Conservation of Energy
... standing in the same place. Will she be struck by the ball when it swings back? ...
... standing in the same place. Will she be struck by the ball when it swings back? ...
EnergyRevisionExercise
... 17. Much of energy around us is stored energy 18. It has the potential to do work, so stored energy is called potential energy 19. The stored energy that something has when it is high up is called gravitational potential energy. 20. When you land on the mat, it moves down, stretching the springs and ...
... 17. Much of energy around us is stored energy 18. It has the potential to do work, so stored energy is called potential energy 19. The stored energy that something has when it is high up is called gravitational potential energy. 20. When you land on the mat, it moves down, stretching the springs and ...
Calculating Kinetic and Potential Energy
... Kinetic Energy – what does it depend on? The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy depends on both mass and velocity. ...
... Kinetic Energy – what does it depend on? The faster an object moves, the more kinetic energy it has. The greater the mass of a moving object, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy depends on both mass and velocity. ...
Endothermic vs_ Exothermic
... What is Heat Energy? o The heat energy of an object determines how active its atoms are. This causes a change in temperature. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
... What is Heat Energy? o The heat energy of an object determines how active its atoms are. This causes a change in temperature. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
Physical Science Plans Week 15
... Energy, potential energy, kinetic energy, mechanical energy, chemical energy, thermal energy, sound energy, radiant energy, electric energy, nuclear energy, law of conservation of energy, heat, conduction, convection, radiation, states of matter. ESOL/ESE MODIFICATIONS: Multiple learning styles; Pro ...
... Energy, potential energy, kinetic energy, mechanical energy, chemical energy, thermal energy, sound energy, radiant energy, electric energy, nuclear energy, law of conservation of energy, heat, conduction, convection, radiation, states of matter. ESOL/ESE MODIFICATIONS: Multiple learning styles; Pro ...
Chapter 7 Section 1 Outline Guide
... Energy can change from one ______ to another. 1. Transforming Electrical Energy Light bulbs transform _______ energy into light. Some of the electrical energy from a light bulb can be converted to _______ energy. 2. Transforming Chemical Energy Fuel stores energy in the form of _______ poten ...
... Energy can change from one ______ to another. 1. Transforming Electrical Energy Light bulbs transform _______ energy into light. Some of the electrical energy from a light bulb can be converted to _______ energy. 2. Transforming Chemical Energy Fuel stores energy in the form of _______ poten ...
File
... provided by the traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work-kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to ...
... provided by the traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work-kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to ...
File
... *Work is measured by multiplying the force used by the distance the force was applied *When work is done on an object, the amount of energy it has changes *A force must be applied over a distance in order to qualify as work *The two main forms of energy are potential and kinetic *Potential energy is ...
... *Work is measured by multiplying the force used by the distance the force was applied *When work is done on an object, the amount of energy it has changes *A force must be applied over a distance in order to qualify as work *The two main forms of energy are potential and kinetic *Potential energy is ...
Tips and Strategies
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
Tips and Strategies
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
Thermodynamics
... invisible microscopic energy on the atomic and molecular scale. • The internal energy is the total energy contained in a thermodynamic system. It is the energy necessary to create the system, but excludes the energy associated with a move as a whole, or due to external force fields. Internal energy ...
... invisible microscopic energy on the atomic and molecular scale. • The internal energy is the total energy contained in a thermodynamic system. It is the energy necessary to create the system, but excludes the energy associated with a move as a whole, or due to external force fields. Internal energy ...
When you get stuck: Think
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
... Under what conditions is work positive and negative? Under what conditions is heat positive and negative? What is the net work done by an entire process? What is the second law of thermodynamics? Describe the relationship between QH, Qc, and W in a heat engine? What is the difference between a heat ...
intro to energy unit 1
... What are 6 forms of Energy? Chemical Energy- usually stored energy that can be released as any of the other forms of energy (ex. A battery stores chemicals and releases it as electrical energy) Electrical Energy- when negatively charged particles are attracted to positively charged particles. Negat ...
... What are 6 forms of Energy? Chemical Energy- usually stored energy that can be released as any of the other forms of energy (ex. A battery stores chemicals and releases it as electrical energy) Electrical Energy- when negatively charged particles are attracted to positively charged particles. Negat ...
Metabolism
... Energy is lost in chemical reactions as __ A reaction that stores/absorbs energy is said to be _____ A reaction that releases energy is _____ The total of all chemical reactions in an organism is called ____ ...
... Energy is lost in chemical reactions as __ A reaction that stores/absorbs energy is said to be _____ A reaction that releases energy is _____ The total of all chemical reactions in an organism is called ____ ...
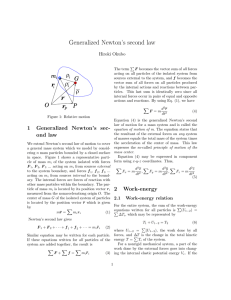
27. Generalized Newton`s second law
... a general mass system which we model by consid- expresses the so-called principle of motion of the ering n mass particles bounded by a closed surface mass center. Equation (4) may be expressed in component in space. Figure 1 shows a representative particle of mass mi of the system isolated with forc ...
... a general mass system which we model by consid- expresses the so-called principle of motion of the ering n mass particles bounded by a closed surface mass center. Equation (4) may be expressed in component in space. Figure 1 shows a representative particle of mass mi of the system isolated with forc ...
Gravity and Potential Energy
... Where K is kinetic energy, m is mass in kilograms, and v is velocity in meters per second. Because the mass is constant, if the velocity is increased then the kinetic energy must also increase. This means that the kinetic energy for the roller coaster system is greatest at the bottom of the highest ...
... Where K is kinetic energy, m is mass in kilograms, and v is velocity in meters per second. Because the mass is constant, if the velocity is increased then the kinetic energy must also increase. This means that the kinetic energy for the roller coaster system is greatest at the bottom of the highest ...
Physics 03-Work, Energy, and Momentum (2016)
... A 1500-kg car is driven off a 50-m cliff during a movie stunt. If it was going 20 m/s as it went off the cliff, how fast is it going as it hits the ground? ...
... A 1500-kg car is driven off a 50-m cliff during a movie stunt. If it was going 20 m/s as it went off the cliff, how fast is it going as it hits the ground? ...