Physics 160 Dynamics worksheet 1) Which of Newton`s laws best
... C) the third law D) the first law 2) When you sit on a chair, the resultant force on you is 2) _______ A) down. B) zero. C) up. D) depending on your weight. 3) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will 3) _______ A) move with constant velocity. B) slow down and eventually come to a s ...
... C) the third law D) the first law 2) When you sit on a chair, the resultant force on you is 2) _______ A) down. B) zero. C) up. D) depending on your weight. 3) In the absence of an external force, a moving object will 3) _______ A) move with constant velocity. B) slow down and eventually come to a s ...
Review Forces Part 2
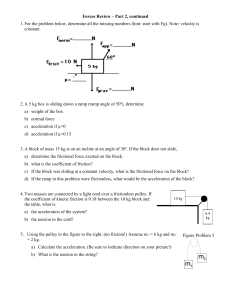
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
Word
... a. What external force is responsible for accelerating the runner at the beginning of the race? Explain how this force is produced. ...
... a. What external force is responsible for accelerating the runner at the beginning of the race? Explain how this force is produced. ...
force
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
2.1 Speed and constant velocity.
... across the table it comes to a stop, why? The force acting on it is the force of friction. Newton’s Second Law: An unbalanced force (or net force) causes an object to accelerate; this acceleration is directly proportional to the unbalanced force and inversely proportional to the object’s mass; calle ...
... across the table it comes to a stop, why? The force acting on it is the force of friction. Newton’s Second Law: An unbalanced force (or net force) causes an object to accelerate; this acceleration is directly proportional to the unbalanced force and inversely proportional to the object’s mass; calle ...
Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... – This is called cosmological _______________. – Proven by observing a faint glow of __________________ that is a remnant of _________ from the Big Bang. – Early Universe = __________ and ____________ – Today’s Universe = __________ and ________ ___________ because of ...
... – This is called cosmological _______________. – Proven by observing a faint glow of __________________ that is a remnant of _________ from the Big Bang. – Early Universe = __________ and ____________ – Today’s Universe = __________ and ________ ___________ because of ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... IX. Acceleration of Fall is Less When Air Drag Acts A. Air drag depends on _________ and ____________ ____________ B. Increased air drag results in reduced acceleration C. When air is present the downward net force = _______________________ D. As an object falls faster and air drag increases, accele ...
... IX. Acceleration of Fall is Less When Air Drag Acts A. Air drag depends on _________ and ____________ ____________ B. Increased air drag results in reduced acceleration C. When air is present the downward net force = _______________________ D. As an object falls faster and air drag increases, accele ...
Chapter 05 - Force and Motion
... The normal force: When a body presses against a surface, the surface (even a seemingly rigid one) deforms and pushes on the body with a normal force, FN, that is perpendicular to the surface. In the figure, forces Fg and FN are the only two forces on the block and they are both vertical. Thus, for t ...
... The normal force: When a body presses against a surface, the surface (even a seemingly rigid one) deforms and pushes on the body with a normal force, FN, that is perpendicular to the surface. In the figure, forces Fg and FN are the only two forces on the block and they are both vertical. Thus, for t ...
Document
... In 1932, Karl Jansky discovered that the MW produced a broad range of radio emission. Later in 1951, several groups detected the 21-cm hyperfine transition of atomic hydrogen which allowed for precise line-of-sight velocities to be determined without the hindrance of dust absorption. •Gas is confin ...
... In 1932, Karl Jansky discovered that the MW produced a broad range of radio emission. Later in 1951, several groups detected the 21-cm hyperfine transition of atomic hydrogen which allowed for precise line-of-sight velocities to be determined without the hindrance of dust absorption. •Gas is confin ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 7: Newton`s Laws
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
Wednesday, October 10, 2007
... This means that the distance to the Moon is about 60 times that of the Earth’s radius, and its acceleration reduced the 1443-002, ratio. This proves that the inverse square law is valid. Wednesday,isOct. 10, 2007by the square of PHYS Fall 2007 ...
