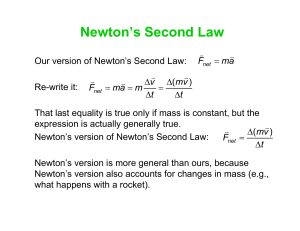
Document
... filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to an empty flask. When the stopcock between them is opened, the br ...
... filling its container. A gas that already fills its container does not collect spontaneously in a small region of the container. A glass cylinder containing a brown gas (upper piece of glassware in the left illustration) is attached to an empty flask. When the stopcock between them is opened, the br ...
Explaining motion - Delivery guide
... mass with weight in common usage should be easy enough to deal with, but the profusion of closely-related terms – work, force, energy, power, distance, displacement, speed, velocity and so on – can cause problems if not clarified. It is important here to make sure that learners understand the relati ...
... mass with weight in common usage should be easy enough to deal with, but the profusion of closely-related terms – work, force, energy, power, distance, displacement, speed, velocity and so on – can cause problems if not clarified. It is important here to make sure that learners understand the relati ...
Friction - e
... That is, weight of the object = perpendicular reaction force. This activity shows that the limiting frictional force increases when the normal reaction between the two forces increases. The above activities show that the limiting frictional force depends on the nature of the contact surfaces and th ...
... That is, weight of the object = perpendicular reaction force. This activity shows that the limiting frictional force increases when the normal reaction between the two forces increases. The above activities show that the limiting frictional force depends on the nature of the contact surfaces and th ...
Chapter 19, part II Notes
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
... Equilibrium Reactions LeChatelier’s Principle Equilibrium Constants ...
Chapter 8
... as we might also have derived from the equations of Table 2-1 (particularly Eq. 2-16). The fact that the answer is independent of mass means that the answer to part (b) is identical to that of part (a), that is, v 12.9 m/s . (c) If Ki 0 , then we find Kf = mgh + Ki (where Ki is necessarily posit ...
... as we might also have derived from the equations of Table 2-1 (particularly Eq. 2-16). The fact that the answer is independent of mass means that the answer to part (b) is identical to that of part (a), that is, v 12.9 m/s . (c) If Ki 0 , then we find Kf = mgh + Ki (where Ki is necessarily posit ...
Sliding Friction
... Example (easy): A block of wood sits on a table. If the coefficient of friction is 0.34 and the block weighs 20 N, what is the force of friction? ...
... Example (easy): A block of wood sits on a table. If the coefficient of friction is 0.34 and the block weighs 20 N, what is the force of friction? ...
Chapter 8
... 16. We place the reference position for evaluating gravitational potential energy at the relaxed position of the spring. We use x for the spring's compression, measured positively downwards (so x > 0 means it is compressed). ...
... 16. We place the reference position for evaluating gravitational potential energy at the relaxed position of the spring. We use x for the spring's compression, measured positively downwards (so x > 0 means it is compressed). ...
Ch 8 LAN 7th Intro Chem Gases Liquids and Solids
... 1. The ideal gas consists of hypothetical particles moving perfectly at random with no attractive forces between them 2. The volume of the ideal gas particle is insignificant compared with the volume of its container 3. The average kinetic energy of ideal gas particles is proportional to the Kelvin ...
... 1. The ideal gas consists of hypothetical particles moving perfectly at random with no attractive forces between them 2. The volume of the ideal gas particle is insignificant compared with the volume of its container 3. The average kinetic energy of ideal gas particles is proportional to the Kelvin ...
Document
... equal net forces F. These net forces are applied for the same amount of time. After the net forces are removed: 1. The disks have the same momentum and kinetic energy. 2. The disks have equal momentum; disk A has more kinetic energy. 3. The disks have equal momentum; disk B has more kinetic energy. ...
... equal net forces F. These net forces are applied for the same amount of time. After the net forces are removed: 1. The disks have the same momentum and kinetic energy. 2. The disks have equal momentum; disk A has more kinetic energy. 3. The disks have equal momentum; disk B has more kinetic energy. ...
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
... One is a forward force of 1140 N provided by traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work–kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to reach 2.0 m/s. 3. A 2.1 × 103 kg car starts from ...
... One is a forward force of 1140 N provided by traction between the wheels and the road. The other is a 950 N resistive force due to various frictional forces. Use the work–kinetic energy theorem to determine how far the car must travel for its speed to reach 2.0 m/s. 3. A 2.1 × 103 kg car starts from ...
Booklet I
... This booklet is a self- contained text to cover the topics in mechanics required in Hong Kong Physics Olympiad (HKPhO). It is written in a style that is probably quite different from the normal textbooks, and is intended for those students who wish to explore outside the scope of normal senior secon ...
... This booklet is a self- contained text to cover the topics in mechanics required in Hong Kong Physics Olympiad (HKPhO). It is written in a style that is probably quite different from the normal textbooks, and is intended for those students who wish to explore outside the scope of normal senior secon ...
Equilibrium and Elasticity
... • Work can be positive (work in) or negative (work out) • We are, for now, ignoring heat. • Thermal energy is…special. When energy changes to thermal energy, this change is irreversible. ...
... • Work can be positive (work in) or negative (work out) • We are, for now, ignoring heat. • Thermal energy is…special. When energy changes to thermal energy, this change is irreversible. ...
Chapter 8—Conservation of Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A single
... 52. Objects A and B, of mass M and 2M respectively, are each pushed a distance d straight up an inclined plane by a force F parallel to the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between each mass and the plane has the same value k. At the highest point, a. KA = Fd = KB. b. KA = (F kMg cos) ...
... 52. Objects A and B, of mass M and 2M respectively, are each pushed a distance d straight up an inclined plane by a force F parallel to the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between each mass and the plane has the same value k. At the highest point, a. KA = Fd = KB. b. KA = (F kMg cos) ...
Study Guide Chapter 16: The Process of Chemical Reactions
... a. The concentration of H2O is increased by the addition of more H2O. (1) Using Le Châtelier's Principle, we predict that the system will shift to more products to partially counteract the increase in H2O. (2) The increase in the concentration of water vapor speeds the forward reaction without i ...
... a. The concentration of H2O is increased by the addition of more H2O. (1) Using Le Châtelier's Principle, we predict that the system will shift to more products to partially counteract the increase in H2O. (2) The increase in the concentration of water vapor speeds the forward reaction without i ...
2.2 Some Common Speeds
... Since acceleration is defined in terms of velocity, a body travelling at constant speed but with a constantly changing _____________ is defined as having an acceleration. So a cyclist travelling around a corner at constant speed is, in fact, _____________________ ! (More of this later). For an accel ...
... Since acceleration is defined in terms of velocity, a body travelling at constant speed but with a constantly changing _____________ is defined as having an acceleration. So a cyclist travelling around a corner at constant speed is, in fact, _____________________ ! (More of this later). For an accel ...