diuretics
... outside the kidney. Here it is important to remember that mannitol does not enter the brain or the eye. Therefore the high concentration of mannitol in the blood tends to draw water from the brain and eye, particularly when intracranial or intraocular pressure is elevated. This action is very useful ...
... outside the kidney. Here it is important to remember that mannitol does not enter the brain or the eye. Therefore the high concentration of mannitol in the blood tends to draw water from the brain and eye, particularly when intracranial or intraocular pressure is elevated. This action is very useful ...
Reprint
... zanamivir resistance in 2.3% of treated patients, with markedly reduced susceptibility to the drug (23). In the model, treatment with zanamivir was assumed to be 50% less prone to generating resistance, with the rate of 0.0036 per day accounting for less than 2% of zanamivir resistance (23). It was ...
... zanamivir resistance in 2.3% of treated patients, with markedly reduced susceptibility to the drug (23). In the model, treatment with zanamivir was assumed to be 50% less prone to generating resistance, with the rate of 0.0036 per day accounting for less than 2% of zanamivir resistance (23). It was ...
Evaluation of potential retinal toxicity of adalimumab (Humira)
... (80 mg/kg body weight), and their retinas were prepared for histological examination. All animals were evaluated prior to the experiment for any media opacities or retinal damage. Adalimumab Humira is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody specific for TNF; it was created using phage display t ...
... (80 mg/kg body weight), and their retinas were prepared for histological examination. All animals were evaluated prior to the experiment for any media opacities or retinal damage. Adalimumab Humira is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody specific for TNF; it was created using phage display t ...
Pharmaceutical excipients and pediatric formulations
... in neonates (85 percent) as compared to the adults (55 percent). pronounced in pediatric population and in many cases interfere with Therefore, drugs that have a propensity to partition into aqueous layers normal growth and development processes (13). Though screening are highly distributed (Volume ...
... in neonates (85 percent) as compared to the adults (55 percent). pronounced in pediatric population and in many cases interfere with Therefore, drugs that have a propensity to partition into aqueous layers normal growth and development processes (13). Though screening are highly distributed (Volume ...
Phase 1 Trial Design: Is 3 + 3 the Best?
... the RP2D. In North America, the highest dose level reached, in most instances due to an unacceptable incidence of DLTs, is referred to as the maximum administered dose (MAD). The MTD is typically defined as the dose level immediately below the MAD and corresponds with the RP2D.9 In the event that th ...
... the RP2D. In North America, the highest dose level reached, in most instances due to an unacceptable incidence of DLTs, is referred to as the maximum administered dose (MAD). The MTD is typically defined as the dose level immediately below the MAD and corresponds with the RP2D.9 In the event that th ...
The Effects of Ibuprofen on the Embryological Development of
... rate had a drastic decrease from the control and low concentration. The average of the control was 145 BPM (beats per minute) and the low concentration was 143 BPM. In contrast, the medium concentration had an average of 99 BPM. From figure 4, observations which were recorded included discolor ...
... rate had a drastic decrease from the control and low concentration. The average of the control was 145 BPM (beats per minute) and the low concentration was 143 BPM. In contrast, the medium concentration had an average of 99 BPM. From figure 4, observations which were recorded included discolor ...
The behavioral pharmacology of hallucinogens
... Fig. 2 – (A and B) Theoretical drug discrimination data illustrating discriminative control by saline (open square) or the training dose of the training drug (filled circle), dose-dependent substitution of the test drug for the training dose (filled triangles), and a parallel rightward shift in this ...
... Fig. 2 – (A and B) Theoretical drug discrimination data illustrating discriminative control by saline (open square) or the training dose of the training drug (filled circle), dose-dependent substitution of the test drug for the training dose (filled triangles), and a parallel rightward shift in this ...
Nausea and Vomiting in Palliative Care
... 8mg IV or 24mg orally 30mins before chemotherapy, 4-8mg 12hrly ...
... 8mg IV or 24mg orally 30mins before chemotherapy, 4-8mg 12hrly ...
