Newton`s second law of motion
... • According to Newton’s first law of motion, unbalanced forces cause the velocity of an object to change • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the net force on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related ...
... • According to Newton’s first law of motion, unbalanced forces cause the velocity of an object to change • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the net force on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related ...
Newton`s Three Laws of Motion
... football games and consuming large quantities of food. What effect (if any) does this practice have upon his inertia? Explain. ...
... football games and consuming large quantities of food. What effect (if any) does this practice have upon his inertia? Explain. ...
Gravity - Lauren - s3.amazonaws.com
... Universal gravity is the force of gravity on every object to an extent. Example: The earth has a bigger gravitational pull on us, because the earth has a greater mass. We have a smaller mass compared to the earth, so our gravitational pull is smaller to the earth. Question: Does someone who is bigge ...
... Universal gravity is the force of gravity on every object to an extent. Example: The earth has a bigger gravitational pull on us, because the earth has a greater mass. We have a smaller mass compared to the earth, so our gravitational pull is smaller to the earth. Question: Does someone who is bigge ...
30 Physics
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object (measured in kilograms) and weight is the force of gravity pulling down on an object (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more i ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object (measured in kilograms) and weight is the force of gravity pulling down on an object (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more i ...
Forces in 1D
... moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the net force acting on that object is zero. ...
... moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the net force acting on that object is zero. ...
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
... 11. The causes for a large momentum: greater mass and high velocity 12. Force: a push or pull that causes a change in motion 13. N= Newtons or kg-m/s2 ( Unit for Force) 14. Friction: Force that acts between two objects in contact ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - Montville Township School District
... If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why don’t moving objects keep moving forever? Things don’t keep moving forever because there’s almost always an unbalanced force acting upon them. A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
... If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, why don’t moving objects keep moving forever? Things don’t keep moving forever because there’s almost always an unbalanced force acting upon them. A book sliding across a table slows down and stops because of the force of friction. ...
forces and the laws of motion - PAMS-Doyle
... 10 x the mass of the other, he wanted to prove that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m ...
... 10 x the mass of the other, he wanted to prove that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m ...
Universal Gravitation
... other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the mass of both objects was doubled, and if the distance between the objects was doubled, then what would be the new force of attraction between the two objects? It would not change ...
... other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the mass of both objects was doubled, and if the distance between the objects was doubled, then what would be the new force of attraction between the two objects? It would not change ...
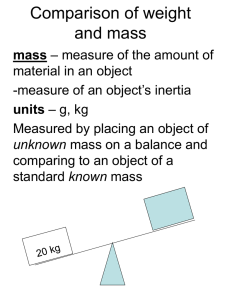
Comparison of weight and mass
... and mass mass – measure of the amount of material in an object -measure of an object’s inertia units – g, kg Measured by placing an object of unknown mass on a balance and comparing to an object of a standard known mass ...
... and mass mass – measure of the amount of material in an object -measure of an object’s inertia units – g, kg Measured by placing an object of unknown mass on a balance and comparing to an object of a standard known mass ...
VOLCANOES AND PLATE TECTONICS
... m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= 800kg* 5m/s2 =4000 N Calculating Force: What is the net force acting on a .15 kg hockey puck accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= .15kg* 12m/s2 = 1.8 N Explain how force, mass and acceleration ...
... m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= 800kg* 5m/s2 =4000 N Calculating Force: What is the net force acting on a .15 kg hockey puck accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s2. (*Show all work: Set-up, Substitute, Solve) F= m*a= .15kg* 12m/s2 = 1.8 N Explain how force, mass and acceleration ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.