Ciclosporin - IARC Monographs
... 1, followed by administration of N-methyl-N' -nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG). at 83 J.g/ml in the drinking-water ad libitum from week 3 to 28; group 3 (15 animaIs) received MNNG in the drinking-water from week 3 to 28; groups 4 and 5 (15 animaIs per group) received MNNG in the drinking-water in wee ...
... 1, followed by administration of N-methyl-N' -nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG). at 83 J.g/ml in the drinking-water ad libitum from week 3 to 28; group 3 (15 animaIs) received MNNG in the drinking-water from week 3 to 28; groups 4 and 5 (15 animaIs per group) received MNNG in the drinking-water in wee ...
- the University of Huddersfield Repository
... minutes and cumulative 24 urinary excretions post Qvar and Clenil compared to Oral. Using 30 minute urinary excretion the mean ratio (90% confidence interval) for Qvar compared to Clenil was 231.4 (209.6, 255.7). The results confirm that the relative lung and systemic bioavailability can be identifi ...
... minutes and cumulative 24 urinary excretions post Qvar and Clenil compared to Oral. Using 30 minute urinary excretion the mean ratio (90% confidence interval) for Qvar compared to Clenil was 231.4 (209.6, 255.7). The results confirm that the relative lung and systemic bioavailability can be identifi ...
Codeine Therapy in the Context of Cytochrome P450 2D6
... Hydrocodone is biotransformed by CYP2D6 into hydromorphone, which has a 10- to 33-fold greater affinity for μ-opioid receptors as compared with the parent drug. Relative to extensive metabolizers, poor metabolizers have been shown to have lower peak concentrations of hydromorphone after a dose of hy ...
... Hydrocodone is biotransformed by CYP2D6 into hydromorphone, which has a 10- to 33-fold greater affinity for μ-opioid receptors as compared with the parent drug. Relative to extensive metabolizers, poor metabolizers have been shown to have lower peak concentrations of hydromorphone after a dose of hy ...
Clearing of Metabolic Waste via Enterohepatic Recirculation Table
... animal models even at high dosages. The enterohepatic recirculation contributes to a delayed elimination of the molecule from the body which can also show a prolonged effect enhanced by its binding to plasmatic proteins. (Latruffe et al. 2006) In this case, the enterohepatic recirculation would be b ...
... animal models even at high dosages. The enterohepatic recirculation contributes to a delayed elimination of the molecule from the body which can also show a prolonged effect enhanced by its binding to plasmatic proteins. (Latruffe et al. 2006) In this case, the enterohepatic recirculation would be b ...
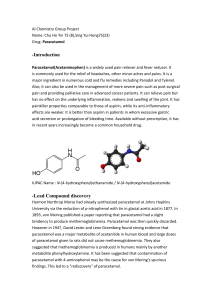
11127sgp03
... Paracetamol toxicity Paracetamol toxicity is caused by excessive use or overdose of the paracetamol. Mainly causing liver injury, paracetamol toxicity is one of the most common causes of poisoning worldwide. ...
... Paracetamol toxicity Paracetamol toxicity is caused by excessive use or overdose of the paracetamol. Mainly causing liver injury, paracetamol toxicity is one of the most common causes of poisoning worldwide. ...
Genetic polymorphisms and drug interactions modulating
... Mattia, 2005). Oxycodone abuse has been of growing concern and associated with a significant number of drug-related deaths (Davis et al., 2003). The long-standing clinical use of oxycodone (Falk, 1917), and lack of sufficient analytical sensitivity to detect active metabolites explain it has bypasse ...
... Mattia, 2005). Oxycodone abuse has been of growing concern and associated with a significant number of drug-related deaths (Davis et al., 2003). The long-standing clinical use of oxycodone (Falk, 1917), and lack of sufficient analytical sensitivity to detect active metabolites explain it has bypasse ...
metronidazole
... When administered orally or intravenously, metronidazole is well tolerated. The most common adverse reactions have involved the gastrointestinal tract, particularly nausea, sometimes accompanied by headache, anorexia and occasionally vomiting, diarrhoea, epigastric distress and abdominal cramping; c ...