Marijuana: Facts and Myths - livedrugfree.org
... Percentage of High School Students Who Currently Used Marijuana,* by Sex,† Grade,† and Race/Ethnicity,† 2013 ...
... Percentage of High School Students Who Currently Used Marijuana,* by Sex,† Grade,† and Race/Ethnicity,† 2013 ...
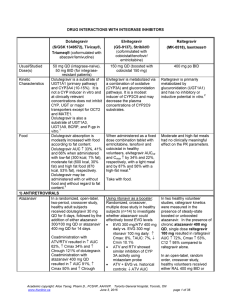
DRUG INTERACTIONS WITH INTEGRASE INHIBITORS
... PR interval increases were observed with atazanavir alone, and remained when raltegravir was coadministered; the clinical relevance of these changes is ...
... PR interval increases were observed with atazanavir alone, and remained when raltegravir was coadministered; the clinical relevance of these changes is ...
COMPARATIVE HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF LIV-52 AND SILYMARINE AGAINST
... alcohol) or impairment of its function may lead to many complications in one’s health. There is a no rational therapy available for liver disorders and it is a still challenge to modern medicine1. Hepatic injury can be life threatening when the entirely or most of the liver is exposed to any hepatot ...
... alcohol) or impairment of its function may lead to many complications in one’s health. There is a no rational therapy available for liver disorders and it is a still challenge to modern medicine1. Hepatic injury can be life threatening when the entirely or most of the liver is exposed to any hepatot ...
Research Article Punica granatum Rind, a Traditional Herbal
... It is mentioned in Holy Qur'an that pomegranates grow in the gardens of paradise and pomegranates three times as examples of good things Allah creates (Surat Al-'An'am). It was found that till present no work is carried out on dried powder of pomegranate. Some scientific work is done on methanol and ...
... It is mentioned in Holy Qur'an that pomegranates grow in the gardens of paradise and pomegranates three times as examples of good things Allah creates (Surat Al-'An'am). It was found that till present no work is carried out on dried powder of pomegranate. Some scientific work is done on methanol and ...
D F PHARMACOKINETICS AND INTRODUCTION
... L). Fifty percent of the drug is metabolized in the liver, primarily to the glucuronide and sulfate of 3-hydroxyguanfacine, oxidized mercapturic acid derivatives, and other minor metabolites. Guanfacine HCl is metabolized primarily by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) 3A4. It is a substrate of CYP 3A4 and CYP ...
... L). Fifty percent of the drug is metabolized in the liver, primarily to the glucuronide and sulfate of 3-hydroxyguanfacine, oxidized mercapturic acid derivatives, and other minor metabolites. Guanfacine HCl is metabolized primarily by cytochrome P-450 (CYP) 3A4. It is a substrate of CYP 3A4 and CYP ...
Vitamin B12 Supplement (SDIS)
... Knowledge of the routes of cobalamin absorption is necessary to understand the rationale for giving cobalamin orally particularly in the treatment of pernicious anemia. The classic pathway is a complex uptake mechanism that involves the binding of cobalamin to intrinsic factor produced by the stomac ...
... Knowledge of the routes of cobalamin absorption is necessary to understand the rationale for giving cobalamin orally particularly in the treatment of pernicious anemia. The classic pathway is a complex uptake mechanism that involves the binding of cobalamin to intrinsic factor produced by the stomac ...
Assessing Statin Therapy: What are Their Differences? - Pri-Med
... Relationship between drug dose and clinical utility, and adverse drug event (ADE) is governed by 2 concepts: ...
... Relationship between drug dose and clinical utility, and adverse drug event (ADE) is governed by 2 concepts: ...
INVITRO ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTIVITY OF METHANOL
... Treatment(s ) Concentration (µg/ml) Absorbance at 660nm % inhibition of proteinase action ...
... Treatment(s ) Concentration (µg/ml) Absorbance at 660nm % inhibition of proteinase action ...
Marijuana - Jean Basile
... Young adults have been shown to be at a great risk for trying marijuana when they leave home. Young adults age 18 to 25 have the highest rate of marijuana related ER episodes, the next highest was individuals between 12 and 17. A study by SAMHSA in Florida found substance abuse treatment admissions ...
