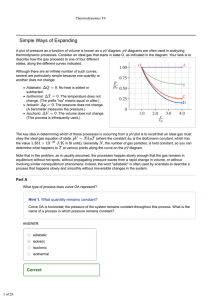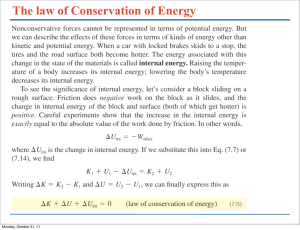
The law of Conservation of Energy
... The work-energy theorem focuses on the distance of force application. The impulse–momentum relationship depends on duration of an impact. Both rest on the foundation of Newton’s laws and are integral principles, relating the motion at two different times separated by a finite interval. Newton’s seco ...
... The work-energy theorem focuses on the distance of force application. The impulse–momentum relationship depends on duration of an impact. Both rest on the foundation of Newton’s laws and are integral principles, relating the motion at two different times separated by a finite interval. Newton’s seco ...
Chapter 6: Work and Energy )(
... nutritional energy content of 8.87×105 J. An 81.0-kg mountain climber eats a Mountain Bar and converts all of its energy to potential energy, gaining 1120 m in elevation. The mass of the mountain climber is then increased before repeating the climb. Strategy: Use the definition of gravitational pote ...
... nutritional energy content of 8.87×105 J. An 81.0-kg mountain climber eats a Mountain Bar and converts all of its energy to potential energy, gaining 1120 m in elevation. The mass of the mountain climber is then increased before repeating the climb. Strategy: Use the definition of gravitational pote ...
Statistical Thermodynamics and Stochastic The
... devoted to the conversion of matter and heat in such biological processes as rotting, fermentation and muscular activity. Helmholtz’s insight led him to infer a new law of nature from the complexities of his measurements on juices and extracts of meat and muscles. From experiments and brilliant gene ...
... devoted to the conversion of matter and heat in such biological processes as rotting, fermentation and muscular activity. Helmholtz’s insight led him to infer a new law of nature from the complexities of his measurements on juices and extracts of meat and muscles. From experiments and brilliant gene ...
Radiant Energy Power Generation
... a motor that implied a commercially significant amount of energy might be derived from the Earth's atmosphere. It has been observed that a potential gradient of 150 volts per meter of height is always available on average. There are three major causes of atmospheric ionization shown in Figure 2. The ...
... a motor that implied a commercially significant amount of energy might be derived from the Earth's atmosphere. It has been observed that a potential gradient of 150 volts per meter of height is always available on average. There are three major causes of atmospheric ionization shown in Figure 2. The ...
"Hidden" Momentum in a Coaxial Cable - Physics
... quantities are averaged over times longer than the time for a charge to move one gap length (≈ one atomic radius), the macroscopic current I is constant and the macroscopic velocity of the center of mass/energy of the charges is zero. ...
... quantities are averaged over times longer than the time for a charge to move one gap length (≈ one atomic radius), the macroscopic current I is constant and the macroscopic velocity of the center of mass/energy of the charges is zero. ...
18 The First Law of Thermodynamics
... in a system can be transformed back into mechanical energy. In this chapter we consider temperature and various ways it can be measured. We then quantify the invisible transfer of thermal energy between objects of different temperatures. We also introduce the first law of thermodynamics, a statement ...
... in a system can be transformed back into mechanical energy. In this chapter we consider temperature and various ways it can be measured. We then quantify the invisible transfer of thermal energy between objects of different temperatures. We also introduce the first law of thermodynamics, a statement ...
NSS Physics Curriculum- Compulsory Part (for students taking 2016
... “Change in momentum” is used instead of the term “impulse” Interpretation of F-t graph is expected Deriving the law of conservation of momentum from Newton’s laws of motion is expected Condition of right-angle fork collision (same mass, elastic) and its applications (e.g. collision between ...
... “Change in momentum” is used instead of the term “impulse” Interpretation of F-t graph is expected Deriving the law of conservation of momentum from Newton’s laws of motion is expected Condition of right-angle fork collision (same mass, elastic) and its applications (e.g. collision between ...
