Kendriyavidyalayasangathan 1 Multiple choice questions in Physics for class IX
... An example of a body moving with constant speed but still accelerating is a. A body moving with constant c. A body moving with constant speed in a circular path speed on a straight road b. A body moving in a helical path d. A body moving with constant with constant speed speed on a straight railway ...
... An example of a body moving with constant speed but still accelerating is a. A body moving with constant c. A body moving with constant speed in a circular path speed on a straight road b. A body moving in a helical path d. A body moving with constant with constant speed speed on a straight railway ...
Connecting Force and Motion, and Newton`s First Law of Motion
... velocity of an object c. How is force calculated? - It is calculated F = M x A where F = Force, M = Mass, and A = Acceleration - The triangle can be applied to this equation - From this equation you can calculate Force, Mass, and Acceleration. - You must take note that you now have 2 ways to calcula ...
... velocity of an object c. How is force calculated? - It is calculated F = M x A where F = Force, M = Mass, and A = Acceleration - The triangle can be applied to this equation - From this equation you can calculate Force, Mass, and Acceleration. - You must take note that you now have 2 ways to calcula ...
Physics 111 HW6 - University of St. Thomas
... GenFMA-01. A block of ice with mass m sits at rest on a friction-free, frozen lake. A constant force F then acts on the block for a specific time T, resulting in the block having a speed v. a) Start the block at rest again. If the force on and mass of the block are unchanged, but the time the force ...
... GenFMA-01. A block of ice with mass m sits at rest on a friction-free, frozen lake. A constant force F then acts on the block for a specific time T, resulting in the block having a speed v. a) Start the block at rest again. If the force on and mass of the block are unchanged, but the time the force ...
Earth in the Universe Answer each in your binder or notebook. Date
... Question 1 A student observes the Milky Way galaxy in the night sky. Which characteristic of the galaxy makes it visible? A. The galaxy’s stellar nebulae reflect the Sun’s light. B. Billions of stars in the galaxy carry out nuclear fusion. C. Tons of compressed matter begin to radiate visible light ...
... Question 1 A student observes the Milky Way galaxy in the night sky. Which characteristic of the galaxy makes it visible? A. The galaxy’s stellar nebulae reflect the Sun’s light. B. Billions of stars in the galaxy carry out nuclear fusion. C. Tons of compressed matter begin to radiate visible light ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... How do you think you can determine the CM of objects that are not symmetric? ...
... How do you think you can determine the CM of objects that are not symmetric? ...
Motion, Forces, and Energy
... Motion, Forces, and Energy • Energy is all around us. • Forces are used to change motion. • Energy comes in many different forms and can be changed from one form to another. • Energy allows you and other objects to do ...
... Motion, Forces, and Energy • Energy is all around us. • Forces are used to change motion. • Energy comes in many different forms and can be changed from one form to another. • Energy allows you and other objects to do ...
Concept Questions
... cylindrical rotor . The inner radius of the washer is R. A massless string, with an object of mass m attached to the other end, is wrapped around the side of the rotor and passes over a massless pulley. Assume that there is a constant frictional torque about the axis of the rotor. The object is rele ...
... cylindrical rotor . The inner radius of the washer is R. A massless string, with an object of mass m attached to the other end, is wrapped around the side of the rotor and passes over a massless pulley. Assume that there is a constant frictional torque about the axis of the rotor. The object is rele ...
Speed and Acceleration
... The Sun to the Earth - 8·5 minutes The Sun to the nearest star - 4·3 light years The diameter of the Milky Way - 120 000 light years Exoplanets An exoplanet, or extrasolar planet, is a planet outside our Solar System. More than a thousand such planets have been discovered. There are at least 100 bil ...
... The Sun to the Earth - 8·5 minutes The Sun to the nearest star - 4·3 light years The diameter of the Milky Way - 120 000 light years Exoplanets An exoplanet, or extrasolar planet, is a planet outside our Solar System. More than a thousand such planets have been discovered. There are at least 100 bil ...
impulse - sportscoachinghigher
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of ...
Document
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of ...
... When the force of gravity acts on a body, it acts through the centre of gravity and always moves towards the centre of the earth. Symmetrical objects like balls and cubes have their CoG in the exact centre of the object. Objects are 3 dimensional, so the CoG will be at the point where the axes of ...
dynamics
... we will treat acceleration due to gravity as a scalar quantity. “g” is used in many forces which do not have a downward direction. The direction of the force will be determined by the student by calculation or analysis. ...
... we will treat acceleration due to gravity as a scalar quantity. “g” is used in many forces which do not have a downward direction. The direction of the force will be determined by the student by calculation or analysis. ...
Net Force: a resultant force acting on object
... free-body diagram for them Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object Apply Newton’s second law. The x- and y-components of Newton second law should be taken from the vector equation and written individually. This often results in two equations and two unknowns Solve for the desired unkno ...
... free-body diagram for them Choose a convenient coordinate system for each object Apply Newton’s second law. The x- and y-components of Newton second law should be taken from the vector equation and written individually. This often results in two equations and two unknowns Solve for the desired unkno ...
Static Equilibrium (print version)
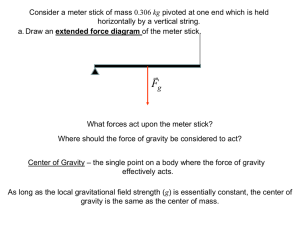
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
Homework 5 - Physics | Oregon State University
... non-inertial frame of the accelerating boxcar. In the car’s frame, the objects hangs without motion so its apparent weight (1) must be balanced by the string’s tension. Hence, the direction of the effective gravity (2) must be opposite to the string’s pull on the object, which is 10.8◦ from the perp ...
... non-inertial frame of the accelerating boxcar. In the car’s frame, the objects hangs without motion so its apparent weight (1) must be balanced by the string’s tension. Hence, the direction of the effective gravity (2) must be opposite to the string’s pull on the object, which is 10.8◦ from the perp ...
Circular Motion Web Quest
... bottom of the loop. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 50-kg body at the top and at the bottom of the loop. 13. Noah Formula is riding a roller coaster and encounters a loop. Noah is traveling 6 m/s at the top of the loop and 18.0 m/s at the bottom of the loop. ...
... bottom of the loop. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 50-kg body at the top and at the bottom of the loop. 13. Noah Formula is riding a roller coaster and encounters a loop. Noah is traveling 6 m/s at the top of the loop and 18.0 m/s at the bottom of the loop. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.