presentation source
... in Cartesian coordinates for an object moving under the influence of a two-dimensional central force of the form F=k/r2, where k is a constant. b) What difficulty you will encounter if you would like to derive the Newton equations of motion in polar coordinates? y ...
... in Cartesian coordinates for an object moving under the influence of a two-dimensional central force of the form F=k/r2, where k is a constant. b) What difficulty you will encounter if you would like to derive the Newton equations of motion in polar coordinates? y ...
Using Newtons Laws
... Drag Force and Terminal Velocity When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on t ...
... Drag Force and Terminal Velocity When an object moves through any fluid, such as air or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on t ...
Topic 6-1 Gravitational Force and Field
... Activity 611 Measuring Gravitational Force between two objects (NB) Activity 612 Investigating Gravitational Field around a mass (NB) Activity 613 Investigating the local gravitational acceleration (NB) ...
... Activity 611 Measuring Gravitational Force between two objects (NB) Activity 612 Investigating Gravitational Field around a mass (NB) Activity 613 Investigating the local gravitational acceleration (NB) ...
Topic 6 and 10 TEST
... The Earth and the Moon may be considered to be two isolated point masses. The masses of the Earth and the Moon are 5.98 1024kg and 7.35 1022 kg respectively and their separation is 3.84 108 m, as shown below. The diagram is not to scale. Earth mass 5.98 1024kg ...
... The Earth and the Moon may be considered to be two isolated point masses. The masses of the Earth and the Moon are 5.98 1024kg and 7.35 1022 kg respectively and their separation is 3.84 108 m, as shown below. The diagram is not to scale. Earth mass 5.98 1024kg ...
Connected Particles and Newton`s 3rd Law
... e.g.2. A particle, A, of mass 0·6 kg, is held at rest on a smooth table. A is connected by a light, inextensible string, which passes over a smooth fixed pulley at the edge of the table, to another particle, B, of mass 0·4 kg hanging freely. The string is horizontal and at right angles to the edge ...
... e.g.2. A particle, A, of mass 0·6 kg, is held at rest on a smooth table. A is connected by a light, inextensible string, which passes over a smooth fixed pulley at the edge of the table, to another particle, B, of mass 0·4 kg hanging freely. The string is horizontal and at right angles to the edge ...
Physics 103-02 Exam IV 4 Dec
... is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk a ...
... is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk a ...
Dynamics Presentation
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
... An object sliding down an incline has three forces acting on it: the normal force, gravity, and the frictional force. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. • The friction force is parallel to it. • The gravitational force points down. If the object is at rest, the forces are the ...
Physical Science Final Study Guide I KEY Name __ ___
... 20. Identify the velocity and acceleration of the object for the following points. (show work, include units) ...
... 20. Identify the velocity and acceleration of the object for the following points. (show work, include units) ...
Physics Unit 2 Review
... c. the weight of the object decreases. b. the object accelerates. d. the inertia of the object increases. 3. As you push a cereal box across a tabletop, the sliding friction acting on the cereal box a. acts in the direction of motion. b. equals the weight of the box. c. is usually greater than stati ...
... c. the weight of the object decreases. b. the object accelerates. d. the inertia of the object increases. 3. As you push a cereal box across a tabletop, the sliding friction acting on the cereal box a. acts in the direction of motion. b. equals the weight of the box. c. is usually greater than stati ...
Catapult Presentation_MiddSchool_Animated
... Gravity is necessary to make a Without Gravity VS. With Gravity projectile land back on the ground. The launching force and angle along with the mass of the object help determine how far and how high the projectile will fly ...
... Gravity is necessary to make a Without Gravity VS. With Gravity projectile land back on the ground. The launching force and angle along with the mass of the object help determine how far and how high the projectile will fly ...
Falling Objects and Gravity
... - Velocity increases uniformly with time indicating the acceleration due to gravity (g) is a CONSTANT VALUE. - Magnitude of the acceleration is given by slope of the line. ...
... - Velocity increases uniformly with time indicating the acceleration due to gravity (g) is a CONSTANT VALUE. - Magnitude of the acceleration is given by slope of the line. ...
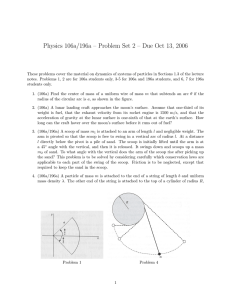
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 2 – Due Oct 13,...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
... 1. (106a) Find the center of mass of a uniform wire of mass m that subtends an arc θ if the radius of the circular arc is a, as shown in the figure. 2. (106a) A lunar landing craft approaches the moon’s surface. Assume that one-third of its weight is fuel, that the exhaust velocity from its rocket e ...
Skating Observations about Skating
... Question 5 Q: Why does a skater need ice or wheels to skate? A: Real-world complications usually mask inertia Solution: minimize or overwhelm complications To observe inertia, therefore, ...
... Question 5 Q: Why does a skater need ice or wheels to skate? A: Real-world complications usually mask inertia Solution: minimize or overwhelm complications To observe inertia, therefore, ...
Atomic Clocks and Gravitational Field Strength
... particles. Kinetic energy is therefore a pressure which is induced either by acceleration or when a fine-grained angular acceleration wave emitted from one body delivers kinetic energy into another body during a collision [5]. When this happens, the other body then linearly accelerates. It is propos ...
... particles. Kinetic energy is therefore a pressure which is induced either by acceleration or when a fine-grained angular acceleration wave emitted from one body delivers kinetic energy into another body during a collision [5]. When this happens, the other body then linearly accelerates. It is propos ...
Newton`s Laws MC test
... 12) When a 45-kg person steps on a scale in an elevator, the scale reads a steady 480 N. Which of the following statements must be true? (There could be more than one correct choice.) A) The elevator is accelerating upward at a constant rate. B) The elevator is accelerating downward at a constant ra ...
... 12) When a 45-kg person steps on a scale in an elevator, the scale reads a steady 480 N. Which of the following statements must be true? (There could be more than one correct choice.) A) The elevator is accelerating upward at a constant rate. B) The elevator is accelerating downward at a constant ra ...
Newton`s 3rd Law
... Newton’s Third Law says your seat is pushing up against you with equal force. ...
... Newton’s Third Law says your seat is pushing up against you with equal force. ...
Newton`s Laws and Roller Coasters
... over and over again in the last three centuries. They are the basis of many of our modern inventions. 2 A roller coaster, a modern invention that uses the laws of motion to thrilling ends, is the best use of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Roller coasters, with their twists, turns, and loops seem to defy ...
... over and over again in the last three centuries. They are the basis of many of our modern inventions. 2 A roller coaster, a modern invention that uses the laws of motion to thrilling ends, is the best use of Newton’s Laws of Motion. Roller coasters, with their twists, turns, and loops seem to defy ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.