Uniform Circular Motion
... Background: An object in uniform circular motion with a radius (r) travels in a circle at a constant speed. Although the speed is constant, the velocity is changing since the mass’s direction of travel is continuously changing. Based on Newton’s second law, we know that where there is acceleration t ...
... Background: An object in uniform circular motion with a radius (r) travels in a circle at a constant speed. Although the speed is constant, the velocity is changing since the mass’s direction of travel is continuously changing. Based on Newton’s second law, we know that where there is acceleration t ...
speed
... unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes more to slow down a charging b ...
... unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate with an acceleration which is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. This one is telling us that big heavy objects don’t move as fast or as easily as smaller lighter objects. It takes more to slow down a charging b ...
Dark Matter Dark Energy The History of the Universe More of the
... life might exist in conditions very different from Earth. For example Antarctic sub-glacial lakes could show what life (if it exists) in Europa’s oceans might be like ...
... life might exist in conditions very different from Earth. For example Antarctic sub-glacial lakes could show what life (if it exists) in Europa’s oceans might be like ...
Newton`s Laws
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
... On Earth, every object will fall at the same rate (not counting air friction) The Acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 meaning that every second, a falling object accelerates 9.8 m/s In other words, every second something is falling it is moving 9.8 m/s faster If you drop a bowling ball and a match b ...
1.3.1 Voltage in Electrical Systems
... • Field forces are alterations in space around the body creating the field. – They are models used by scientists to help them understand and predict how forces are transmitted from one object to another. ...
... • Field forces are alterations in space around the body creating the field. – They are models used by scientists to help them understand and predict how forces are transmitted from one object to another. ...
Physics Lab Exam - La Salle University
... A block (not cart) of mass 1009.7 g is placed on an inclined track of length 228.1 cm and height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the bl ...
... A block (not cart) of mass 1009.7 g is placed on an inclined track of length 228.1 cm and height 88 cm. One end of a string is attached to the block and the other end to hanger. A range of masses can be placed on the hanger without setting the system into motion. Draw all the forces acting on the bl ...
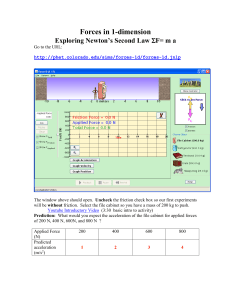
Forces in 1
... Below show how the numbers go together and conjunction with Newton’s second Law (Net force= mass x acceleration) to give an acceleration of 1.4 m/s/s. Include all steps so you could repeat this later. Net force = Mass (acceleration) 280 N=200 kg (1.4 m/s/s) 280 N=280 N Left and right side of F=ma ag ...
... Below show how the numbers go together and conjunction with Newton’s second Law (Net force= mass x acceleration) to give an acceleration of 1.4 m/s/s. Include all steps so you could repeat this later. Net force = Mass (acceleration) 280 N=200 kg (1.4 m/s/s) 280 N=280 N Left and right side of F=ma ag ...
Example
... ping-pong ball from the same point. Neglecting air resistance, what can we say about the motion of the two balls? A) The bowling ball will hit the ground more than one second before the ping-pong ball. B) The bowling ball and the ping-pong ball will hit the ground at the same time. C) The bowling ba ...
... ping-pong ball from the same point. Neglecting air resistance, what can we say about the motion of the two balls? A) The bowling ball will hit the ground more than one second before the ping-pong ball. B) The bowling ball and the ping-pong ball will hit the ground at the same time. C) The bowling ba ...
Newton`s Laws
... Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. Normal words: For every action, there is a equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. Normal words: For every action, there is a equal and opposite reaction. ...
Honors or AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment (part 1)
... Mark either as True or False. Some may require certain conditions to be true or false. If so, state the conditions. 1. History has no place in science. 2. Two objects side by side must have the same speed. 3. Acceleration and velocity are always in the same direction. 4. Velocity is a force. 5. If v ...
... Mark either as True or False. Some may require certain conditions to be true or false. If so, state the conditions. 1. History has no place in science. 2. Two objects side by side must have the same speed. 3. Acceleration and velocity are always in the same direction. 4. Velocity is a force. 5. If v ...
Newton`s 1st Law Newton`s 2nd Law net Newton`s 3rd Law SI Units
... We frequently can have knowledge of forces acting on an object ...
... We frequently can have knowledge of forces acting on an object ...
lab report sci class (1) - Sites @ Suffolk University
... 3. Apparatus: The kit we were given was 20-25g of weight, small machinery (the Lego brain) that would be able to pull the weight. 4. Procedure: We had 8 different trials that were separated into 2 parts. The first 4 trials were had to change the power level and keep the same mass. For the other 4 tr ...
... 3. Apparatus: The kit we were given was 20-25g of weight, small machinery (the Lego brain) that would be able to pull the weight. 4. Procedure: We had 8 different trials that were separated into 2 parts. The first 4 trials were had to change the power level and keep the same mass. For the other 4 tr ...
How do Newton`s Laws describe motion?
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
... What about the ladder on top of the truck? The ladder is in motion because the truck is in motion. When the truck stops, the ladder stays in motion. The truck is stopped by the force of the car, but the ladder is not. What force stops the ladder? ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.