Animals Organ Systems - Austin Community College
... throughout evolution of vertebrates these three subdivisions become more complex generally, brain mass increases with body mass eg. birds and mammals have larger brains than fishes amphibians and reptiles eg. largest brains: whales and elephants but humans have ~7x’s more brain for relative body siz ...
... throughout evolution of vertebrates these three subdivisions become more complex generally, brain mass increases with body mass eg. birds and mammals have larger brains than fishes amphibians and reptiles eg. largest brains: whales and elephants but humans have ~7x’s more brain for relative body siz ...
Respiratory System Notes Main Idea Details 1. What human body
... from the body? 1. Where does air enter the respiratory system? 2. What is the purpose of the mucous in the lining of the nose? 3. What is the purpose of the hair in the lining of the nose? 4. What is the flap of tissue called that keeps food and water from entering the trachea? 5. Label the nose and ...
... from the body? 1. Where does air enter the respiratory system? 2. What is the purpose of the mucous in the lining of the nose? 3. What is the purpose of the hair in the lining of the nose? 4. What is the flap of tissue called that keeps food and water from entering the trachea? 5. Label the nose and ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... Most of the bony fishes we ear are ray-finned fishes. The lobe-finned fishes are the ancestors of amphibians; they had fleshy appendages that could be adapted to land locomotion and most had a lung that was used for respiration. Amphibians: Jointed Appendages Amphibians include frogs, toads, newts, ...
... Most of the bony fishes we ear are ray-finned fishes. The lobe-finned fishes are the ancestors of amphibians; they had fleshy appendages that could be adapted to land locomotion and most had a lung that was used for respiration. Amphibians: Jointed Appendages Amphibians include frogs, toads, newts, ...
Chapter 24 The Origin of Species Part C
... retains features that are present in the juvenile form. Ex. – gills in adult salamanders ...
... retains features that are present in the juvenile form. Ex. – gills in adult salamanders ...
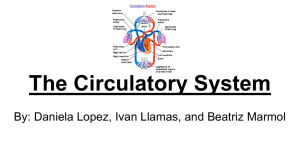
The Circulatory System
... Another disease, hypertension, commonly called high blood pressure, is often associated with arteriosclerosis A substance called plaque can build up in the arteries, restricting blood flow and ultimately stopping or blocking it altogether. This plaque can cause serious cardiovascular disease that le ...
... Another disease, hypertension, commonly called high blood pressure, is often associated with arteriosclerosis A substance called plaque can build up in the arteries, restricting blood flow and ultimately stopping or blocking it altogether. This plaque can cause serious cardiovascular disease that le ...
Plain Local Schools 5th Grade Science
... Many organisms have adaptations. For example, organisms that live in the water breathe in oxygen from the water through their gills. Organisms that live outside the pond breathe oxygen from the air through their lungs. Some animals can swim in the water but still breathe once out of the pond on land ...
... Many organisms have adaptations. For example, organisms that live in the water breathe in oxygen from the water through their gills. Organisms that live outside the pond breathe oxygen from the air through their lungs. Some animals can swim in the water but still breathe once out of the pond on land ...
Chapter 33: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Every breath
... Millions of alveoli in the lung provide enormous surface area for gas exchange. Oxygen breathed into the lung diffuses across the alveoli into thin capillary walls containing blood. The capillaries connect with larger arteries and veins and transport the oxygenated blood. At the same time CO2 diffus ...
... Millions of alveoli in the lung provide enormous surface area for gas exchange. Oxygen breathed into the lung diffuses across the alveoli into thin capillary walls containing blood. The capillaries connect with larger arteries and veins and transport the oxygenated blood. At the same time CO2 diffus ...
Respiratory
... everyone's balloon is and write down the numbers next to the persons names. Let air out of balloons and repeat two more times. Take an average of three tests. ...
... everyone's balloon is and write down the numbers next to the persons names. Let air out of balloons and repeat two more times. Take an average of three tests. ...
Birds (cont.)
... • High metabolism to get energy to fly • Eat large amounts of food in proportion to body weight • Large eyes ...
... • High metabolism to get energy to fly • Eat large amounts of food in proportion to body weight • Large eyes ...
