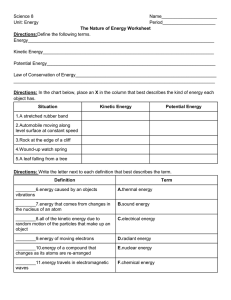
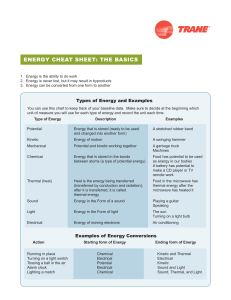
Name Date Energy in One Form or Another ENERGY
... 3. What happened to the kinetic energy of a moving automobile that was moving and stopped? What happens to the energy in sound waves from a radio when the sound is turned off? What happened to the kinetic energy of a pendulum bob as it slowed down and came to rest? ...
... 3. What happened to the kinetic energy of a moving automobile that was moving and stopped? What happens to the energy in sound waves from a radio when the sound is turned off? What happened to the kinetic energy of a pendulum bob as it slowed down and came to rest? ...
Unit 6 Mechanical Principles and Applications
... In the first diagram a mass is raised on a pulley. Work is done and the energy of the mass increases. This energy is stored in the mass as potential energy. In the second diagram a truck is accelerated along a surface. A force is needed to do this and work is done. The energy used to accelerate the ...
... In the first diagram a mass is raised on a pulley. Work is done and the energy of the mass increases. This energy is stored in the mass as potential energy. In the second diagram a truck is accelerated along a surface. A force is needed to do this and work is done. The energy used to accelerate the ...
$doc.title
... You toss a ball (mass = 140 g) straight up into the air. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 10 m/s, at a height of 1.5 meters above the ground, such that the initial position ve ...
... You toss a ball (mass = 140 g) straight up into the air. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 10 m/s, at a height of 1.5 meters above the ground, such that the initial position ve ...
End-semester Examination 2013 Mechanics (PHY102A/N
... (b) Einstein’s theory of relativity is valid for high speeds, but not for small speeds.! (c) √ According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, no particle can have velocity greater than speed of light.! (d) √ Time interval between two events remains invariant under Galilean transformation.! 3. Which ...
... (b) Einstein’s theory of relativity is valid for high speeds, but not for small speeds.! (c) √ According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, no particle can have velocity greater than speed of light.! (d) √ Time interval between two events remains invariant under Galilean transformation.! 3. Which ...
Energy & Power
... • The total mechanical energy of an object or group of objects is ME = KE + PE • If there is no friction, then ME is conserved: MEi = MEf KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf ½mvi2 + mghi = ½mvf2 + mghf (PEelastic = 0) ...
... • The total mechanical energy of an object or group of objects is ME = KE + PE • If there is no friction, then ME is conserved: MEi = MEf KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf ½mvi2 + mghi = ½mvf2 + mghf (PEelastic = 0) ...
Exercises
... However, this change in momentum results in an extreme change in velocity for the bug and a negligible change in velocity for the bus. The collision would be more damaging if the cars bounced off of each other. This is a greater change in velocity and momentum and therefore a greater danger to the p ...
... However, this change in momentum results in an extreme change in velocity for the bug and a negligible change in velocity for the bus. The collision would be more damaging if the cars bounced off of each other. This is a greater change in velocity and momentum and therefore a greater danger to the p ...
Notes 5.1: Work and Kinetic Energy - Physics Honors I
... Energy can be transformed from one type to another and transferred from one object to another, but the total amount is always the same. Energy is conserved. ...
... Energy can be transformed from one type to another and transferred from one object to another, but the total amount is always the same. Energy is conserved. ...
Energy lab Day 8 KEY
... 1. What is the Law of Conservation of Energy? The energy neither can be created nor destroyed _______________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the units of work, kinetic energy and potential energy? joule ____________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is the Law of Conservation of Energy? The energy neither can be created nor destroyed _______________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the units of work, kinetic energy and potential energy? joule ____________________________________________________________ ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
... Example : Find the kinetic energy of a 400-kg car moving with a speed of 10 m/s. Solution : K.E. = 1/2 . m . v2 = 1/2 . 400 . 100 = 20000j Work-Energy Theorem : Work is change I n kinetic energy. If work is done on an object its the amount of work. W = K.E. ...
... Example : Find the kinetic energy of a 400-kg car moving with a speed of 10 m/s. Solution : K.E. = 1/2 . m . v2 = 1/2 . 400 . 100 = 20000j Work-Energy Theorem : Work is change I n kinetic energy. If work is done on an object its the amount of work. W = K.E. ...
Cochise College
... A 4.60 kg bowling ball is suspended from the ceiling as a simple pendulum by a cable. If the pendulum is 6.00 m long and is pulled back until the cable makes an angle of 42 with the vertical, calculate: (a) the potential energy of the bowling ball (b) the maximum kinetic energy that it will develop ...
... A 4.60 kg bowling ball is suspended from the ceiling as a simple pendulum by a cable. If the pendulum is 6.00 m long and is pulled back until the cable makes an angle of 42 with the vertical, calculate: (a) the potential energy of the bowling ball (b) the maximum kinetic energy that it will develop ...
Work and Energy - IES Guillermina Brito
... The law of conservation of energy is an empirical law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time. In mechanics, conservation of energy is usually stated as ...
... The law of conservation of energy is an empirical law of physics. It states that the total amount of energy in an isolated system remains constant over time. In mechanics, conservation of energy is usually stated as ...
Review
... 15. A moving car has kinetic energy. If it speeds up until it is going 3 times the original speed, how much kinetic energy does it have compared to the original? ...
... 15. A moving car has kinetic energy. If it speeds up until it is going 3 times the original speed, how much kinetic energy does it have compared to the original? ...
Document
... 2. Students will describe how work is affected by the angle of the force. 3. Students will explain the relationship of work and the change in energy. 4. Students will compare and contrast conservative and non-conservative forces. ...
... 2. Students will describe how work is affected by the angle of the force. 3. Students will explain the relationship of work and the change in energy. 4. Students will compare and contrast conservative and non-conservative forces. ...
Problem 1. An unstable Pu-‐240 nucleus (mass
... You toss a ball (mass = 140 g) straight up into the air. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 10 m/s, at a height of 1.5 meters above the ground, such that the initial position ve ...
... You toss a ball (mass = 140 g) straight up into the air. The ball leaves your hand with a speed of 10 m/s, at a height of 1.5 meters above the ground, such that the initial position ve ...
Learning goals: Draw a picture that explains potential energy Draw
... Draw a picture that explains potential energy Draw a picture that explains kinetic energy Write an explanation of “conservation of energy” in your own words with pictures Note: When I say “conservation of energy”, I’m really talking about conservation of mechanical energy here. Background: The ...
... Draw a picture that explains potential energy Draw a picture that explains kinetic energy Write an explanation of “conservation of energy” in your own words with pictures Note: When I say “conservation of energy”, I’m really talking about conservation of mechanical energy here. Background: The ...