FORMULATION, CHARACTERIZATION AND COMPARATIVE IN VITRO IN VIVO EVALUATION
... while toxicity usually appear at concentration above 20 μg/mL and the fluctuations of its serum concentrations can result in variability in clinical response1,5. Therefore, there is an obvious need for SR dosage form which will be able to maintain therapeutic serum levels of theophylline throughout ...
... while toxicity usually appear at concentration above 20 μg/mL and the fluctuations of its serum concentrations can result in variability in clinical response1,5. Therefore, there is an obvious need for SR dosage form which will be able to maintain therapeutic serum levels of theophylline throughout ...
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapies HMG CoAa REDUCTASE
... based on a typical dosing regimen. c - Clinically important pharmacokinetic drug interactions; not meant to be all-inclusive. Refer to additional references or consult pharmacist for more detail. ...
... based on a typical dosing regimen. c - Clinically important pharmacokinetic drug interactions; not meant to be all-inclusive. Refer to additional references or consult pharmacist for more detail. ...
10.4103_0975-1483.63169
... drugs (statins) are prescribed in patients of diabetes for the prevention of complications of diabetes like cardiovascular diseases or diabetic dyslipidemia.[4,5] The greatest effects are seen with the most potent statins such as simvastatin, atorvastatin, and rosuvastatin in higher doses.[6] One st ...
... drugs (statins) are prescribed in patients of diabetes for the prevention of complications of diabetes like cardiovascular diseases or diabetic dyslipidemia.[4,5] The greatest effects are seen with the most potent statins such as simvastatin, atorvastatin, and rosuvastatin in higher doses.[6] One st ...
Sabiduría Spring 2015 Table of Contents
... important and heavy reliance on the scientific data that was achieved via calculus for drug pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. In short, applications of calculus are used for discerning the science. Then, that scientific data is used for determining cost effectiveness by insurance companies. Thi ...
... important and heavy reliance on the scientific data that was achieved via calculus for drug pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. In short, applications of calculus are used for discerning the science. Then, that scientific data is used for determining cost effectiveness by insurance companies. Thi ...
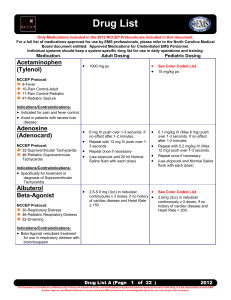
Drug List - The North Carolina Office of EMS
... Only Medications included in the 2012 NCCEP Protocols are included in this document. For a full list of medications approved for use by EMS professionals, please refer to the North Carolina Medical Board document entitled: Approved Medications for Credentialed EMS Personnel. Individual systems shoul ...
... Only Medications included in the 2012 NCCEP Protocols are included in this document. For a full list of medications approved for use by EMS professionals, please refer to the North Carolina Medical Board document entitled: Approved Medications for Credentialed EMS Personnel. Individual systems shoul ...
L07.OTC - ISpatula
... maintenance therapy is needed , which is defined as the lowest effective dose of the acid suppressor treatment , and so , hypothetically , if a patient is on a standard dose of omeprazole and he or she wanted to stop it , then the patient is faced with two options , either lower the dose of ppi , or ...
... maintenance therapy is needed , which is defined as the lowest effective dose of the acid suppressor treatment , and so , hypothetically , if a patient is on a standard dose of omeprazole and he or she wanted to stop it , then the patient is faced with two options , either lower the dose of ppi , or ...
acute pain relief in children with renal impairment
... renal clearance. Impaired renal function may lead not only to an accumulation of ingested components that are predominantly excreted by the kidney, but active or toxic metabolites may accumulate as well and increase the frequency of adverse reactions. Modification of drug doses in renal disease is u ...
... renal clearance. Impaired renal function may lead not only to an accumulation of ingested components that are predominantly excreted by the kidney, but active or toxic metabolites may accumulate as well and increase the frequency of adverse reactions. Modification of drug doses in renal disease is u ...
PR BEZALIP SR
... MAO-inhibitors: MAO-inhibitors (with hepatotoxic potential) must not be administered together with BEZALIP SR. Resins: When bezafibrate is used concurrently with cholestyramine or any other resin, an interval ...
