Placebo
... Clinical Senior Lecturer, Pain Medicine, Sydney Medical School University of Sydney Pain Management Research Institute ...
... Clinical Senior Lecturer, Pain Medicine, Sydney Medical School University of Sydney Pain Management Research Institute ...
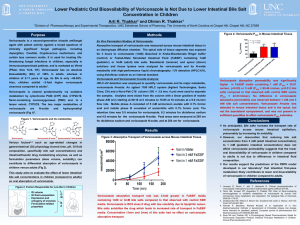
Lower Pediatric Oral Bioavailability of Voriconazole is Not Due to
... composition, specifically bile salt concentrations) and intestinal/hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes, as well as formulation parameters (dose volume, solubility) can contribute to differential absorption of voriconazole in children versus adults (Fig 2). This study aims to evaluate the effect of low ...
... composition, specifically bile salt concentrations) and intestinal/hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes, as well as formulation parameters (dose volume, solubility) can contribute to differential absorption of voriconazole in children versus adults (Fig 2). This study aims to evaluate the effect of low ...
pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, metabolism, and excretion of
... validated by analyzing aliquots of control tissues fortified with known amounts of radioactivity. The mean recovery of radioactivity was 98.2%. Tissue levels of radioactivity were expressed as microgram equivalents per gram of tissue and were calculated by dividing the dpm per gram of tissue by the ...
... validated by analyzing aliquots of control tissues fortified with known amounts of radioactivity. The mean recovery of radioactivity was 98.2%. Tissue levels of radioactivity were expressed as microgram equivalents per gram of tissue and were calculated by dividing the dpm per gram of tissue by the ...
Metoprolol beta 2
... Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that affects the heart and circulation (blood flow through arteries and veins). Metoprolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and. TOPROL-XL, metoprolol succinate, is a beta 1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoceptor blocking agent, for oral administration, available a ...
... Metoprolol is a beta-blocker that affects the heart and circulation (blood flow through arteries and veins). Metoprolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and. TOPROL-XL, metoprolol succinate, is a beta 1-selective (cardioselective) adrenoceptor blocking agent, for oral administration, available a ...
Monitored Anesthesia Care with Dexmedetomidine: A
... laboratory tests, vital signs, and concomitant medications. Protocol-defined relative changes in arterial blood pressure (30% or more change from baseline, which was Vol. 110, No. 1, January 2010 ...
... laboratory tests, vital signs, and concomitant medications. Protocol-defined relative changes in arterial blood pressure (30% or more change from baseline, which was Vol. 110, No. 1, January 2010 ...
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Analysis
... of this analysis confirmed that the proposed method was suitable for determination of drug in pharmaceutical formulation with virtually no interference of additives. Hence the proposed method can be successfully applied in simultaneous estimation of mosapride and pantoprazole in marketed formulation ...
... of this analysis confirmed that the proposed method was suitable for determination of drug in pharmaceutical formulation with virtually no interference of additives. Hence the proposed method can be successfully applied in simultaneous estimation of mosapride and pantoprazole in marketed formulation ...
- University of Mississippi
... jumping, and rapidly tapping one of the back paws. Because mice lick their front paws during grooming, only the activity of the back paws is marked as perception of pain. Additionally, the cut-off time for this assay is 45 seconds to reduce the possibility of tissue damage to the subject. The purpos ...
... jumping, and rapidly tapping one of the back paws. Because mice lick their front paws during grooming, only the activity of the back paws is marked as perception of pain. Additionally, the cut-off time for this assay is 45 seconds to reduce the possibility of tissue damage to the subject. The purpos ...
The BC Public Health Opiod Overdose Emergency
... overdose. Illegal fentanyl was detected in 60% of these fatalities (based on data to October, 2016). In 2016, 744 of the 922 deaths (81%) were in men. However, only 2/3 of Emergency Department patients were males. This raises questions about if males are more likely to use substances alone, not ha ...
... overdose. Illegal fentanyl was detected in 60% of these fatalities (based on data to October, 2016). In 2016, 744 of the 922 deaths (81%) were in men. However, only 2/3 of Emergency Department patients were males. This raises questions about if males are more likely to use substances alone, not ha ...
of Pharmacy and Pharmacology African Journal
... quantities significantly in herbs (Mustafa et al., 2004). It is important to have a good quality control for herbal medicines in order to protect consumers from contamination (Chwan-Bor et al., 2003). Therefore, it is a critical challenge to determine the concentration of essential elements, heavy a ...
... quantities significantly in herbs (Mustafa et al., 2004). It is important to have a good quality control for herbal medicines in order to protect consumers from contamination (Chwan-Bor et al., 2003). Therefore, it is a critical challenge to determine the concentration of essential elements, heavy a ...
Variability of aerosol delivery via spacer devices in young
... using plastic and metal spacers [1, 5, 13]. In clinical practice the performance of inhalation devices should be known in order to prescribe medication dosages correctly and consistently. There are several sources of dose variability. Electrostatic charge which retains the drug in the spacer can bui ...
... using plastic and metal spacers [1, 5, 13]. In clinical practice the performance of inhalation devices should be known in order to prescribe medication dosages correctly and consistently. There are several sources of dose variability. Electrostatic charge which retains the drug in the spacer can bui ...
