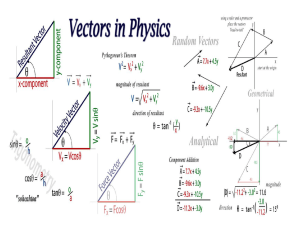
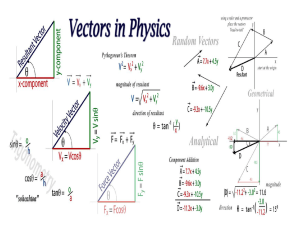
Discussion 8
... is used with an appropriate fulcrum or pivot point to multiply the mechanical force that can be applied to another object. A lever has a long and a short arm. The short arm creates large forces but moves short distances. (Short arm force)*(Short arm distance) = (Long arm force)*(Long arm distance) W ...
... is used with an appropriate fulcrum or pivot point to multiply the mechanical force that can be applied to another object. A lever has a long and a short arm. The short arm creates large forces but moves short distances. (Short arm force)*(Short arm distance) = (Long arm force)*(Long arm distance) W ...
MATH 203 Lab 1 solutions Spring 2005
... ~ + OD ~ + OF ~ is (2) Let OABCDEFG be a cube, labelled as shown in the diagram below. Show that OB ...
... ~ + OD ~ + OF ~ is (2) Let OABCDEFG be a cube, labelled as shown in the diagram below. Show that OB ...
wbm-physics
... To stretch a spring 3.00 cm from its unstretched length, 12.0 J of work must be done. How much work must be done to compress this spring 4.00 cm from its ...
... To stretch a spring 3.00 cm from its unstretched length, 12.0 J of work must be done. How much work must be done to compress this spring 4.00 cm from its ...
MATH 2414 - Calculus II Units of Measurement and Some Applications
... Density, usually denoted by the Greek letter rho ( ρ ), is mass per volume, such as kg/m3 or slug/ft 3 . The€density of water is 1000 kg/m3. ...
... Density, usually denoted by the Greek letter rho ( ρ ), is mass per volume, such as kg/m3 or slug/ft 3 . The€density of water is 1000 kg/m3. ...
Mechatronics Presentation
... Cantilever beams are very structurally popular and can be found anywhere from pool diving boards to bridges ...
... Cantilever beams are very structurally popular and can be found anywhere from pool diving boards to bridges ...
The Laws of Motion
... Would a larger block accelerate as quickly with the same amount of force it took to move the first one? The answer is no – it would take more force to move the larger block at the same acceleration So there is an inverse relationship between acceleration and a property of the object called its “mass ...
... Would a larger block accelerate as quickly with the same amount of force it took to move the first one? The answer is no – it would take more force to move the larger block at the same acceleration So there is an inverse relationship between acceleration and a property of the object called its “mass ...
newton`s laws of motion
... • an object that is in motion will not change its velocity (uniform motion) unless an external, unbalanced, force acts upon it. An object continues doing whatever it happens to be doing unless a force (unbalanced) is exerted upon it. If it is at rest, it continues in a state of rest. On a book lying ...
... • an object that is in motion will not change its velocity (uniform motion) unless an external, unbalanced, force acts upon it. An object continues doing whatever it happens to be doing unless a force (unbalanced) is exerted upon it. If it is at rest, it continues in a state of rest. On a book lying ...