LSD
... The physical effects include dilated pupils, higher body temperature, increased heart rate and blood pressure, sweating, loss of appetite, sleeplessness, dry mouth, and tremors. Sensations may seem to "cross over" for the user, giving the feeling of hearing colors and seeing sounds. If taken in a la ...
... The physical effects include dilated pupils, higher body temperature, increased heart rate and blood pressure, sweating, loss of appetite, sleeplessness, dry mouth, and tremors. Sensations may seem to "cross over" for the user, giving the feeling of hearing colors and seeing sounds. If taken in a la ...
Phentermine hydrochloride
... amines. Also, agitated states, those with a history of drug abuse, during or within 14 days following the administration of MAO inhibitors (hypertensive crisis may occur). Use with other drugs for weight loss, as well as with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors is not recommended. Lactation. Use ...
... amines. Also, agitated states, those with a history of drug abuse, during or within 14 days following the administration of MAO inhibitors (hypertensive crisis may occur). Use with other drugs for weight loss, as well as with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors is not recommended. Lactation. Use ...
VM 8314
... What does it mean Volume of distribution is increased The cycle itself is a space where drug “remains” ...
... What does it mean Volume of distribution is increased The cycle itself is a space where drug “remains” ...
•
... - check the dose, read the container label, calculate the dose & check with a RN if necessary - use proper measuring devices for liquids, do not crush tablets or open capsules unless directed to by the pharmacist. (do not crush enteric coated tablets). - if a drug is required in another form you may ...
... - check the dose, read the container label, calculate the dose & check with a RN if necessary - use proper measuring devices for liquids, do not crush tablets or open capsules unless directed to by the pharmacist. (do not crush enteric coated tablets). - if a drug is required in another form you may ...
Clinical Considerations During Phase 2 and Phase 3 of - M
... to Phase 3) and select adequate doses for approval – Does treatment effect/adverse event increase with dose/exposures? – A dose may be selected for Phase 3 or approval even if it was not evaluated in previous trials. ...
... to Phase 3) and select adequate doses for approval – Does treatment effect/adverse event increase with dose/exposures? – A dose may be selected for Phase 3 or approval even if it was not evaluated in previous trials. ...
Antiepileptic Medication: Topamax (topiramate)
... You might be more aware of dose related side effects at this time if you have them. It takes 19-25 hours for half of the Topamax to leave your body. This allows you to take the medication twice a day. Less than 20% of the drug binds to proteins. This portion of the drug is not active. It is metaboli ...
... You might be more aware of dose related side effects at this time if you have them. It takes 19-25 hours for half of the Topamax to leave your body. This allows you to take the medication twice a day. Less than 20% of the drug binds to proteins. This portion of the drug is not active. It is metaboli ...
BP 703T. PHARMACY PRACTICE (Theory)
... Scope: In the changing scenario of pharmacy practice in India, for successful practice of Hospital Pharmacy, the students are required to learn various skills like drug distribution, drug information, and therapeutic drug monitoring for improved patient care. In community pharmacy, students will be ...
... Scope: In the changing scenario of pharmacy practice in India, for successful practice of Hospital Pharmacy, the students are required to learn various skills like drug distribution, drug information, and therapeutic drug monitoring for improved patient care. In community pharmacy, students will be ...
Drug Eruptions
... is distinct from erythema multiforme major, which is usually caused by infections and runs a benign course. SJS is usually drug induced and can be fatal. SJS and TEN usually occur 1-3 weeks after exposure, but can occur more rapidly with re-exposure, which suggests an immunologic mechanism. Muco ...
... is distinct from erythema multiforme major, which is usually caused by infections and runs a benign course. SJS is usually drug induced and can be fatal. SJS and TEN usually occur 1-3 weeks after exposure, but can occur more rapidly with re-exposure, which suggests an immunologic mechanism. Muco ...
Gemfibrozil is completely absorbed after oral administration of Lopid
... Gemfibrozil is completely absorbed after oral administration of Lopid tablets, reaching peak plasma concentrations 1 to 2 hours after dosing. Gemfibrozil pharmacokinetics are affected by the timing of meals relative to time of dosing. In one study (2), both the rate and extent of absorption of the d ...
... Gemfibrozil is completely absorbed after oral administration of Lopid tablets, reaching peak plasma concentrations 1 to 2 hours after dosing. Gemfibrozil pharmacokinetics are affected by the timing of meals relative to time of dosing. In one study (2), both the rate and extent of absorption of the d ...
Rohypnol - Addictions Foundation Manitoba
... • the inability to think clearly • the inability to make proper judgments about the situation they are in • greater inhibition (doing things they normally would not do) • feeling and acting aggressively • slurred speech • clumsiness • lower heart rate, breathing rate and blood pressure • amnesia (ca ...
... • the inability to think clearly • the inability to make proper judgments about the situation they are in • greater inhibition (doing things they normally would not do) • feeling and acting aggressively • slurred speech • clumsiness • lower heart rate, breathing rate and blood pressure • amnesia (ca ...
Adverse Effects of Antibiotics
... • Hematological adverse effects • Distributes to bone + mitochondrial toxicity ...
... • Hematological adverse effects • Distributes to bone + mitochondrial toxicity ...
Document
... SO, I double the dose and the plasma concentrations double (I get what I expect). The pharmacokinetics PREDICT that I when I double the dose the concentrations double so THE PHARMACOKINETICS are dose independent. ...
... SO, I double the dose and the plasma concentrations double (I get what I expect). The pharmacokinetics PREDICT that I when I double the dose the concentrations double so THE PHARMACOKINETICS are dose independent. ...
