Equianalgesic Chart (Page 1)
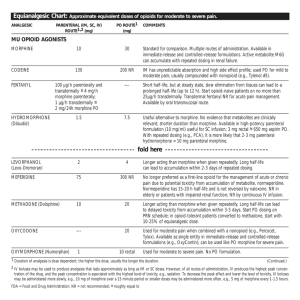
... Longer acting than morphine when given repeatedly. Long half-life can lead to accumulation within 2-3 days of repeated dosing. No longer preferred as a first-line opioid for the management of acute or chronic pain due to potential toxicity from accumulation of metabolite, normeperidine. Normeperidin ...
... Longer acting than morphine when given repeatedly. Long half-life can lead to accumulation within 2-3 days of repeated dosing. No longer preferred as a first-line opioid for the management of acute or chronic pain due to potential toxicity from accumulation of metabolite, normeperidine. Normeperidin ...
Modeling and Simulation of Biochemical Processes
... chemical concentrations. To determine the slowest rate, the smallest possible concentrations for each chemical species are used. Similarly, the fastest rate can be determined by using the highest possible concentrations. Since the reaction rates depend on the concentrations, reactions may be classifi ...
... chemical concentrations. To determine the slowest rate, the smallest possible concentrations for each chemical species are used. Similarly, the fastest rate can be determined by using the highest possible concentrations. Since the reaction rates depend on the concentrations, reactions may be classifi ...
The Neurobiology of Alcoholism: Insights from the Dark Side of
... Key Findings and Conclusions Acute reinforcing effects of drugs of abuse— depend on neurochemical substrates such as GABA, opioid peptides, serotonin, glutamate and dopamine in the ventral striatum of the basal forebrain. ...
... Key Findings and Conclusions Acute reinforcing effects of drugs of abuse— depend on neurochemical substrates such as GABA, opioid peptides, serotonin, glutamate and dopamine in the ventral striatum of the basal forebrain. ...
Mechanism of Action
... but sometimes used to treat major depression as a second-line treatment. Mechanism of Action Imipramine, a tertiary amine, inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. it blocks the reuptake of neurotransmitters serotonin and noradrenaline almost ...
... but sometimes used to treat major depression as a second-line treatment. Mechanism of Action Imipramine, a tertiary amine, inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. it blocks the reuptake of neurotransmitters serotonin and noradrenaline almost ...
Acute Pain Management
... class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of an antagonist ...
... class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of an antagonist ...
Acute Pain Management - Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine
... class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of an antagonist ...
... class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of an antagonist ...
Level of Evidence Associated with FDA Safety Communications with
... with the rigor of controlled clinical trials. However, controlled clinical trials are not the best way to evaluate adverse drug reactions associated with drug products. This study confirms that LOE B is associated more frequently with labeling changes. Previous studies have evaluated drug safety lab ...
... with the rigor of controlled clinical trials. However, controlled clinical trials are not the best way to evaluate adverse drug reactions associated with drug products. This study confirms that LOE B is associated more frequently with labeling changes. Previous studies have evaluated drug safety lab ...
REVERSE PHASE HPLC METHOD FOR THE ANALYSIS OF ANASTRAZOLE IN PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS Research Article
... After several systematic trails the present study was aimed at developing a sensitive, precise and accurate RP‐HPLC method for the analysis of anastrazole in pharmaceutical dosage forms .The present method contains mobile phase 10 Mm ammonium acetate buffer and acetonitrile in the r ...
... After several systematic trails the present study was aimed at developing a sensitive, precise and accurate RP‐HPLC method for the analysis of anastrazole in pharmaceutical dosage forms .The present method contains mobile phase 10 Mm ammonium acetate buffer and acetonitrile in the r ...
Antimalarial drug discovery: efficacy models for compound
... secondary in vivo methods include: Dose ranging test: Here, compounds are tested at a minimum of 4 different doses (the “dose ranging, full 4-day test”, typically 100, 30, 10 and 3 mg/kg, by both s.c. and p.o. routes of administration). ED5 0 and ED9 0 values are calculated by plotting the log dose ...
