Chapter 20
... 20.2 Mechanisms of Gaseous Exchange As animals increase in size most of their cells are some distance from the surface and cannot receive adequate oxygen. Many larger animals also have an increased metabolic rate which increases their oxygen demand. These organisms need to develop specialized ...
... 20.2 Mechanisms of Gaseous Exchange As animals increase in size most of their cells are some distance from the surface and cannot receive adequate oxygen. Many larger animals also have an increased metabolic rate which increases their oxygen demand. These organisms need to develop specialized ...
How do human bodies
... • Large scale deforestation in tropical areas, for timber and to provide land for agriculture, has: − increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (because of burning and the activities of microorganisms) − reduced the rate at which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and ‘l ...
... • Large scale deforestation in tropical areas, for timber and to provide land for agriculture, has: − increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (because of burning and the activities of microorganisms) − reduced the rate at which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and ‘l ...
Arthropods
... • Insects – reason for evolutionary success is: – Ability to fly allows insects to colonize new habitats. – They may use many sense organs to respond to stimuli. – Many have a life cycle in which the young are very different from adults. – The body is divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. – Sens ...
... • Insects – reason for evolutionary success is: – Ability to fly allows insects to colonize new habitats. – They may use many sense organs to respond to stimuli. – Many have a life cycle in which the young are very different from adults. – The body is divided into a head, thorax, and abdomen. – Sens ...
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
... The Respiratory System takes in O2 and gets rid of CO2. Air enters through your nostrils or mouth, moves down the trachea, and then into the bronchi of your lungs. The bronchi branches into many smaller tubes. At the end of the smallest tubes are tiny air sacs called alveoli. Each is surrounded by c ...
... The Respiratory System takes in O2 and gets rid of CO2. Air enters through your nostrils or mouth, moves down the trachea, and then into the bronchi of your lungs. The bronchi branches into many smaller tubes. At the end of the smallest tubes are tiny air sacs called alveoli. Each is surrounded by c ...
Name - SMIC Biology
... oxygen-poor blood – but gills get oxygen from water, so process is slowed down at that point (2 pts.) Most efficient – high pressure, so blood travels very quickly throughout the body – separation of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood lungs get oxygen from the air, so more can diffuse ...
... oxygen-poor blood – but gills get oxygen from water, so process is slowed down at that point (2 pts.) Most efficient – high pressure, so blood travels very quickly throughout the body – separation of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood lungs get oxygen from the air, so more can diffuse ...
Respiratory Unit Test Review
... What is the active ingredient in marijuana and where does it go when it enters your body? What are four signs that your lungs have been damaged by smoking? Compare/contrast a healthy lung with a smoker’s lung. List and explain four health-related side effects related to smoking. Identify 4 chemicals ...
... What is the active ingredient in marijuana and where does it go when it enters your body? What are four signs that your lungs have been damaged by smoking? Compare/contrast a healthy lung with a smoker’s lung. List and explain four health-related side effects related to smoking. Identify 4 chemicals ...
Breath of Life Reading
... these lung compartments is not actually inside the internal environment of your body. Instead, the tissues of the lungs themselves separate this air from the rest of the cells of your body. How does oxygen move from your lungs into the internal environment of your body? And how does carbon dioxide m ...
... these lung compartments is not actually inside the internal environment of your body. Instead, the tissues of the lungs themselves separate this air from the rest of the cells of your body. How does oxygen move from your lungs into the internal environment of your body? And how does carbon dioxide m ...
42 Circulation
... Carbon dioxide is largely transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma although some is transported by hemoglobin ...
... Carbon dioxide is largely transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma although some is transported by hemoglobin ...
Chapter 18
... Gradual accumulation of differences in the gene pools of populations Natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation can contribute to divergence Gene flow counters divergence ...
... Gradual accumulation of differences in the gene pools of populations Natural selection, genetic drift, and mutation can contribute to divergence Gene flow counters divergence ...
The trachea is lined with cilia.
... 7. The nose contains …………….. and ……………….. to filter the inhaled air from dust and microbes. 8. Nose is lined with ……………, ……………and ………………………… 9. Larynx is called …………………………. 10. Trachea is lined with …………………to …………………….. 11. Alveoli have …………………………walls for exchange of gases 12. Exchange of gases occ ...
... 7. The nose contains …………….. and ……………….. to filter the inhaled air from dust and microbes. 8. Nose is lined with ……………, ……………and ………………………… 9. Larynx is called …………………………. 10. Trachea is lined with …………………to …………………….. 11. Alveoli have …………………………walls for exchange of gases 12. Exchange of gases occ ...
hyperoxia and hyperbaria - San Jose State University
... BEING DISSOLVED AND THEREFORE CAN SATURATE TISSUES) , AT A GIVEN TEMPERATURE THE CONCENTRATION IN THE LIQUID WILL BE NEARLY PROPORTIONAL TO THE PRESSURE OF THAT GAS IN THE GAS PHASE • GASES WITH LOW SOLUBILITY REQUIRE LESS TIME TO SATURATE A LIQUID THAN GASES OF A HIGHER SOLUBILITY • THE LONGER AND ...