... When administered orally or intravenously, metronidazole is well tolerated. The most common adverse reactions have involved the gastrointestinal tract, particularly nausea, sometimes accompanied by headache, anorexia and occasionally vomiting, diarrhoea, epigastric distress and abdominal cramping; c ...
Inhaled and intranasal fluticasone propionate and haematoma
... fluticasone propionate related haematomas or purpura. These symptoms were reported both in users and non-users of the fluticasone propionate/salmeterol combination preparation, so confounding by concomitant use of salmeterol due to an unknown ADR is unlikely. Concomitant use of medications leading t ...
... fluticasone propionate related haematomas or purpura. These symptoms were reported both in users and non-users of the fluticasone propionate/salmeterol combination preparation, so confounding by concomitant use of salmeterol due to an unknown ADR is unlikely. Concomitant use of medications leading t ...
Medication Guide
... 2.6 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse events occur, the dosage should be reduced, or, if necessary, the drug should be discontinued. If improvement is not observed after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period, the drug should b ...
... 2.6 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse events occur, the dosage should be reduced, or, if necessary, the drug should be discontinued. If improvement is not observed after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period, the drug should b ...
to the Akten FAQs PDF
... have been performed in both rats and rabbits. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus at subcutaneous doses up to 50 mg/kg lidocaine (more than 800 fold greater than the human dose on a body weight basis) in the rat model. There are however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant wom ...
... have been performed in both rats and rabbits. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus at subcutaneous doses up to 50 mg/kg lidocaine (more than 800 fold greater than the human dose on a body weight basis) in the rat model. There are however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant wom ...
Morphine Sulfate Extended-Release Tablets
... individuals, they are influenced by a wide variety of factors and are not generally useful as a guide to the clinical use of morphine. The effective dose in opioid-tolerant patients may be 10-50 times as great (or greater) than the appropriate dose for opioid-naive individuals. Dosages of morphine s ...
... individuals, they are influenced by a wide variety of factors and are not generally useful as a guide to the clinical use of morphine. The effective dose in opioid-tolerant patients may be 10-50 times as great (or greater) than the appropriate dose for opioid-naive individuals. Dosages of morphine s ...
EFFECTS OF POMEGRANATE JUICE ON HUMAN CYTOCHROME
... 10,11-epoxide were obtained from the actual data recorded after oral administration. The plasma concentration-time profile (0 –24 h) of each rat was analyzed by a model-independent method using the MULTI computer program (Yamaoka and Nakagawa, 1983). The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) ...
... 10,11-epoxide were obtained from the actual data recorded after oral administration. The plasma concentration-time profile (0 –24 h) of each rat was analyzed by a model-independent method using the MULTI computer program (Yamaoka and Nakagawa, 1983). The area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) ...
HYZAAR® HYZAAR® DS
... (decreased renal function; oligohydramnios, skull ossification retardation) and neonatal toxicity (renal failure, hypotension, hyperkalemia). Infants with a history of in utero exposure to ARBs should be closely observed for hypotension, oliguria, and hyperkalemia. If oliguria occurs, attention shou ...
... (decreased renal function; oligohydramnios, skull ossification retardation) and neonatal toxicity (renal failure, hypotension, hyperkalemia). Infants with a history of in utero exposure to ARBs should be closely observed for hypotension, oliguria, and hyperkalemia. If oliguria occurs, attention shou ...
product information
... Pregabalin is rapidly absorbed when administered in the fasted state, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1 hour following both single and multiple dose administration. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is estimated to be 90% and is independent of dose. Following repeated administration ...
... Pregabalin is rapidly absorbed when administered in the fasted state, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 1 hour following both single and multiple dose administration. Pregabalin oral bioavailability is estimated to be 90% and is independent of dose. Following repeated administration ...