... secondary in vivo methods include: Dose ranging test: Here, compounds are tested at a minimum of 4 different doses (the “dose ranging, full 4-day test”, typically 100, 30, 10 and 3 mg/kg, by both s.c. and p.o. routes of administration). ED5 0 and ED9 0 values are calculated by plotting the log dose ...
Antimicrobial1
... especially in pregnant patients and those having very poor diets. These blood disorders can be reversed by the simultaneous administration of folinic acid, which does not enter bacteria. ...
... especially in pregnant patients and those having very poor diets. These blood disorders can be reversed by the simultaneous administration of folinic acid, which does not enter bacteria. ...
Guidelines for Monitoring and Reporting Adverse Drug Reactions
... active constituents, effects of by-products of the active constituents derived from chemical synthesis and effects of additives, solubilizing, stabilizing, colouring agents and excipients commonly incorporated in pharmaceutical preparations. Therefore, alteration in production methods may have marke ...
... active constituents, effects of by-products of the active constituents derived from chemical synthesis and effects of additives, solubilizing, stabilizing, colouring agents and excipients commonly incorporated in pharmaceutical preparations. Therefore, alteration in production methods may have marke ...
Drug receptors and Pharmacodynamics
... The extent of inhibition depends on the antagonist’s concentration. Thus the extent and duration of an antagonists action depends upon its concentration in the plasma which in turn is influenced by the rate of its metabolic clearance or excretion. Different patients receiving a fixed dose of propran ...
... The extent of inhibition depends on the antagonist’s concentration. Thus the extent and duration of an antagonists action depends upon its concentration in the plasma which in turn is influenced by the rate of its metabolic clearance or excretion. Different patients receiving a fixed dose of propran ...
ROUTING SLIP GENERATED BY:
... spokesman Greg Aiello, quoted in a Los Angeles Times article stated that “the purpose is to protect our players who operate in a very unique and stressful environment”. Aiello also said “because of the research that’s out there on ephedra, the commissioner [Paul Tagliabue] has reached the conclusion ...
... spokesman Greg Aiello, quoted in a Los Angeles Times article stated that “the purpose is to protect our players who operate in a very unique and stressful environment”. Aiello also said “because of the research that’s out there on ephedra, the commissioner [Paul Tagliabue] has reached the conclusion ...
Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of - e
... an advantage of easy accessibility, larger surface area, porous endothelial membrane, increased blood flow, and avoidance of the first-pass metabolism.9 Although nasal delivery is routinely used for sinusitis as well as nasal allergy, infection, and congestion, the use of this route for systemic adm ...
... an advantage of easy accessibility, larger surface area, porous endothelial membrane, increased blood flow, and avoidance of the first-pass metabolism.9 Although nasal delivery is routinely used for sinusitis as well as nasal allergy, infection, and congestion, the use of this route for systemic adm ...
Antidepressants and suicide
... and SSRIs and were very similar for 37 of 42 identified symptoms. However, they were not described as dependence for SSRIs. To define similar problems as “dependence” for benzodiazepines and as “withdrawal reactions” for SSRIs is irrational. For patients, the symptoms are just the same; it can be ve ...
... and SSRIs and were very similar for 37 of 42 identified symptoms. However, they were not described as dependence for SSRIs. To define similar problems as “dependence” for benzodiazepines and as “withdrawal reactions” for SSRIs is irrational. For patients, the symptoms are just the same; it can be ve ...
US Charges 50 Colombian guerrillas in drug
... Orlando Gonzalez, a real estate developer who moved to Florida from Colombia eight years ago, supports the U.S. government's efforts to prosecute Colombian drug traffickers. But he said officials have to tackle the source of the problem -- drug consumption in the United States. Gonzalez said the ind ...
... Orlando Gonzalez, a real estate developer who moved to Florida from Colombia eight years ago, supports the U.S. government's efforts to prosecute Colombian drug traffickers. But he said officials have to tackle the source of the problem -- drug consumption in the United States. Gonzalez said the ind ...
Metacam Risks in Cats
... Metacam Solution for Injection (for cats) and Metacam Oral Suspension (for dogs). Metacam’s FDA Approval Status Metacam Solution for Injection was approved for one-time use only in cats on 28 Nov 2004 (NADA 141-219). Metacam Oral Suspension was approved for dogs only on 15 Apr 2003 (NADA 141-213). A ...
