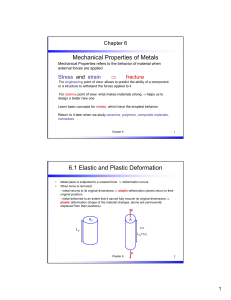
Mechanical Properties of Metals
... original position) - metal deformed to an extent that it cannot fully recover its original dimensions ⇒ plastic deformation (shape of the material changes, atoms are permanently displaced from their positions) ...
... original position) - metal deformed to an extent that it cannot fully recover its original dimensions ⇒ plastic deformation (shape of the material changes, atoms are permanently displaced from their positions) ...
Work and Energy
... If the initial position is the position of zero spring deformation so that x1=0, then the work is negative for any final position x2≠0.This is verified by recognizing that if the body begins at undeformed spring position and then moves to the right, the spring force is to the left; if the body begi ...
... If the initial position is the position of zero spring deformation so that x1=0, then the work is negative for any final position x2≠0.This is verified by recognizing that if the body begins at undeformed spring position and then moves to the right, the spring force is to the left; if the body begi ...
Lecture 10
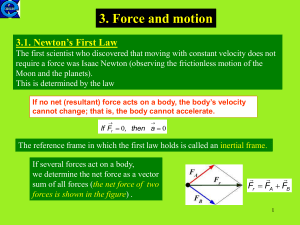
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
Glossary
... Energy [J]: Capacity for performing work or to cause heat flow. Like work itself, it is measured in Joules. End-quench hardenability test: A laboratory procedure for determining the hardenability of a steel or other ferrous alloy; widely referred to as the Jominy test. Hardenability is determined by ...
... Energy [J]: Capacity for performing work or to cause heat flow. Like work itself, it is measured in Joules. End-quench hardenability test: A laboratory procedure for determining the hardenability of a steel or other ferrous alloy; widely referred to as the Jominy test. Hardenability is determined by ...
Newton*s 1st Law * Objectives:
... 5. Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the resultant vector. ...
... 5. Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the resultant vector. ...
Appendix I
... of things. Gravity is a force, and it is shared by all objects in the universe. It causes the planets to move in orbits around the sun and a dropped book to fall to the floor. There are many other forces (electric, magnetic, friction, etc.); for each force there is an associated work and an associat ...
... of things. Gravity is a force, and it is shared by all objects in the universe. It causes the planets to move in orbits around the sun and a dropped book to fall to the floor. There are many other forces (electric, magnetic, friction, etc.); for each force there is an associated work and an associat ...
Revision
... A billiard ball strikes the smooth cushion of a billiard table at an angle and rebounds with the same speed. (ii) A rocket rises vertically upward during launching in the atmosphere near the earth’s surface. (iii) A radioactive nucleus emits an -particle. (3 marks) (b) A ball of mass m1 moving with ...
... A billiard ball strikes the smooth cushion of a billiard table at an angle and rebounds with the same speed. (ii) A rocket rises vertically upward during launching in the atmosphere near the earth’s surface. (iii) A radioactive nucleus emits an -particle. (3 marks) (b) A ball of mass m1 moving with ...
Lecture 16 - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... mechanical energy of the system is not constant • The work done by all nonconservative forces acting on parts of a system equals the change in the mechanical energy of the system ...
... mechanical energy of the system is not constant • The work done by all nonconservative forces acting on parts of a system equals the change in the mechanical energy of the system ...
Elastic Potential Energy Practice
... b) Find the (instantaneous) velocity of the ball once the spring in the gun is released. c) What will be the maximum height hmax of the ball? d) Which of the following actions, if done independently, would increase the maximum height reached by the ball? Briefly explain your reasoning for any and al ...
... b) Find the (instantaneous) velocity of the ball once the spring in the gun is released. c) What will be the maximum height hmax of the ball? d) Which of the following actions, if done independently, would increase the maximum height reached by the ball? Briefly explain your reasoning for any and al ...