Document
... •Advantages attributed by those who have been treated with ibogaine are higher tolerability relative to other standard treatments for acute opioid withdrawal, and post-treatment interval of diminished drug craving that may last days to month. •Low dose protocols involving repeated administration of ...
... •Advantages attributed by those who have been treated with ibogaine are higher tolerability relative to other standard treatments for acute opioid withdrawal, and post-treatment interval of diminished drug craving that may last days to month. •Low dose protocols involving repeated administration of ...
CUBICIN ® Product Monograph - Sunovion Pharmaceuticals
... Direct effects on the central nervous system have not been investigated. In a small number of patients in Phase 1 and Phase 2 studies at doses up to 6 mg/kg, administration of CUBICIN® was associated with decreases in nerve conduction velocity and with adverse events (e.g., paresthesias, Bell’s pals ...
... Direct effects on the central nervous system have not been investigated. In a small number of patients in Phase 1 and Phase 2 studies at doses up to 6 mg/kg, administration of CUBICIN® was associated with decreases in nerve conduction velocity and with adverse events (e.g., paresthesias, Bell’s pals ...
Thyroid and Parathyroid Agents
... Because the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease mimic many other problems that are common to older adults—hair loss, slurred speech, fluid retention, heart failure, and so on it is important to screen older adults for thyroid disease carefully before beginning any therapy. The dose should be start ...
... Because the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease mimic many other problems that are common to older adults—hair loss, slurred speech, fluid retention, heart failure, and so on it is important to screen older adults for thyroid disease carefully before beginning any therapy. The dose should be start ...
Molly: The Not So Convincing Truth of MDMA
... patients who have battled with low self esteem, poor communication skills, and anxiety disorders (4). No other substance has lead patients to break away from their issues and look at themselves with a rational frame of mind (4). Paired with the lack of addictive nature, the therapeutic effects of MD ...
... patients who have battled with low self esteem, poor communication skills, and anxiety disorders (4). No other substance has lead patients to break away from their issues and look at themselves with a rational frame of mind (4). Paired with the lack of addictive nature, the therapeutic effects of MD ...
Phenobarbital
... metabolite) is detected in urine or blood, or increased serum nicotine levels occur. ...
... metabolite) is detected in urine or blood, or increased serum nicotine levels occur. ...
Prescribing Information
... 7 to 15 ng/mL (with basiliximab induction) 10 to 15 ng/mL (without basiliximab induction) ...
... 7 to 15 ng/mL (with basiliximab induction) 10 to 15 ng/mL (without basiliximab induction) ...
Word 68KB
... The PBAC recommended the Section 100 (Efficient Funding of Chemotherapy) Authority Required (STREAMLINED) listing of nivolumab for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic, squamous or non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients who meet certain conditions. The PBAC considere ...
... The PBAC recommended the Section 100 (Efficient Funding of Chemotherapy) Authority Required (STREAMLINED) listing of nivolumab for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic, squamous or non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients who meet certain conditions. The PBAC considere ...
comparative studies on the cytochrome p450
... ingestion was not available for all subjects. The use of tissue surplus to requirement was approved by the appropriate ethics committee in each university. Microsomes were prepared according to standard procedures. The final microsomal pellet was suspended in 0.1 M phosphate buffer to a concentratio ...
... ingestion was not available for all subjects. The use of tissue surplus to requirement was approved by the appropriate ethics committee in each university. Microsomes were prepared according to standard procedures. The final microsomal pellet was suspended in 0.1 M phosphate buffer to a concentratio ...
Evaluation of the efficacy of albendazole sulphoxide and
... and praziquantel were prepared in DMSO and ethanol, respectively. To determine the concentration that produced 50% effect (EC50), working solutions of praziquantel and albendazole sulphoxide were prepared in culture medium to obtain concentrations from 0.005 to 0.04 mg/mL and from 0.021 to 0.16 mg/m ...
... and praziquantel were prepared in DMSO and ethanol, respectively. To determine the concentration that produced 50% effect (EC50), working solutions of praziquantel and albendazole sulphoxide were prepared in culture medium to obtain concentrations from 0.005 to 0.04 mg/mL and from 0.021 to 0.16 mg/m ...
Ibogaine
... differences in absorption kinetics. High hepatic first pass effect Distribution: High hepatic extraction Highly lipophilic [Ibogaine] 100 times grater in fat and 30 times greater in brain Platelets might sequester Ibogaine ...
... differences in absorption kinetics. High hepatic first pass effect Distribution: High hepatic extraction Highly lipophilic [Ibogaine] 100 times grater in fat and 30 times greater in brain Platelets might sequester Ibogaine ...
product monograph serc
... Distribution The percentage of betahistine dihydrochloride that is bound by blood plasma proteins is less than ...
... Distribution The percentage of betahistine dihydrochloride that is bound by blood plasma proteins is less than ...
Addressing specific regulatory excipient requirements
... qualitative composition, specification as a whole and of each component required. ¾ This nebulous guidance offers much space for interpretation ¾ IPEC differentiates between „mixed“ and „co-processed excipients“ (combined excipients with physically modified properties; not achievable by simple mixin ...
... qualitative composition, specification as a whole and of each component required. ¾ This nebulous guidance offers much space for interpretation ¾ IPEC differentiates between „mixed“ and „co-processed excipients“ (combined excipients with physically modified properties; not achievable by simple mixin ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.