Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
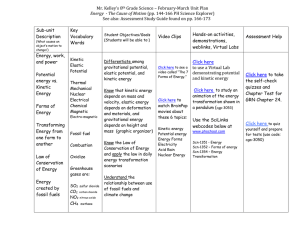
... Differentiate among gravitational potential, elastic potential, and kinetic energy Know that kinetic energy depends on mass and velocity, elastic energy depends on deformation and materials, and gravitational energy depends on height and mass (graphic organizer) Know the Law of Conservation of Energ ...
... Differentiate among gravitational potential, elastic potential, and kinetic energy Know that kinetic energy depends on mass and velocity, elastic energy depends on deformation and materials, and gravitational energy depends on height and mass (graphic organizer) Know the Law of Conservation of Energ ...
Energy and Power Test Study Guide – answer key
... 3. A person is using a force of 300N to push a cart. How much power does the person need to push the cart a distance of 5m in 20s? 75 watts (Power = Work ÷ time) 4. In competition, weightlifter 1 lifts 150 kg weight from the floor. Weightlifter 2 also lifts 150kg weight to the same height above the ...
... 3. A person is using a force of 300N to push a cart. How much power does the person need to push the cart a distance of 5m in 20s? 75 watts (Power = Work ÷ time) 4. In competition, weightlifter 1 lifts 150 kg weight from the floor. Weightlifter 2 also lifts 150kg weight to the same height above the ...
Energy and Power Test Study Guide – answer key
... 3. A person is using a force of 300N to push a cart. How much power does the person need to push the cart a distance of 5m in 20s? 75 watts (Power = Work ÷ time) 4. In competition, weightlifter 1 lifts 150 kg weight from the floor. Weightlifter 2 also lifts 150kg weight to the same height above the ...
... 3. A person is using a force of 300N to push a cart. How much power does the person need to push the cart a distance of 5m in 20s? 75 watts (Power = Work ÷ time) 4. In competition, weightlifter 1 lifts 150 kg weight from the floor. Weightlifter 2 also lifts 150kg weight to the same height above the ...
Mechanical Energy
... • Make sure there are only conservative forces and kinetic energy in the problem • Identify all the potential and kinetic energy at the beginning • Identify all the potential and kinetic energy at the end • Set the initial and final energy equal to one another ...
... • Make sure there are only conservative forces and kinetic energy in the problem • Identify all the potential and kinetic energy at the beginning • Identify all the potential and kinetic energy at the end • Set the initial and final energy equal to one another ...
Answers
... Prove it. I have a marble with a mass of .0032 kg. It rolls down a ramp at a speed of 2.4 m/s. How much kinetic energy does my marble possess? Show your work. Include your unit! KE = (.5) x (.0032 kg) x (2.4 m/s2) .0092 J A roller coaster cart with a mass of 500 kg is speeding down the track at 53 m ...
... Prove it. I have a marble with a mass of .0032 kg. It rolls down a ramp at a speed of 2.4 m/s. How much kinetic energy does my marble possess? Show your work. Include your unit! KE = (.5) x (.0032 kg) x (2.4 m/s2) .0092 J A roller coaster cart with a mass of 500 kg is speeding down the track at 53 m ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy
... Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change. Energy can be the ability to do work (potential energy) or the energy it has due to its motion (kinetic energy). Kinetic Energy (KE) or the energy of motion (kine = motion in Greek) is determined by the mass of the object and its velocity ...
... Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change. Energy can be the ability to do work (potential energy) or the energy it has due to its motion (kinetic energy). Kinetic Energy (KE) or the energy of motion (kine = motion in Greek) is determined by the mass of the object and its velocity ...
P2 definitions quiz. - New College Leicester
... The maximum speed an object can reach. This can be changed by producing a non-zero resultant force (often by increasing / reducing the resistance). Terminal velocity ...
... The maximum speed an object can reach. This can be changed by producing a non-zero resultant force (often by increasing / reducing the resistance). Terminal velocity ...
Quest:
... The amount of energy an object has because of its location is dependent on the mass of the object, times the acceleration due to gravity at that point (for us, almost always -9.8 m/s2), times the height from which it can fall from. The object is said to have Potential Energy, or PE, because it could ...
... The amount of energy an object has because of its location is dependent on the mass of the object, times the acceleration due to gravity at that point (for us, almost always -9.8 m/s2), times the height from which it can fall from. The object is said to have Potential Energy, or PE, because it could ...
Work Energy KE PPT from class
... The Work Energy Theorem And so what we really have is called the WORK-ENERGY THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! ...
... The Work Energy Theorem And so what we really have is called the WORK-ENERGY THEOREM. It basically means that if we impart work to an object it will undergo a CHANGE in speed and thus a change in KINETIC ENERGY. Since both WORK and KINETIC ENERGY are expressed in JOULES, they are EQUIVALENT TERMS! ...
Energy and Forces
... During this unit, we will address the following Maine Learning Results: D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or d ...
... During this unit, we will address the following Maine Learning Results: D3h Describe several different types of energy forms including heat energy, chemical energy, and mechanical energy D3i Use examples of energy transformations from one form to another to explain that energy cannot be created or d ...
ME, PE, and KE part 2 - Kleins
... Therefore, the Kinetic energy formula uses both mass and velocity ...
... Therefore, the Kinetic energy formula uses both mass and velocity ...
Questions - TTU Physics
... State the Principle of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. You may supplement the sentences with equations if you explain what each symbols in the equations means. ...
... State the Principle of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. You may supplement the sentences with equations if you explain what each symbols in the equations means. ...
5.2 Physics section 5.2
... because of its position, shape, or condition of the object. Types of potential energy 1. Gravitational – due to its position in a gravitational ...
... because of its position, shape, or condition of the object. Types of potential energy 1. Gravitational – due to its position in a gravitational ...
Link-2
... explain how the improvement to performance was attained. Presentation [12 minutes maximum] 1. Each group member is to present for approximately 3-4 minutes on ONE of the following topics: #1 Forces & Motion: analyze forces causing acceleration. Use real data from the Speed Chek’R, or video footage ( ...
... explain how the improvement to performance was attained. Presentation [12 minutes maximum] 1. Each group member is to present for approximately 3-4 minutes on ONE of the following topics: #1 Forces & Motion: analyze forces causing acceleration. Use real data from the Speed Chek’R, or video footage ( ...























