LarCalc10_ch07_sec5
... Work Done by a Constant Force In the U.S. measurement system, work is typically expressed in foot-pounds (ft-lb), inch-pounds, or foot-tons. In the International System of Units (SI), the basic unit of force is the newton – the force required to produce an acceleration of 1 meter per second per sec ...
... Work Done by a Constant Force In the U.S. measurement system, work is typically expressed in foot-pounds (ft-lb), inch-pounds, or foot-tons. In the International System of Units (SI), the basic unit of force is the newton – the force required to produce an acceleration of 1 meter per second per sec ...
PPT - LSU Physics
... where W is the work required to move the ball from point P (at distance R) to infinity. Work can also be expressed in terms of potential energies as ...
... where W is the work required to move the ball from point P (at distance R) to infinity. Work can also be expressed in terms of potential energies as ...
Types of Variation
... Newton’s First Law states that in the absence of a net (unbalanced) force an object will persist in its original state of motion (either continue in uniform motion or remain at rest). Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely a ...
... Newton’s First Law states that in the absence of a net (unbalanced) force an object will persist in its original state of motion (either continue in uniform motion or remain at rest). Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely a ...
Types of Variation
... Newton’s First Law states that in the absence of a net (unbalanced) force an object will persist in its original state of motion (either continue in uniform motion or remain at rest). Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely a ...
... Newton’s First Law states that in the absence of a net (unbalanced) force an object will persist in its original state of motion (either continue in uniform motion or remain at rest). Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely a ...
Exercises - cloudfront.net
... fuels in mechanical engines? How are the processes different? In both cases, the reaction is self-sustaining once it starts. Also, the same principle of combustion occurs in both cases, but the reaction rate of metabolism is much slower and energy is released only as it is needed by the body. ...
... fuels in mechanical engines? How are the processes different? In both cases, the reaction is self-sustaining once it starts. Also, the same principle of combustion occurs in both cases, but the reaction rate of metabolism is much slower and energy is released only as it is needed by the body. ...
Chapter 6
... After A has rolled down the hill, the potential energy lost by A has been converted to random motions of the components of the hill (frictional heating) and to the increase in the potential energy of B. ...
... After A has rolled down the hill, the potential energy lost by A has been converted to random motions of the components of the hill (frictional heating) and to the increase in the potential energy of B. ...
Document
... h Work done = energy given to box W = force x distance = Fh W = mgh Initial and final kinetic energy is zero (v=0) Energy of box is that associated with its position Gravitational potential energy ...
... h Work done = energy given to box W = force x distance = Fh W = mgh Initial and final kinetic energy is zero (v=0) Energy of box is that associated with its position Gravitational potential energy ...
$doc.title
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics devoted to the study of energy processes, which involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer, and the relationship between processes and thermal properties of matter. The unit begins by introducing the concept of temperature a ...
... Thermodynamics is the branch of physics devoted to the study of energy processes, which involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer, and the relationship between processes and thermal properties of matter. The unit begins by introducing the concept of temperature a ...
Chapter 4 Kinetics of a particle
... After completion of a closed path under a conservati ve force, K .E. 0 ...
... After completion of a closed path under a conservati ve force, K .E. 0 ...
Grade Level 8, Science Content
... Power Standard #3 ‐ Physical Science: Students describe motion and demonstrate how forces affect motion. (Aligns with Vermont Standard ...
... Power Standard #3 ‐ Physical Science: Students describe motion and demonstrate how forces affect motion. (Aligns with Vermont Standard ...
water displacement _ Matter
... Water Displacement displacement occurs when an object is immersed in a fluid, pushing it out of the way and taking its place. The volume of the fluid displaced can then be measured, as in the illustration, and from this the volume of the immersed object can be deduced ...
... Water Displacement displacement occurs when an object is immersed in a fluid, pushing it out of the way and taking its place. The volume of the fluid displaced can then be measured, as in the illustration, and from this the volume of the immersed object can be deduced ...
Presentation Lesson 15 Work and Energy
... ground level, and the floor of the attic is 5.0 m above ground level. What is the change in potential energy if ...
... ground level, and the floor of the attic is 5.0 m above ground level. What is the change in potential energy if ...
The shortest path between two points, Geodesics and Mechanics
... In mathematics, a geodesic denotes the shortest path between two points. For all of us (and not only the mathematicians), this notion is very intuitive and the answer is clear: The shortest path between two points A and B is the straight line joining A and B. We become aware of this fact very early ...
... In mathematics, a geodesic denotes the shortest path between two points. For all of us (and not only the mathematicians), this notion is very intuitive and the answer is clear: The shortest path between two points A and B is the straight line joining A and B. We become aware of this fact very early ...
kinetic energy - MashrekPhysics
... “The work done by a force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts”. ...
... “The work done by a force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts”. ...
Lecture7_Torque_Newtons3rdLaw
... The cue ball traveling with speed v strikes a stationary billiard ball head-on. A. The cue ball rebounds backward, while its target is sent moving forward. B. The cue ball stops while its target continues forward with the speed v. C. The cue ball and target ball roll forward together with a speed < ...
... The cue ball traveling with speed v strikes a stationary billiard ball head-on. A. The cue ball rebounds backward, while its target is sent moving forward. B. The cue ball stops while its target continues forward with the speed v. C. The cue ball and target ball roll forward together with a speed < ...
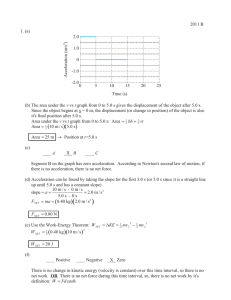
2011 B 1. (a) 2.0 0
... error of up to 10 m). To calculate au the equation x u = x 0 + v 0 t u + 12 au t u , where x0 is zero (the starting line), v0 is zero (the runner starts from rest), and x is the position that corresponds to time tu. Method two would calculate the magnitude of the average velocity for every 10 m that ...
... error of up to 10 m). To calculate au the equation x u = x 0 + v 0 t u + 12 au t u , where x0 is zero (the starting line), v0 is zero (the runner starts from rest), and x is the position that corresponds to time tu. Method two would calculate the magnitude of the average velocity for every 10 m that ...
Chapter 4
... Energy = work done To have one joule of energy, I must do 1 joule of work to raise the object. The units of work are also joules. The force of gravity is mass times the acceleration of gravity ...
... Energy = work done To have one joule of energy, I must do 1 joule of work to raise the object. The units of work are also joules. The force of gravity is mass times the acceleration of gravity ...
abstract Materials Marwan abstract
... products (geopolymers) through geopolymerization. The goal is to produce low cost construction materials for green housing. The produced construction materials are characterized by high strength, high heat resistance, low production cost, low energy consumption, and low CO2 emissions. The results ha ...
... products (geopolymers) through geopolymerization. The goal is to produce low cost construction materials for green housing. The produced construction materials are characterized by high strength, high heat resistance, low production cost, low energy consumption, and low CO2 emissions. The results ha ...