Read Document - MotherToBaby
... How long does isotretinoin stay in the body? • The average elimination half-life (the time it takes for the body to eliminate one-half of the drug) of isotretinoin is 21 hours (with a a standard deviation 8.2 hours). However, the elimination half-life of some of its breakdown products is up to 50 ho ...
... How long does isotretinoin stay in the body? • The average elimination half-life (the time it takes for the body to eliminate one-half of the drug) of isotretinoin is 21 hours (with a a standard deviation 8.2 hours). However, the elimination half-life of some of its breakdown products is up to 50 ho ...
Nicotine increases sucrose selfadministration and seeking in rats
... secondary reinforcement. In the present study, we examined both primary and secondary reinforcing (cuereactivity) qualities of sucrose in rats that were injected with nicotine immediately prior to sucrose SA sessions. To ...
... secondary reinforcement. In the present study, we examined both primary and secondary reinforcing (cuereactivity) qualities of sucrose in rats that were injected with nicotine immediately prior to sucrose SA sessions. To ...
... 45 Å in depth spanning both sides of the bilayer [25]. LEWELL [29] has calculated the dimensions of the beta2adrenoceptor to be 18×33×45 Å. The peptide backbone of the individual alpha-helices is approximately 5 Å in diameter, and the helices are thought to be separated by approximately 10 Å. A sche ...
Full-Text PDF
... thrombin level, and activation and aggregation of the platelets reduced the risk of bleeding when compared with traditional anti-coagulants [2]. In addition, FXa plays a vital role in amplifying the process, and is endued with the ability to produce more than one thousand thrombin molecules [2,4]. F ...
... thrombin level, and activation and aggregation of the platelets reduced the risk of bleeding when compared with traditional anti-coagulants [2]. In addition, FXa plays a vital role in amplifying the process, and is endued with the ability to produce more than one thousand thrombin molecules [2,4]. F ...
Epidural Analgesia and Anesthesia
... slowly, allowing the practitioner to appreciate the various tissue planes that the needle passes through. Before entry into the epidural space, a "pop" is often felt as the needle passes through the ligamentum flavum. Once the needle has been advanced to a point where the practitioner thnks that the ...
... slowly, allowing the practitioner to appreciate the various tissue planes that the needle passes through. Before entry into the epidural space, a "pop" is often felt as the needle passes through the ligamentum flavum. Once the needle has been advanced to a point where the practitioner thnks that the ...
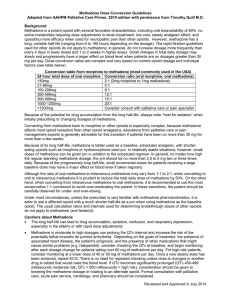
Methadone Conversion Guideline
... A 50-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer has good pain control with sustained-release oral morphine 200 mg, two tablets twice a day. However, she develops persistent myoclonus. A decision is made to rotate opioids to methadone. (Our conversion table [Table 2.1] always requires that the equi ...
... A 50-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer has good pain control with sustained-release oral morphine 200 mg, two tablets twice a day. However, she develops persistent myoclonus. A decision is made to rotate opioids to methadone. (Our conversion table [Table 2.1] always requires that the equi ...
Performance Enhancing Hormone Doping in Sport
... The illicit use of banned drugs (doping) to influence the outcome of a sporting contest, constitutes a fraud against competitors, spectators, sport, sponsors and the public no different from other personal, professional or commercial frauds. While performance enhancement is almost invariably the int ...
... The illicit use of banned drugs (doping) to influence the outcome of a sporting contest, constitutes a fraud against competitors, spectators, sport, sponsors and the public no different from other personal, professional or commercial frauds. While performance enhancement is almost invariably the int ...
The challenge of selecting protein kinase assays
... The myriad of screening technologies have given scientists the freedom to pick the screening parameters that suit their individual drug discovery platforms or personal preferences. However, the plethora of assay formats also poses a great challenge to scientists who must decide on a technology that ...
... The myriad of screening technologies have given scientists the freedom to pick the screening parameters that suit their individual drug discovery platforms or personal preferences. However, the plethora of assay formats also poses a great challenge to scientists who must decide on a technology that ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.