... BEING DISSOLVED AND THEREFORE CAN SATURATE TISSUES) , AT A GIVEN TEMPERATURE THE CONCENTRATION IN THE LIQUID WILL BE NEARLY PROPORTIONAL TO THE PRESSURE OF THAT GAS IN THE GAS PHASE • GASES WITH LOW SOLUBILITY REQUIRE LESS TIME TO SATURATE A LIQUID THAN GASES OF A HIGHER SOLUBILITY • THE LONGER AND ...
9B Fit and Healthy
... Cigarettes contain 3 harmful things: 1. NICOTINE, which is an ___________ drug that raises the heart beat, narrows the arteries and so causes ____ _____ _____. This leads to heart _________. 2. TAR, which coats the lining of the _______ making them less able to take in oxygen. It also contains carci ...
... Cigarettes contain 3 harmful things: 1. NICOTINE, which is an ___________ drug that raises the heart beat, narrows the arteries and so causes ____ _____ _____. This leads to heart _________. 2. TAR, which coats the lining of the _______ making them less able to take in oxygen. It also contains carci ...
Adaptation and Natural Selection Adaptation Points of View Paley`s
... Our opsins have similarities with those of insects and cephalopods. All opsins show evidence of common descent. All eyes had a single origin. (Chang, Crandall, Carulli, and Hartl, 1995) ...
... Our opsins have similarities with those of insects and cephalopods. All opsins show evidence of common descent. All eyes had a single origin. (Chang, Crandall, Carulli, and Hartl, 1995) ...
Function of the blood
... The plasma is also responsible for the transportation of hormones, which have been secreted by the endocrine glands, to the target organs. Hormones like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, ...
... The plasma is also responsible for the transportation of hormones, which have been secreted by the endocrine glands, to the target organs. Hormones like erythropoietin, which are responsible for stimulating the production of erythrocytes, are transported in plasma. Other hormones like testosterone, ...
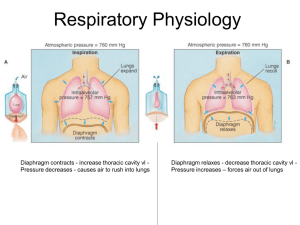
Respiratory Physiology
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
... Lung cancer –most common cancer and most common cause of cancer deaths in U.S. males. There are several forms of lung cancer, but the most common (and most rapidly increasing) types are those involving the epithelial cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles. Ordinarily, the lining of these airways c ...
Unit 3-5 Respiratory System Notes File
... – outer surface sponges, planaria etc – Skin Earthworms – gills Clamworm (parapodium), crayfish, fish (lancets) – Tracheae Grasshoppers – lungs Birds, Mammals ...
... – outer surface sponges, planaria etc – Skin Earthworms – gills Clamworm (parapodium), crayfish, fish (lancets) – Tracheae Grasshoppers – lungs Birds, Mammals ...
Circulatory System Red
... the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries • The body needs to get rid of CO2 (a product of cell respiration) and needs to take in O2 (needed for cell respiration to make ATP) (2) • Low concentration of carbon dioxide in the alveoli > carbon dioxide can diffuse out of the blood in the capillaries ...
... the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries • The body needs to get rid of CO2 (a product of cell respiration) and needs to take in O2 (needed for cell respiration to make ATP) (2) • Low concentration of carbon dioxide in the alveoli > carbon dioxide can diffuse out of the blood in the capillaries ...
Nematoda
... An open circulatory system is good for a bivalve because they are mainly sedentary, while squids have relatively low oxygen needs, and bivalves have high oxygen needs. Most of parasitic flatworms don’t need a complex digestive system because they take nutrients from other organisms. Insects are succ ...
... An open circulatory system is good for a bivalve because they are mainly sedentary, while squids have relatively low oxygen needs, and bivalves have high oxygen needs. Most of parasitic flatworms don’t need a complex digestive system because they take nutrients from other organisms. Insects are succ ...
population
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
Contracts and relaxes helping to force air into and out of the lungs
... Respiratory System Air can also be taken in through the mouth. These two openings of the airway (the nasal cavity and the mouth) meet at the pharynx, or throat, at the back of the nose and mouth. The pharynx is part of the digestive system as well as the respiratory system because it carries both f ...
... Respiratory System Air can also be taken in through the mouth. These two openings of the airway (the nasal cavity and the mouth) meet at the pharynx, or throat, at the back of the nose and mouth. The pharynx is part of the digestive system as well as the respiratory system because it carries both f ...
Topic D (Evolution)
... Topic D.1.2. Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds. – In the 1920’s, A.I. Oparin of Russia and J.B.S. Haldane of Great Britain independently postulated that conditions on the primitive Earth favored chemical reactions that synthesized organic compounds from ...
... Topic D.1.2. Outline the experiments of Miller and Urey into the origin of organic compounds. – In the 1920’s, A.I. Oparin of Russia and J.B.S. Haldane of Great Britain independently postulated that conditions on the primitive Earth favored chemical reactions that synthesized organic compounds from ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.