Physics I Honors
... 4. Note potential energy can be +, –, 0 depending on reference. 5. Note differences of potential energy are unique. 6. Contrast conservative and non-conservative forces. 7. Distinguish between kinetic, potential, total energy. 8. State law of conservation of mechanical energy. 9. Relate the work don ...
... 4. Note potential energy can be +, –, 0 depending on reference. 5. Note differences of potential energy are unique. 6. Contrast conservative and non-conservative forces. 7. Distinguish between kinetic, potential, total energy. 8. State law of conservation of mechanical energy. 9. Relate the work don ...
am-ii_unit-v-3
... drum and flywheel are related by v r For the drum and flywheel, I 10.5 lb ft s 2 . The bearing friction is equivalent to a couple of 60 lb ft. At the instant shown, the block is moving downward at 6 ft/s. ...
... drum and flywheel are related by v r For the drum and flywheel, I 10.5 lb ft s 2 . The bearing friction is equivalent to a couple of 60 lb ft. At the instant shown, the block is moving downward at 6 ft/s. ...
Tro Chemistry a Molecular Approach, 3E
... temperature, pressure, concentration, and physical state (solid, liquid, or gas). Consider the mountain-climbing analogy depicted in Figure 6.5 ▶. The elevation at any point during a mountain climb is analogous to a state function. For example, when we reach 10,000 ft, our elevation is 10,000 ft, no ...
... temperature, pressure, concentration, and physical state (solid, liquid, or gas). Consider the mountain-climbing analogy depicted in Figure 6.5 ▶. The elevation at any point during a mountain climb is analogous to a state function. For example, when we reach 10,000 ft, our elevation is 10,000 ft, no ...
ME12001 Thermodynamics T7
... To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 20.1 Heat Engines. Steam at a temperature TH = 155 ∘ C and p = 1.00 atm enters a heat engine at an unknown flow rate. After passing through the heat engine, it is released at a temperature TC = 100 ∘ C and p = 1.00 atm . The measured power output P of the engine ...
... To practice Problem-Solving Strategy 20.1 Heat Engines. Steam at a temperature TH = 155 ∘ C and p = 1.00 atm enters a heat engine at an unknown flow rate. After passing through the heat engine, it is released at a temperature TC = 100 ∘ C and p = 1.00 atm . The measured power output P of the engine ...
Ch04_Clicker_Questions - Saint Leo University Faculty
... energy strikes and sticks to a heavy bowling ball initially at rest. After the clay sticks, both ideally move with a combined kinetic energy of a) b) c) d) ...
... energy strikes and sticks to a heavy bowling ball initially at rest. After the clay sticks, both ideally move with a combined kinetic energy of a) b) c) d) ...
The same paper as Word Document
... This is quite easier and it takes not 70 pages but only one paragraph. Here is a list of past Physics assumptions that I consider that the 21th century and the new millennium physics has already started and will eventually turn all of them false 1) The inertial mass of bodies ( of constant amount of ...
... This is quite easier and it takes not 70 pages but only one paragraph. Here is a list of past Physics assumptions that I consider that the 21th century and the new millennium physics has already started and will eventually turn all of them false 1) The inertial mass of bodies ( of constant amount of ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science
... systems, work is the amount of energy transferred as an object is moved through a distance, W = F d, where d is in the same direction as F. The total work done on an object depends on the net force acting on the object and the object’s displacement. Explain why work has a more precise scientific mea ...
... systems, work is the amount of energy transferred as an object is moved through a distance, W = F d, where d is in the same direction as F. The total work done on an object depends on the net force acting on the object and the object’s displacement. Explain why work has a more precise scientific mea ...
10.2 Simple Harmonic Motion and the Reference Circle
... The device consists of a spring-mounted chair in which the astronaut sits. The spring has a spring constant of 606 N/m and the mass of the chair is 12.0 kg. The measured period is 2.41 s. Find the mass of the ...
... The device consists of a spring-mounted chair in which the astronaut sits. The spring has a spring constant of 606 N/m and the mass of the chair is 12.0 kg. The measured period is 2.41 s. Find the mass of the ...
Thermal Physics Concepts and Practice
... 4 A mathematical digression 4.1 Thermodynamic differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.1 Exact differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.2 Exactness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 4 A mathematical digression 4.1 Thermodynamic differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.1 Exact differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.2 Exactness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...