Evolutionary Mechanisms - 1 The Gene Pool and Genetic
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, all individuals must be equally adaptive in their environment for all of their genetic characteristics. In real populations this is not the case. • The many variants in a population will have different responses to the common environment in which they live. • The c ...
... In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, all individuals must be equally adaptive in their environment for all of their genetic characteristics. In real populations this is not the case. • The many variants in a population will have different responses to the common environment in which they live. • The c ...
Birds (cont.)
... • High metabolism to get energy to fly • Eat large amounts of food in proportion to body weight • Large eyes ...
... • High metabolism to get energy to fly • Eat large amounts of food in proportion to body weight • Large eyes ...
Cherstie Meskey 11/26/10 Chemistry Elements of Your Body
... means they will automatically move from an area of higher concentration to an area of low concentration. This is a passive movement, and therefore disrupts our membrane potential. The pumps use active transport to pump the ions back into where they came from, creating a constant cycle of sodium and ...
... means they will automatically move from an area of higher concentration to an area of low concentration. This is a passive movement, and therefore disrupts our membrane potential. The pumps use active transport to pump the ions back into where they came from, creating a constant cycle of sodium and ...
Climate Change Biology - Romberg Tiburon Center
... of climate change.” We need more research aimed at identifying which populations are vulnerable to ocean acidification, she adds. “We also need a clear understanding of the costs associated with the synergistic interactions of ocean acidification and ocean warming.” Although environmental issues dep ...
... of climate change.” We need more research aimed at identifying which populations are vulnerable to ocean acidification, she adds. “We also need a clear understanding of the costs associated with the synergistic interactions of ocean acidification and ocean warming.” Although environmental issues dep ...
Development and Growth
... • An egg hatches into a nymph which usually looks like an adult without wings. • As the nymph grows it may shed it’s exoskeleton several times. ...
... • An egg hatches into a nymph which usually looks like an adult without wings. • As the nymph grows it may shed it’s exoskeleton several times. ...
Respiratory System
... i. consists of a single layer of cells fused to the surface of a connective tissue layer, it envelopes both lungs ii. The pleura for the right and left lung meet near the midline, where it reflects upward (dorsally), turns back on the inner thoracic wall, and provides for its lining. iii. The space ...
... i. consists of a single layer of cells fused to the surface of a connective tissue layer, it envelopes both lungs ii. The pleura for the right and left lung meet near the midline, where it reflects upward (dorsally), turns back on the inner thoracic wall, and provides for its lining. iii. The space ...
1 Chapter 5
... oxygen from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. • Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) • Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the va ...
... oxygen from the atmosphere. This process is called ventilation. • Diffusion – Exchange of gases based on concentration levels (High to low). Occurs at a cellular level (In the lungs and in the muscle cell) • Cardiac output (Heart rate x stroke volume) - The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the va ...
Birds and Mammals
... with blood. Their lungs are modified to maintain good levels of oxygen for their blood. They have light bones for flight. Care for Offspring – Birds care for their young until they are old enough to search for food and fly on their own. Birds sit on their eggs “called brooding” and incubate them unt ...
... with blood. Their lungs are modified to maintain good levels of oxygen for their blood. They have light bones for flight. Care for Offspring – Birds care for their young until they are old enough to search for food and fly on their own. Birds sit on their eggs “called brooding” and incubate them unt ...
Chapter 22
... Forks into two bronchi. 5. Bronchi (Sing. Bronchus): Each bronchus leads into a lung and branches into smaller and smaller bronchioles, resembling an inverted tree. 6. Bronchioles: Fine tubes that allow passage of air. Muscle layer constricts bronchioles. Epithelium of bronchioles is covered with ci ...
... Forks into two bronchi. 5. Bronchi (Sing. Bronchus): Each bronchus leads into a lung and branches into smaller and smaller bronchioles, resembling an inverted tree. 6. Bronchioles: Fine tubes that allow passage of air. Muscle layer constricts bronchioles. Epithelium of bronchioles is covered with ci ...
Ch.6 Lecture (2012)
... a theory of evolution that is still studied today. • Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection is the process by which populations with variations that help them survive in their environments live longer and reproduce more than those without beneficial variations. Over time, beneficial varia ...
... a theory of evolution that is still studied today. • Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection is the process by which populations with variations that help them survive in their environments live longer and reproduce more than those without beneficial variations. Over time, beneficial varia ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.