... MAO-inhibitors: MAO-inhibitors (with hepatotoxic potential) must not be administered together with BEZALIP SR. Resins: When bezafibrate is used concurrently with cholestyramine or any other resin, an interval ...
Basics in drug approval process with ref. to:
... phosphate complex, 250mg capsules; quinidine sulfate, 200mg tablets vs. quinidine sulfate, 200mg capsules). ...
... phosphate complex, 250mg capsules; quinidine sulfate, 200mg tablets vs. quinidine sulfate, 200mg capsules). ...
Absorica - Blue Cross Blue Shield of Arizona
... A single course of therapy for 15 to 20 weeks has been shown to result in complete and prolonged remission of disease in many patients. If a second course of therapy is needed, it should not be initiated until at least 8 weeks after completion of the first course, because experience has shown that p ...
... A single course of therapy for 15 to 20 weeks has been shown to result in complete and prolonged remission of disease in many patients. If a second course of therapy is needed, it should not be initiated until at least 8 weeks after completion of the first course, because experience has shown that p ...
EAPA - Virginia Summer Institute for Addiction Studies
... Yucatan Fire and many others” • Since the national ban on five synthetic cannabinoids, new brand names have developed, such as K2 Sky, K3, and K4 ...
... Yucatan Fire and many others” • Since the national ban on five synthetic cannabinoids, new brand names have developed, such as K2 Sky, K3, and K4 ...
hydrogen bond acceptor - e
... distributed round the body and not get mopped up by fat tissue. It has to have a reasonable life time within the body, not too short and not too long. Finally, it should not be excreted too quickly. The study of how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and excreted (known as ADME in the phar ...
... distributed round the body and not get mopped up by fat tissue. It has to have a reasonable life time within the body, not too short and not too long. Finally, it should not be excreted too quickly. The study of how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized and excreted (known as ADME in the phar ...
Balancing the outcomes: reporting adverse events
... It is not possible to assess the significance of AEs from reports in which the treatment allocation remains blinded and the number of participants exposed to the trial medications is unknown. Hence, Data and Safety Monitoring Boards (with the ability to review events and their frequencies unblinded, ...
... It is not possible to assess the significance of AEs from reports in which the treatment allocation remains blinded and the number of participants exposed to the trial medications is unknown. Hence, Data and Safety Monitoring Boards (with the ability to review events and their frequencies unblinded, ...
Interactions with Drugs and Dietary Supplements Used
... norepinephrine and dopamine levels along with inhibition of their reuptake is proposed as the mechanism of diethylpropion anorectic effects [22]. Diethylpropion is indicated for short term management of obesity in patients with a body mass index (BMI) of > 30 kg/m2 who have not responded to diet and ...
... norepinephrine and dopamine levels along with inhibition of their reuptake is proposed as the mechanism of diethylpropion anorectic effects [22]. Diethylpropion is indicated for short term management of obesity in patients with a body mass index (BMI) of > 30 kg/m2 who have not responded to diet and ...
RYTHMOL SR Extended Release Capsules
... prior to and during therapy to determine whether the response to RYTHMOL SR supports continued treatment. Because propafenone prolongs the QRS interval in the electrocardiogram, changes in the QT interval are difficult to interpret [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. In the RYTHMOL SR Atrial Fibrill ...
... prior to and during therapy to determine whether the response to RYTHMOL SR supports continued treatment. Because propafenone prolongs the QRS interval in the electrocardiogram, changes in the QT interval are difficult to interpret [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. In the RYTHMOL SR Atrial Fibrill ...
Bath Salts and Spice
... HR/BP elevation, chest pains Dehydration Mydriasis, nystagmus Painful nasal drip/ulcers in mouth (after insufflation) Insomnia, paranoia, anxiety, dysphoria, psychosis http://theblackheartofgrahamquirk.blogspot.com/ ...
... HR/BP elevation, chest pains Dehydration Mydriasis, nystagmus Painful nasal drip/ulcers in mouth (after insufflation) Insomnia, paranoia, anxiety, dysphoria, psychosis http://theblackheartofgrahamquirk.blogspot.com/ ...
