distorted current can also lead to distortion in the supply voltage. Moreover, many modern equipments use digital controllers, based on microprocessors sensitive to variations in the voltage and current waveforms. The first attempt to overcome the ef ...
... significantly from a sinusoidal waveform and this distorted current can also lead to distortion in the supply voltage. Moreover, many modern equipments use digital controllers, based on microprocessors sensitive to variations in the voltage and current waveforms. The first attempt to overcome the ef ...
Low drop fixed and adjustable positive voltage
... • Available in ± 2% (at 25 °C) and 4% in full temperature range • High supply voltage rejection: – 80 dB typ. (at 25 °C) • Temperature range: 0 °C to 125 °C ...
... • Available in ± 2% (at 25 °C) and 4% in full temperature range • High supply voltage rejection: – 80 dB typ. (at 25 °C) • Temperature range: 0 °C to 125 °C ...
PDF
... Keywords – ADC, CMOS, Continuous Time, Sigma Delta Modulator, Dynamic Range (DR), Signal to noise ratio (SNR). ...
... Keywords – ADC, CMOS, Continuous Time, Sigma Delta Modulator, Dynamic Range (DR), Signal to noise ratio (SNR). ...
ORANGIS - Ambient control (Section)
... Most of our products are available in the industrial engineering software: ...
... Most of our products are available in the industrial engineering software: ...
Charge Pump, Loop Filter and VCO for Phase Lock
... loop filter at the output of the charge pump serves two functions. The second-order loop filter has the second capacitor to smooth out current spikes. This type of filter has two poles one at low frequency and one have high frequency and a zero which will add the stability of the system. The passive ...
... loop filter at the output of the charge pump serves two functions. The second-order loop filter has the second capacitor to smooth out current spikes. This type of filter has two poles one at low frequency and one have high frequency and a zero which will add the stability of the system. The passive ...
Mechanical filter

A mechanical filter is a signal processing filter usually used in place of an electronic filter at radio frequencies. Its purpose is the same as that of a normal electronic filter: to pass a range of signal frequencies, but to block others. The filter acts on mechanical vibrations which are the analogue of the electrical signal. At the input and output of the filter, transducers convert the electrical signal into, and then back from, these mechanical vibrations.The components of a mechanical filter are all directly analogous to the various elements found in electrical circuits. The mechanical elements obey mathematical functions which are identical to their corresponding electrical elements. This makes it possible to apply electrical network analysis and filter design methods to mechanical filters. Electrical theory has developed a large library of mathematical forms that produce useful filter frequency responses and the mechanical filter designer is able to make direct use of these. It is only necessary to set the mechanical components to appropriate values to produce a filter with an identical response to the electrical counterpart.Steel and nickel–iron alloys are common materials for mechanical filter components; nickel is sometimes used for the input and output couplings. Resonators in the filter made from these materials need to be machined to precisely adjust their resonance frequency before final assembly.While the meaning of mechanical filter in this article is one that is used in an electromechanical role, it is possible to use a mechanical design to filter mechanical vibrations or sound waves (which are also essentially mechanical) directly. For example, filtering of audio frequency response in the design of loudspeaker cabinets can be achieved with mechanical components. In the electrical application, in addition to mechanical components which correspond to their electrical counterparts, transducers are needed to convert between the mechanical and electrical domains. A representative selection of the wide variety of component forms and topologies for mechanical filters are presented in this article.The theory of mechanical filters was first applied to improving the mechanical parts of phonographs in the 1920s. By the 1950s mechanical filters were being manufactured as self-contained components for applications in radio transmitters and high-end receivers. The high ""quality factor"", Q, that mechanical resonators can attain, far higher than that of an all-electrical LC circuit, made possible the construction of mechanical filters with excellent selectivity. Good selectivity, being important in radio receivers, made such filters highly attractive. Contemporary researchers are working on microelectromechanical filters, the mechanical devices corresponding to electronic integrated circuits.