Pharmacogenomics and nutrigenomics
... Metabolism: Isozymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A3/4 are responsible for the metabolism of cevimeline. After 24 hours 86.7% of the dose was recovered (16.0% Unchanged, 44.5% as cis and trans-sulfoxide, 22.3% of the dose as glucuronic acid conjugate and 4% of the dose as Noxide of cevimeline). Approximately 8% o ...
... Metabolism: Isozymes CYP2D6 and CYP3A3/4 are responsible for the metabolism of cevimeline. After 24 hours 86.7% of the dose was recovered (16.0% Unchanged, 44.5% as cis and trans-sulfoxide, 22.3% of the dose as glucuronic acid conjugate and 4% of the dose as Noxide of cevimeline). Approximately 8% o ...
Drug Interactions - STA HealthCare Communications
... enzyme.5 Metoprolol is processed by this enzyme. Therefore, deficient patients would not be able to process metoprolol and, hence, even a small dose would result in very high blood levels of metoprolol. Another example involves codeine. Codeine is a prodrug that requires CYP 2D6 to convert it into m ...
... enzyme.5 Metoprolol is processed by this enzyme. Therefore, deficient patients would not be able to process metoprolol and, hence, even a small dose would result in very high blood levels of metoprolol. Another example involves codeine. Codeine is a prodrug that requires CYP 2D6 to convert it into m ...
Drug Slides Ch. 3
... Activation – How and where does the drug produce its effects? Biotransformation and elimination – How is the drug inactivated, metabolized, and/or excreted from the body? ...
... Activation – How and where does the drug produce its effects? Biotransformation and elimination – How is the drug inactivated, metabolized, and/or excreted from the body? ...
DRUG INTERACTIONS
... the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system that are responsible for many of the phase 1 biotransformations of drugs. These metabolic transformations, such as oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis, produce a molecule that is suitable for conjugation. Those of importance in the metabolism of psychotropic drugs ar ...
... the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system that are responsible for many of the phase 1 biotransformations of drugs. These metabolic transformations, such as oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis, produce a molecule that is suitable for conjugation. Those of importance in the metabolism of psychotropic drugs ar ...
powerpoint - Med Referrals
... He led all laboratory operations for an investigator initiated Phase I clinical trial using stem cells to treat cardiac disease and helped develop a proprietary cardiovascular disease gene data set for a publicly traded genomics company. In addition to clinical trial design and management for FDA re ...
... He led all laboratory operations for an investigator initiated Phase I clinical trial using stem cells to treat cardiac disease and helped develop a proprietary cardiovascular disease gene data set for a publicly traded genomics company. In addition to clinical trial design and management for FDA re ...
GNRS4Pharmacotherapy
... • FDA and off-label indications are expanding • Formularies change frequently • Knowledge of drug-drug interactions advances • Drugs change from prescription to OTC • “Nutraceuticals” (herbal preparations, nutritional supplements) are booming ...
... • FDA and off-label indications are expanding • Formularies change frequently • Knowledge of drug-drug interactions advances • Drugs change from prescription to OTC • “Nutraceuticals” (herbal preparations, nutritional supplements) are booming ...
Pharmacokinetics
... and it has an extra layer of cells surrounding them (glial cells). However, fever/inflammation can make the membrane more permeable to some drugs. Exception: The placenta has the ability to block SOME drugs from affecting the fetus with its barrier. ...
... and it has an extra layer of cells surrounding them (glial cells). However, fever/inflammation can make the membrane more permeable to some drugs. Exception: The placenta has the ability to block SOME drugs from affecting the fetus with its barrier. ...
(Pharmaceutics) Syllabus
... rate constants and different plots (direct, scatchard and reciprocal), significance volume of distribution, implications and in vitro methodologies. ...
... rate constants and different plots (direct, scatchard and reciprocal), significance volume of distribution, implications and in vitro methodologies. ...
drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic (DMPK)
... In Vitro Metabolism By providing critical information early in the drug development process, our ADMET screening assays help you identify and focus efforts on compounds that have the greatest likelihood of success. Once a lead candidate is selected, both qualitative and quantitative analyses of radi ...
... In Vitro Metabolism By providing critical information early in the drug development process, our ADMET screening assays help you identify and focus efforts on compounds that have the greatest likelihood of success. Once a lead candidate is selected, both qualitative and quantitative analyses of radi ...
Drug Discovery and Development
... Identifying a Drug Target (cont.) • Example: In addition to their being able to inhibit the uptake of noradrenaline, the older tricyclic antidepressants were observed to “incidentally” inhibit serotonin uptake. Thus, it was decided to prepare molecules which could specifically inhibit ...
... Identifying a Drug Target (cont.) • Example: In addition to their being able to inhibit the uptake of noradrenaline, the older tricyclic antidepressants were observed to “incidentally” inhibit serotonin uptake. Thus, it was decided to prepare molecules which could specifically inhibit ...
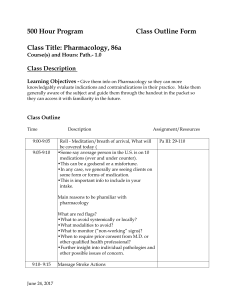
86a-CO-Pharmacology
... Roll - Meditation/breath of arrival, What will be covered today ( •Some say average person in the U.S. is on 10 medications (over and under counter). •This can be a godsend or a misfortune. •In any case, we generally are seeing clients on some form or forms of medication. •This is important info to ...
... Roll - Meditation/breath of arrival, What will be covered today ( •Some say average person in the U.S. is on 10 medications (over and under counter). •This can be a godsend or a misfortune. •In any case, we generally are seeing clients on some form or forms of medication. •This is important info to ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.