... Young adults have been shown to be at a great risk for trying marijuana when they leave home. Young adults age 18 to 25 have the highest rate of marijuana related ER episodes, the next highest was individuals between 12 and 17. A study by SAMHSA in Florida found substance abuse treatment admissions ...
The proportion of patient reports of suspected ADRs to
... Each incoming ADR report to a pharmacovigilance centre represents a possible association between one or more suspected ADRs and one or more suspected drugs, along with patient characteristics.1 For the detection of signals at the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb each ADR report undergoes a ...
... Each incoming ADR report to a pharmacovigilance centre represents a possible association between one or more suspected ADRs and one or more suspected drugs, along with patient characteristics.1 For the detection of signals at the Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb each ADR report undergoes a ...
Version 1
... For oral preparations A dose adjustment is not usually necessary in elderly patients. For parenteral preparations The lowest dose should be administered with careful titration to pain control. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment The dose initiation should follow a conservative approach in thes ...
... For oral preparations A dose adjustment is not usually necessary in elderly patients. For parenteral preparations The lowest dose should be administered with careful titration to pain control. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment The dose initiation should follow a conservative approach in thes ...
Are we addicted to coffee?
... “A maladaptive pattern of substance use, leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by 3 or more of the following, occuring at any time in the same 12-month period: 1) Tolerance, as defined by either a need for markedly increased amounts of the substance to achieve int ...
... “A maladaptive pattern of substance use, leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by 3 or more of the following, occuring at any time in the same 12-month period: 1) Tolerance, as defined by either a need for markedly increased amounts of the substance to achieve int ...
Effects of a P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor on Brain and Plasma
... steady state in plasma. Previous pharmacokinetic studies have shown that plasma and brain steady-state levels for 6-Cl-ddP are reached within 30 min at the dose used in this study (Anderson et al., 1990; Morgan et al., 1992). Nelfinavir’s elimination half-life is ⬃1.3 h in rats (Shetty et al., 1996) ...
... steady state in plasma. Previous pharmacokinetic studies have shown that plasma and brain steady-state levels for 6-Cl-ddP are reached within 30 min at the dose used in this study (Anderson et al., 1990; Morgan et al., 1992). Nelfinavir’s elimination half-life is ⬃1.3 h in rats (Shetty et al., 1996) ...
Chemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of
... extensively bound to plasma proteins (Table II), and as a result systemic exposure to unbound, pharmacologically active drug is relatively low [9]. Although circulating levels of unbound pravastatin are high relative to those of the other statins, widespread tissue distribution is prevented by the h ...
... extensively bound to plasma proteins (Table II), and as a result systemic exposure to unbound, pharmacologically active drug is relatively low [9]. Although circulating levels of unbound pravastatin are high relative to those of the other statins, widespread tissue distribution is prevented by the h ...
MS_349Formated - University of Alberta
... Received May 27, 2006; Accepted June 15, 2006; published, Novemver 27, 2006. ...
... Received May 27, 2006; Accepted June 15, 2006; published, Novemver 27, 2006. ...
What is Methamphetamine? Pushback Fact Sheet
... disorder, narcolepsy, weight loss and other conditions, although it is rarely used medically, and only at doses much lower than those typically abused. It is classified as a Schedule II drug, meaning it has high potential for abuse and is available only through a prescription that cannot be refilled ...
... disorder, narcolepsy, weight loss and other conditions, although it is rarely used medically, and only at doses much lower than those typically abused. It is classified as a Schedule II drug, meaning it has high potential for abuse and is available only through a prescription that cannot be refilled ...
pdf - Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences
... 200mg/kg, p.o) did not produce statistically any significant reduction in locomotor activity as compared to the control animals receiving only the vehicle. Diazepam treated groups revealed a statistically significant decrease in locomotor activity as compared to the control. Results were shown in ta ...
... 200mg/kg, p.o) did not produce statistically any significant reduction in locomotor activity as compared to the control animals receiving only the vehicle. Diazepam treated groups revealed a statistically significant decrease in locomotor activity as compared to the control. Results were shown in ta ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.