PSC1341 Chapter 3
... 1. A large (heavy) and a small (light) sphere are released at the same time from the same height above the ground. Which one of the following quantities associated with the spheres will be the same for both after 1 second, if frictional effects are ignored? (A) speed (B) momentum (C) potential energ ...
... 1. A large (heavy) and a small (light) sphere are released at the same time from the same height above the ground. Which one of the following quantities associated with the spheres will be the same for both after 1 second, if frictional effects are ignored? (A) speed (B) momentum (C) potential energ ...
Light and other electromagnetic radiation – applications in biology
... application of quantum principles to matter was obtained in experiments in which the diffraction of a beam of electrons was observed (left). The diffraction pattern seen when the electron beam was accelerated to give a wavelength of 0.5 Å gave a pattern similar to that seen when a beam of Xrays of s ...
... application of quantum principles to matter was obtained in experiments in which the diffraction of a beam of electrons was observed (left). The diffraction pattern seen when the electron beam was accelerated to give a wavelength of 0.5 Å gave a pattern similar to that seen when a beam of Xrays of s ...
m 0
... In classical mechanics, mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is closely related to its momentum and mass Since in SR we have redefined the classical mass and momentum to that of relativistic version mclass(cosnt) –> mSR = m0g pclass = mclass u –> pSR = (m0g)u we must also modify the ...
... In classical mechanics, mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is closely related to its momentum and mass Since in SR we have redefined the classical mass and momentum to that of relativistic version mclass(cosnt) –> mSR = m0g pclass = mclass u –> pSR = (m0g)u we must also modify the ...
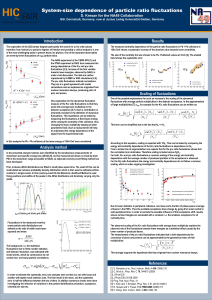
91.5x122 cm Poster Template
... From a similar line of argumentation one expects that for the p/ ratio fluctuations shows that the correlation term dominates. Therefore scaling is tested versus NpN. For both, K/ and p/ ratio fluctuations a common scaling of the energy and centrality dependence with the average number of produc ...
... From a similar line of argumentation one expects that for the p/ ratio fluctuations shows that the correlation term dominates. Therefore scaling is tested versus NpN. For both, K/ and p/ ratio fluctuations a common scaling of the energy and centrality dependence with the average number of produc ...
Lecture #30 - Galileo - University of Virginia
... Photon energy = Planck constant · frequency An atom’s orbitals have specific energy differences Energy differences establish photon energies An atom emits a specific spectrum of photons ...
... Photon energy = Planck constant · frequency An atom’s orbitals have specific energy differences Energy differences establish photon energies An atom emits a specific spectrum of photons ...
midterm study guide answer key
... The force that opposes the motion of objects that touch as they move pass each other is called _____FRICTION_______________. A car’s speedometer measures ___SPEED_____________________. When a falling object reaches terminal velocity, the net force acting on it is _____ZERO_______________. The force ...
... The force that opposes the motion of objects that touch as they move pass each other is called _____FRICTION_______________. A car’s speedometer measures ___SPEED_____________________. When a falling object reaches terminal velocity, the net force acting on it is _____ZERO_______________. The force ...
L cos
... According to conservation of energy, the work done by friction must be included if we are to truly keep an accurate count of the energy. Note that friction does work. This work is manifested as energy – in this case heat energy. If you brake quickly, you smell your brake linings burning – friction g ...
... According to conservation of energy, the work done by friction must be included if we are to truly keep an accurate count of the energy. Note that friction does work. This work is manifested as energy – in this case heat energy. If you brake quickly, you smell your brake linings burning – friction g ...
Atoms and Energies
... Light exhibits wavelike properties when traveling Light exhibits particlelike properties when interacting with matter deBroglie suggested that traditional “particles”, like the electron, also exhibit wavelike properties p=h/l, so large (macroscopic) momentum means small (undetectable) wavelength ...
... Light exhibits wavelike properties when traveling Light exhibits particlelike properties when interacting with matter deBroglie suggested that traditional “particles”, like the electron, also exhibit wavelike properties p=h/l, so large (macroscopic) momentum means small (undetectable) wavelength ...
Document
... • Beam tests with muons to measure m capture cross section m-+H Hm+ e+’s muon initially captured in high n orbit, then cascades down to n=1. ...
... • Beam tests with muons to measure m capture cross section m-+H Hm+ e+’s muon initially captured in high n orbit, then cascades down to n=1. ...
Forms of energy
... • Recognize the transfer that can take place between different energy forms. Success Criteria: o Can you identify which energy forms are present? ...
... • Recognize the transfer that can take place between different energy forms. Success Criteria: o Can you identify which energy forms are present? ...
WORK AND ENERGY
... If there is friction we write KEi + PEi – fkd = KEf + PEf if the frictional force fk acts over a displacement d. Example: Penguins are sliding on wet ice (assume frictionless). They begin with vi = 4.00 m/s, but slide up a hill inclined an angle above the horizontal. How far up the hill will they ...
... If there is friction we write KEi + PEi – fkd = KEf + PEf if the frictional force fk acts over a displacement d. Example: Penguins are sliding on wet ice (assume frictionless). They begin with vi = 4.00 m/s, but slide up a hill inclined an angle above the horizontal. How far up the hill will they ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... b. an archer’s bow that is drawn back c. a rolling bowling ball d. a car waiting at a red light ______ 2. A car starts from a stopped position at a red light. At the end of 30 seconds, its speed is 20 meters per second. What is the acceleration of the car? a. 1.5 m/s c. 0.7 m/s2 b. 0.7 m/s d. 1.5 m/ ...
... b. an archer’s bow that is drawn back c. a rolling bowling ball d. a car waiting at a red light ______ 2. A car starts from a stopped position at a red light. At the end of 30 seconds, its speed is 20 meters per second. What is the acceleration of the car? a. 1.5 m/s c. 0.7 m/s2 b. 0.7 m/s d. 1.5 m/ ...
Example Problems for Diffusional Equilibrium
... the subsystems, carrying internal energy with them, the internal wall serves no real physical purpose; we could regard it merely as an imaginary boundary between two regions of a single physical system. Thus, the equilibrium state must be one in which the two subsystems have the same particle densit ...
... the subsystems, carrying internal energy with them, the internal wall serves no real physical purpose; we could regard it merely as an imaginary boundary between two regions of a single physical system. Thus, the equilibrium state must be one in which the two subsystems have the same particle densit ...