Methylphenidate and erectile dysfunction
... Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors [3]. Erection is mediated by cholinergic parasympathetic pathways, and nonadrenergic, noncholinergic pathways, which release nitric oxide. Endothelial cells also release nitric oxide, whic ...
... Penile erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular and endocrine factors [3]. Erection is mediated by cholinergic parasympathetic pathways, and nonadrenergic, noncholinergic pathways, which release nitric oxide. Endothelial cells also release nitric oxide, whic ...
Gentamicin Pharmacokinetics in Asphyxiated Neonates
... these patients often experience HIE and undergo therapeutic hypothermia, it is important to understand the relationship between HIE and gentamicin pharmacokinetics. Currently, controversy exists in both animal and human studies regarding the effect of asphyxia and therapeutic hypothermia on gentamic ...
... these patients often experience HIE and undergo therapeutic hypothermia, it is important to understand the relationship between HIE and gentamicin pharmacokinetics. Currently, controversy exists in both animal and human studies regarding the effect of asphyxia and therapeutic hypothermia on gentamic ...
development and validation of rp-hplc method for simultaneous
... Aim: A HPLC method has been described for simultaneous determination of Pamabrom and Paracetamol in marketed formulation. Methods: This method is based on HPLC separation of the two drugs on the Kromasil C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5.0μ), with isocratic conditions and mobile phase containing water: ...
... Aim: A HPLC method has been described for simultaneous determination of Pamabrom and Paracetamol in marketed formulation. Methods: This method is based on HPLC separation of the two drugs on the Kromasil C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5.0μ), with isocratic conditions and mobile phase containing water: ...
hydrochlorothiazide
... can lead to permanent vision loss. The primary treatment is to discontinue hydrochlorothiazide as rapidly as possible. Prompt medical or surgical treatments may need to be considered if the intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled. Risk factors for developing acute angle-closure glaucoma may includ ...
... can lead to permanent vision loss. The primary treatment is to discontinue hydrochlorothiazide as rapidly as possible. Prompt medical or surgical treatments may need to be considered if the intraocular pressure remains uncontrolled. Risk factors for developing acute angle-closure glaucoma may includ ...
Designer Drugs
... amphetamine, but psychologically its what's known as an empathogenentactogen Shares similarities to both mescaline (a hallucinogen) and amphetamines (A type of Stimulant) ...
... amphetamine, but psychologically its what's known as an empathogenentactogen Shares similarities to both mescaline (a hallucinogen) and amphetamines (A type of Stimulant) ...
Dexmedetomidine: A Useful Adjunct to Consider in Some High Risk
... is unique in that patients can be easily aroused and then can return to a sleep-like state when not stimulated. Patients sedated with α2 agonists may be more cooperative and communicative than patients sedated with other drugs in the ICU. The characteristics of DEX may make it a useful anxiolytic, e ...
... is unique in that patients can be easily aroused and then can return to a sleep-like state when not stimulated. Patients sedated with α2 agonists may be more cooperative and communicative than patients sedated with other drugs in the ICU. The characteristics of DEX may make it a useful anxiolytic, e ...
sult4a1-1 positive - PGXL Laboratories
... The COMT Met/Met genotype results in decreased COMT activity and increased dopamine levels in the prefrontal cortex. Compared to Val/Val, Met/Met patients with depression are more likely to achieve remission when treated with SSRI antidepressants, and Met/Met patients with schizophrenia are more lik ...
... The COMT Met/Met genotype results in decreased COMT activity and increased dopamine levels in the prefrontal cortex. Compared to Val/Val, Met/Met patients with depression are more likely to achieve remission when treated with SSRI antidepressants, and Met/Met patients with schizophrenia are more lik ...
Brief Receptor Theory
... • Specific activity depends on half-life, and is totally independent of mode or energy of decay. • When decay occurs for all of the biologically important isotopes (14C; 3H; 32P; 35S; 125I; etc.), the decay event changes the chemical identity of the decaying atom, and in the process, destroys the mo ...
... • Specific activity depends on half-life, and is totally independent of mode or energy of decay. • When decay occurs for all of the biologically important isotopes (14C; 3H; 32P; 35S; 125I; etc.), the decay event changes the chemical identity of the decaying atom, and in the process, destroys the mo ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.