... Metacam Solution for Injection (for cats) and Metacam Oral Suspension (for dogs). Metacam’s FDA Approval Status Metacam Solution for Injection was approved for one-time use only in cats on 28 Nov 2004 (NADA 141-219). Metacam Oral Suspension was approved for dogs only on 15 Apr 2003 (NADA 141-213). A ...
Nasal fentanyl for pre-hospital pain - Quiz answer
... c. All of the above are true. Answer – a, b or c 14. Which of the following items improve absorption of IN medications? a. Recent use of nasal cocaine. b. Ongoing upper respiratory tract infection with runny nose and cough c. Chronic sinusitis with multiple previous nasal surgical procedures d. High ...
... c. All of the above are true. Answer – a, b or c 14. Which of the following items improve absorption of IN medications? a. Recent use of nasal cocaine. b. Ongoing upper respiratory tract infection with runny nose and cough c. Chronic sinusitis with multiple previous nasal surgical procedures d. High ...
7 Intro to Antibiotic Therapy- A
... Selecting an appropriate antimicrobial drug to treat a specific infection involves several important factors: First, the microorganism must be isolated and identified’ generally through growing a culture. Then its susceptibility to various drugs must be determined. Because culture and sensitivit ...
... Selecting an appropriate antimicrobial drug to treat a specific infection involves several important factors: First, the microorganism must be isolated and identified’ generally through growing a culture. Then its susceptibility to various drugs must be determined. Because culture and sensitivit ...
PPT
... • In elderly < 80 years old with SBP ≥160 mmHg there is solid evidence to reducing SBP to 150 and 140 mmHg (IA) • In fit elderly patients < 80 years old SBP values <140 mmHg may be considered, whereas in the fragile elderly population SBP goals should be adapted to individual tolerability (IIb C) • ...
... • In elderly < 80 years old with SBP ≥160 mmHg there is solid evidence to reducing SBP to 150 and 140 mmHg (IA) • In fit elderly patients < 80 years old SBP values <140 mmHg may be considered, whereas in the fragile elderly population SBP goals should be adapted to individual tolerability (IIb C) • ...
CHEMICAL STABILITY STUDIES OF BIOADHESIVE TOPICAL GEL Research Article LALIT KUMAR
... gel with continuous stirring till drug get dispersed in gel completely. Six formulations of bioadhesive topical gel were prepared by using Natural polymer and Hydroxyethyl cellulose in different ratio. The prepared gels were packed in wide mouth glass jar covered with ...
... gel with continuous stirring till drug get dispersed in gel completely. Six formulations of bioadhesive topical gel were prepared by using Natural polymer and Hydroxyethyl cellulose in different ratio. The prepared gels were packed in wide mouth glass jar covered with ...
Chapter 86,91,92
... • Elderly and young and sick – Neuromuscular blockade – Hypersensitivity & blood dyscrasias (rare) ...
... • Elderly and young and sick – Neuromuscular blockade – Hypersensitivity & blood dyscrasias (rare) ...
The National Association of Health lJnderwriters is an organization of individuals
... FDA officials and industry lawyers agree that federal drug law is clear on some important points: All drugs safe enough to be sold over the counter must be made available that way. Also, the law permits anyone, from a private citizen to the FDA itself, to initiate the evaluation of whether a drug sh ...
... FDA officials and industry lawyers agree that federal drug law is clear on some important points: All drugs safe enough to be sold over the counter must be made available that way. Also, the law permits anyone, from a private citizen to the FDA itself, to initiate the evaluation of whether a drug sh ...
ijlbpr_23
... low systemic toxicity, low cytotoxicity and lesser side effects. Most of the polysaccharides used in the processing of pharmaceutical formulations have an approved status of generally accepted as safe which includes accepted food additives for human use or as excipients in various dosage forms. Thei ...
... low systemic toxicity, low cytotoxicity and lesser side effects. Most of the polysaccharides used in the processing of pharmaceutical formulations have an approved status of generally accepted as safe which includes accepted food additives for human use or as excipients in various dosage forms. Thei ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.