notebook- Universal Gravitation
... What we want to know… What is Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation? How does distance affect gravitational force between two objects? What is weight and how can something appear weightless? What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion? ...
... What we want to know… What is Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation? How does distance affect gravitational force between two objects? What is weight and how can something appear weightless? What are Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion? ...
Course Expectations
... The structure (layers) and composition of the sun Fusion occurs in the core of the sun The sun rotates and has cycles The Nebular Theory for Star formation The purpose and function of an HR Diagram Why the spectra of stars changes along the spectral sequence Mass determines the life of a star How st ...
... The structure (layers) and composition of the sun Fusion occurs in the core of the sun The sun rotates and has cycles The Nebular Theory for Star formation The purpose and function of an HR Diagram Why the spectra of stars changes along the spectral sequence Mass determines the life of a star How st ...
Test #4
... a) too many stars, b) glowing interstellar gas, c) interstellar dust, d) planetary nebulae 13. The mass of the galaxy has been found by a) counting the stars it contains, b) determining its gravitational force on nearby galaxies c) estimating the number of interstellar clouds, d) applying Kepler’s 3 ...
... a) too many stars, b) glowing interstellar gas, c) interstellar dust, d) planetary nebulae 13. The mass of the galaxy has been found by a) counting the stars it contains, b) determining its gravitational force on nearby galaxies c) estimating the number of interstellar clouds, d) applying Kepler’s 3 ...
crct/final exam review forces and motion #1
... 44. What is the relationship between mass, weight, friction, and gravity? ...
... 44. What is the relationship between mass, weight, friction, and gravity? ...
Forces And Motion
... • Cause an object at rest to stay at rest or an object in motion to stay in motion (inertia) • Cause an object moving at a constant speed to continue at a constant speed • In your notes, describe an example of a balanced force affecting an object. Study Jams - 1st Law of Motion Video ...
... • Cause an object at rest to stay at rest or an object in motion to stay in motion (inertia) • Cause an object moving at a constant speed to continue at a constant speed • In your notes, describe an example of a balanced force affecting an object. Study Jams - 1st Law of Motion Video ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
... In the Einstein model for a solid, atoms are treated as one-dimensional quantum mechanical oscillators that can each accept an arbitrary number of energy units above the ground state. Recall that the multiplicity Ω(N, q) = (q + N − 1)!/(q!(N − 1)!) gives the number of states available to a system co ...
Standard Set 2 - Atascadero High School
... universe’s visible matter; that is, matter that emits or reflects light or some other electromagnetic radiation that is detectable on Earth. The presence of otherwise invisible matter can be inferred from the effect of its gravity on visible matter, and the mass of the invisible matter in the univer ...
... universe’s visible matter; that is, matter that emits or reflects light or some other electromagnetic radiation that is detectable on Earth. The presence of otherwise invisible matter can be inferred from the effect of its gravity on visible matter, and the mass of the invisible matter in the univer ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... If both a golf ball and a bowling ball are moving at the same velocity, which ball has more momentum? If the driver of a car suddenly makes a sharp turn, why will the passenger slide to the side of the car? If an astronaut throws a ball in space, when will the ball stop? Which of the following objec ...
... If both a golf ball and a bowling ball are moving at the same velocity, which ball has more momentum? If the driver of a car suddenly makes a sharp turn, why will the passenger slide to the side of the car? If an astronaut throws a ball in space, when will the ball stop? Which of the following objec ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton’s Laws of Motion
... scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
... scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
Describing Motion - Science
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
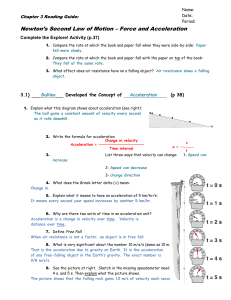
Chapter 3 Reading Guide
... 20. What will happen to the acceleration if we double both the mass and the net force acting on an object? Explain. Acceleration will be unchanged because although the mass is doubled, which will cut the acceleration in half, the fore is also doubled which will double the acceleration. 21. Complete ...
... 20. What will happen to the acceleration if we double both the mass and the net force acting on an object? Explain. Acceleration will be unchanged because although the mass is doubled, which will cut the acceleration in half, the fore is also doubled which will double the acceleration. 21. Complete ...
4.3 Acceleration Acceleration describes how quickly speed changes
... of falling objects, the effects of air or water would have to be ignored. As a result, we will investigate falling, but only as a result of one force, gravity. ...
... of falling objects, the effects of air or water would have to be ignored. As a result, we will investigate falling, but only as a result of one force, gravity. ...
Student Review Sheet Physics Semester A Examination
... collaboration and review of concepts in preparation for the entire exam (not just the BCRs). Teachers should not address these BCRs during the course of their instruction nor should they assist in preparing students for the BCRs during exam review. Students are able to collaborate and use other reso ...
... collaboration and review of concepts in preparation for the entire exam (not just the BCRs). Teachers should not address these BCRs during the course of their instruction nor should they assist in preparing students for the BCRs during exam review. Students are able to collaborate and use other reso ...
Lecture 7 Gravity and satellites
... gravitational field strength at that location, the motion of the object could be considered as free falling. A person during free falling would experience apparent weightlessness (a = g and N = 0) Motion of the planets A satellite is an object that is in a stable orbit around a more massive central ...
... gravitational field strength at that location, the motion of the object could be considered as free falling. A person during free falling would experience apparent weightlessness (a = g and N = 0) Motion of the planets A satellite is an object that is in a stable orbit around a more massive central ...
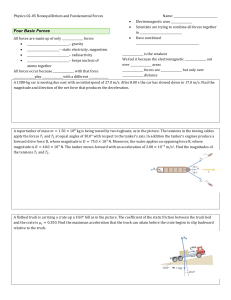
Four Basic Forces In
... 4.50 × 106 N. What is the rocket’s acceleration? (OpenStax 4.23) 6.20 m/s2 11. The wheels of a midsize car exert a force of 2100 N backward on the road to accelerate the car in the forward direction. If the force of friction including air resistance is 250 N and the acceleration of the car is 1.80 m ...
... 4.50 × 106 N. What is the rocket’s acceleration? (OpenStax 4.23) 6.20 m/s2 11. The wheels of a midsize car exert a force of 2100 N backward on the road to accelerate the car in the forward direction. If the force of friction including air resistance is 250 N and the acceleration of the car is 1.80 m ...
Chapter 2
... • Newton’s third law of motion states that: Whenever two objects interact, the force exerted on one object is equal in size and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the other object. • Forces always occur in matched pairs that act in opposite directions and on two different bodies: • FA due ...
... • Newton’s third law of motion states that: Whenever two objects interact, the force exerted on one object is equal in size and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the other object. • Forces always occur in matched pairs that act in opposite directions and on two different bodies: • FA due ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.