Galaxies and the Universe
... – Much greater and the Universe would already have collapsed in on itself – Much less and stars could not have formed ...
... – Much greater and the Universe would already have collapsed in on itself – Much less and stars could not have formed ...
Feeding Time - Waterford Public Schools
... amount of matter in an object • It is typically measured in kilograms ...
... amount of matter in an object • It is typically measured in kilograms ...
Are You suprised
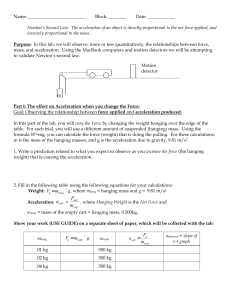
... For part I and II of the lab: 1. Comment on any differences you saw between the acceleration you calculated and the acceleration you measured with the motion sensor. 2. If there were differences, what may have caused them? 3. What types of error might be present in this experiment? Conclusion: (Shou ...
... For part I and II of the lab: 1. Comment on any differences you saw between the acceleration you calculated and the acceleration you measured with the motion sensor. 2. If there were differences, what may have caused them? 3. What types of error might be present in this experiment? Conclusion: (Shou ...
Newton`s Laws, Numbers 1 and 2
... ____7. A net positive force acting on an object will cause will cause the object to change its course and/or velocity. ...
... ____7. A net positive force acting on an object will cause will cause the object to change its course and/or velocity. ...
Midterm Review
... b. All aspects of an object’s motion c. Motion when a balanced force acts on an object. d. Motion when an unbalanced force acts on an object. 14. A force a. Can cause an object to change its motion c. Is a push or pull b. Gives energy to an object d. can do all of the above 15. Which of the followin ...
... b. All aspects of an object’s motion c. Motion when a balanced force acts on an object. d. Motion when an unbalanced force acts on an object. 14. A force a. Can cause an object to change its motion c. Is a push or pull b. Gives energy to an object d. can do all of the above 15. Which of the followin ...
From Heaven to Hell
... Law 1: Every body continues in its state of resting or of moving uniformly in a straight line, except insofar as it is driven by impressed forces to alter its state. Newton’s foundation is geometrical, meaning mathematical, but Newton birthed a thought never entirely grasped before, that of calculus ...
... Law 1: Every body continues in its state of resting or of moving uniformly in a straight line, except insofar as it is driven by impressed forces to alter its state. Newton’s foundation is geometrical, meaning mathematical, but Newton birthed a thought never entirely grasped before, that of calculus ...
PF1.1: FORCES: NEWTON`S LAWS OF MOTION
... Seatbelts are fitted in cars to take into account Newton’s 1st Law of Motion. If, for instance, you had to brake suddenly and you were not wearing your seatbelt, then by Newton’s 1st Law, you would continue to travel at a uniform speed – the speed of the car just before braking – until you made cont ...
... Seatbelts are fitted in cars to take into account Newton’s 1st Law of Motion. If, for instance, you had to brake suddenly and you were not wearing your seatbelt, then by Newton’s 1st Law, you would continue to travel at a uniform speed – the speed of the car just before braking – until you made cont ...
force
... forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 12.0 m/s? (c) After reaching this speed, the pilot turns off the engine and drifts to a stop over a distance of 50.0 m. Find the resistance force, assuming its ...
... forces of resistance. (a) Find the acceleration of the airboat (b) Starting from rest, how long does it take the airboat to reach a speed of 12.0 m/s? (c) After reaching this speed, the pilot turns off the engine and drifts to a stop over a distance of 50.0 m. Find the resistance force, assuming its ...
TAP 407-1: Worked examples – Coulomb`s law
... Given the difference in magnitudes of gravitational and electrical forces you’ve just discovered, why do you feel gravitational attraction from the earth, but no electrical forces? ...
... Given the difference in magnitudes of gravitational and electrical forces you’ve just discovered, why do you feel gravitational attraction from the earth, but no electrical forces? ...
Chapter 13 - Gravitation
... it suddenly but only momentarily disappears. Then the capsule travels through the second half of the tunnel, to the north pole. Check this story by finding the gravitational force on the capsule of mass m when it reaches a distance r from Earth’s center. Assume that Earth is a sphere of uniform dens ...
... it suddenly but only momentarily disappears. Then the capsule travels through the second half of the tunnel, to the north pole. Check this story by finding the gravitational force on the capsule of mass m when it reaches a distance r from Earth’s center. Assume that Earth is a sphere of uniform dens ...
P. LeClair - The University of Alabama
... where ρ is the uniform density (mass per unit volume) of the spherical planet. The volume of a sphere is 43 πr3 , where r is the radius of the sphere. 12. The period of the earth’s rotation about the sun is 365.256 days. It would be more convenient to have a period of exactly 365 days. How should th ...
... where ρ is the uniform density (mass per unit volume) of the spherical planet. The volume of a sphere is 43 πr3 , where r is the radius of the sphere. 12. The period of the earth’s rotation about the sun is 365.256 days. It would be more convenient to have a period of exactly 365 days. How should th ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... 1) You must apply a force F1 to begin pushing a crate from rest across the floor, you must apply a force F2 to keep the crate moving at a constant velocity once its in motion. Which statement is true? a) F1 = F2 b) F1 > F2 c) F1 < F2 2) When do action and reaction pairs of forces not cancel one anot ...
... 1) You must apply a force F1 to begin pushing a crate from rest across the floor, you must apply a force F2 to keep the crate moving at a constant velocity once its in motion. Which statement is true? a) F1 = F2 b) F1 > F2 c) F1 < F2 2) When do action and reaction pairs of forces not cancel one anot ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.