... This means that the distance to the Moon is about 60 times that of the Earth’s radius, and its acceleration reduced the 1443-002, ratio. This proves that the inverse square law is valid. Wednesday,isOct. 10, 2007by the square of PHYS Fall 2007 ...
Gravity Equation
... Acceleration due to Gravity (g) The acceleration of a body arising from the earth’s gravitational pull. Units are ft/sec2 or m/sec2 At the earth’s surface g is: 9.8 m/sec2 ...
... Acceleration due to Gravity (g) The acceleration of a body arising from the earth’s gravitational pull. Units are ft/sec2 or m/sec2 At the earth’s surface g is: 9.8 m/sec2 ...
Name - westlake-science
... 21. What force is responsible for your socks sticking together after they have been in a clothes dryer? ...
... 21. What force is responsible for your socks sticking together after they have been in a clothes dryer? ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law relates the ___________ of a Cepheid to its _____________. Hubble’s Law relates ___________ of a g ...
... The Sun is located ________ away from the center of the Milky Way. The mass of the Milky Way is ________________ solar masses. The closest galaxy to the Milky Way is the ________________. Leavitt’s Law relates the ___________ of a Cepheid to its _____________. Hubble’s Law relates ___________ of a g ...
Unit 4 Review - Clayton School District
... on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 2. If object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 moves at constant speed, then the push on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 3. A boy stands on ...
... on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 2. If object 1 pushes on object 2 and object 2 moves at constant speed, then the push on object 1 by object 2 is (greather than, less than, equal to) the push on object 2 by object 1. 3. A boy stands on ...
Morgan Rezer
... 16. Explain how an object can have forces acting on it but not be accelerating. If the forces are balanced, then the object will not move. 17. What force should Lori apply to a 5 kg. box to give it an acceleration of 2 m/s 2? Use f = m x a F=mxa F = 5 kg x 2 m/s2 F = 10 N 18. If a 10 N force acceler ...
... 16. Explain how an object can have forces acting on it but not be accelerating. If the forces are balanced, then the object will not move. 17. What force should Lori apply to a 5 kg. box to give it an acceleration of 2 m/s 2? Use f = m x a F=mxa F = 5 kg x 2 m/s2 F = 10 N 18. If a 10 N force acceler ...
Newton`s first law of motion
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
... speed of the parachutist is zero. However he will immediately be acted upon by his weight acting vertically downwards and since the external resultant force is not zero he will accelerate downwards. As the parachutist’s speed increases so does the air resistance. This opposes the downwards force of ...
Newton*s third Law of Motion
... • THIS CAN HAPPEN IF ONE OF THE OBJECTS INVOLVED IS MUCH MORE MASSIVE THAN THE OTHER. THIS IS WHY THE MASSIVE OBJECT MIGHT SEEM TO REMAIN MOTIONLESS. • EXAMPLE: A PERSON WALKING ON THE GROUND. (GROUND/EARTH IS MASSIVE=MOTION IS UNDETECTED) ...
... • THIS CAN HAPPEN IF ONE OF THE OBJECTS INVOLVED IS MUCH MORE MASSIVE THAN THE OTHER. THIS IS WHY THE MASSIVE OBJECT MIGHT SEEM TO REMAIN MOTIONLESS. • EXAMPLE: A PERSON WALKING ON THE GROUND. (GROUND/EARTH IS MASSIVE=MOTION IS UNDETECTED) ...
How Far is far ?
... Yet another method results from the fact that as we look out farther, we look back in time : light takes billions of years to reach us from the edges of the universe. Since clusters of galaxies were denser and hotter in the early universe, the farther away a galaxy cluster is, the hotter it should ...
... Yet another method results from the fact that as we look out farther, we look back in time : light takes billions of years to reach us from the edges of the universe. Since clusters of galaxies were denser and hotter in the early universe, the farther away a galaxy cluster is, the hotter it should ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.