Work - TeacherWeb
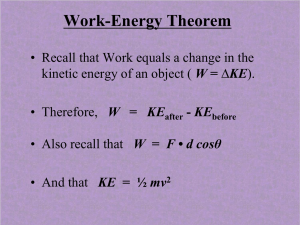
... When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of ...
... When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of ...
energy diagrams
... c) At what value of x is the kinetic energy of the particle a maximum? d) What is the force on the particle when it is at point C? ...
... c) At what value of x is the kinetic energy of the particle a maximum? d) What is the force on the particle when it is at point C? ...
Lecture 6
... Work & Energy • A box sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface runs into a fixed spring, compressing it a distance x1 from its relaxed position while momentarily coming to rest. – If the initial speed of the box were doubled and its mass were halved, how far x2 would the ...
... Work & Energy • A box sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface runs into a fixed spring, compressing it a distance x1 from its relaxed position while momentarily coming to rest. – If the initial speed of the box were doubled and its mass were halved, how far x2 would the ...
6-1,2,3
... object of mass m has by virtue of its position relative to the surface of the earth. That position is measured by the height h of the object relative to an arbitrary zero level: ...
... object of mass m has by virtue of its position relative to the surface of the earth. That position is measured by the height h of the object relative to an arbitrary zero level: ...
Mechanics & Molecular Kinetic Theory
... • 6.02x1023 particles in 1 mole • e.g. 1 mole of He has a mass of 4 grams 1 mole of O2 has a mass of 32 grams Mass (g) = number of moles x molar mass ...
... • 6.02x1023 particles in 1 mole • e.g. 1 mole of He has a mass of 4 grams 1 mole of O2 has a mass of 32 grams Mass (g) = number of moles x molar mass ...
Work and kinetic energy
... W = ΔKE = - ΔPE => (KE2 - KE1) = - (PE2 - PE1) => (KE1 + PE1) = (KE2 + PE2) • E = KE + PE has the same value throughout the motion • E is "total mechanical energy" ...
... W = ΔKE = - ΔPE => (KE2 - KE1) = - (PE2 - PE1) => (KE1 + PE1) = (KE2 + PE2) • E = KE + PE has the same value throughout the motion • E is "total mechanical energy" ...
Slide 1
... Bond energies are the amount of energy given off when bonds are formed, or the amount of energy used when bonds are broken. Bond energies deal with reactants and products in their gaseous state ...
... Bond energies are the amount of energy given off when bonds are formed, or the amount of energy used when bonds are broken. Bond energies deal with reactants and products in their gaseous state ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 1 Notes
... Work/Kinetic Energy Theorem: Wnet = Fnet s = m a s = m (v2 –v02)/2 Ekin = m v2/2 is called the kinetic energy of an object. {Net Work done on an object} ...
... Work/Kinetic Energy Theorem: Wnet = Fnet s = m a s = m (v2 –v02)/2 Ekin = m v2/2 is called the kinetic energy of an object. {Net Work done on an object} ...
Work and Power - reynardearthsci
... No. He could carry around that tray all day and according to physics he wouldn’t be doing any work. There is a force (the waiter pushes up on the tray) and there is a displacement (the tray is moved horizontally across the room). Yet the force does not cause the displacement. To cause a displacement ...
... No. He could carry around that tray all day and according to physics he wouldn’t be doing any work. There is a force (the waiter pushes up on the tray) and there is a displacement (the tray is moved horizontally across the room). Yet the force does not cause the displacement. To cause a displacement ...
Gravitational Potential Energy (PE)
... At pt.A, the reference level is the At pt.B, the reference level is the At pt.C, the reference level is the They all have a value of zero for Potential Energy. (PE = 0) ...
... At pt.A, the reference level is the At pt.B, the reference level is the At pt.C, the reference level is the They all have a value of zero for Potential Energy. (PE = 0) ...
5.1,2 Work and Energy Theorem. Work has different meaning in physics.
... Thus, in any isolated system of objects the nonconservative forces. changing. The equation above shows that the interacting only through gravitational force, the ...
... Thus, in any isolated system of objects the nonconservative forces. changing. The equation above shows that the interacting only through gravitational force, the ...
Chapter 19 Outline The First Law of Thermodynamics - Help-A-Bull
... • It is crucially important to indicate who/what is doing the work and who/what the work is done upon. ...
... • It is crucially important to indicate who/what is doing the work and who/what the work is done upon. ...
KE - baier10physics
... An 875.0-kg car speeds up from 22.0 m/s to 44.0 m/s while passing another car. What are its initial and final energies? How much work is done on the car to increase its speed? ...
... An 875.0-kg car speeds up from 22.0 m/s to 44.0 m/s while passing another car. What are its initial and final energies? How much work is done on the car to increase its speed? ...
thermochem-prob-solns
... energy of the system. U is the change in internal energy of system. It is a state function. q- heat energy absorbed (q is positive) or given off (q is negative) by the system. w- work done by the system(w is negative) on its surroundings or done on the system(w is positive) by its surroundings. Ex ...
... energy of the system. U is the change in internal energy of system. It is a state function. q- heat energy absorbed (q is positive) or given off (q is negative) by the system. w- work done by the system(w is negative) on its surroundings or done on the system(w is positive) by its surroundings. Ex ...
The history of thoughta and science
... guardian of propriety, ensuring that causality causes only legitimate actions because energy is conserved. Newton’s second law proves the fact that total energy is constant. The conservation of energy is related with the symmetry of spacetime. Heat is energy transferred between two objects as a resu ...
... guardian of propriety, ensuring that causality causes only legitimate actions because energy is conserved. Newton’s second law proves the fact that total energy is constant. The conservation of energy is related with the symmetry of spacetime. Heat is energy transferred between two objects as a resu ...
Work, Energy and Power
... Work, Energy and Power (A) Work and energy In physics, work is done when a force exerts on an object over a displacement. It is defined in the following way: Work = Force in the direction of displacement × Displacement W = F// × s The Sl unit of work is J (joule) or N m. 1 J of work is done whenever ...
... Work, Energy and Power (A) Work and energy In physics, work is done when a force exerts on an object over a displacement. It is defined in the following way: Work = Force in the direction of displacement × Displacement W = F// × s The Sl unit of work is J (joule) or N m. 1 J of work is done whenever ...