Work and Energy
... converted in “internal energy” (e.g.: Heat) of the system and it can not be directly converted to work. ...
... converted in “internal energy” (e.g.: Heat) of the system and it can not be directly converted to work. ...
2nd Term Exam - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... of which 50J was spent to change the box’s kinetic energy, and the remainder was spent to overcome friction. 10. If you push twice as hard against a stationary brick wall, the amount of work you do a) doubles b) is cut in half c) remains constant but non-zero d) remains constant at zero Solution: Si ...
... of which 50J was spent to change the box’s kinetic energy, and the remainder was spent to overcome friction. 10. If you push twice as hard against a stationary brick wall, the amount of work you do a) doubles b) is cut in half c) remains constant but non-zero d) remains constant at zero Solution: Si ...
1. Trying to break down a door, a man pushes futilely against it with
... b) If the child is actually moving at 3.0 m/s at the lowest point, how much energy has been lost to dissipative forces? (Wnc = 71 J) 29. A skier starts from rest at the top of a 45 m hill. He skis down a 30 degree incline into a valley, then up a 40 m hill. Ignore friction. a) What is the skier’s sp ...
... b) If the child is actually moving at 3.0 m/s at the lowest point, how much energy has been lost to dissipative forces? (Wnc = 71 J) 29. A skier starts from rest at the top of a 45 m hill. He skis down a 30 degree incline into a valley, then up a 40 m hill. Ignore friction. a) What is the skier’s sp ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Kinetic 7. The car is speeding down the highway. What type of energy is found in the speeding car? ...
... Kinetic 7. The car is speeding down the highway. What type of energy is found in the speeding car? ...
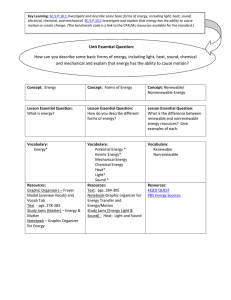
Energy Curriculum Map
... electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources available for the standard.) ...
... electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources available for the standard.) ...
Energy is.. - mjburns.net
... – Sound (energy in vibrations) – Chemical (energy stored in molecular bonds) ...
... – Sound (energy in vibrations) – Chemical (energy stored in molecular bonds) ...
Mechanical Energy - Bibb County Schools
... A 0.06 kg tennis ball starts to fall from a height of 2.9m. What was its gravitational potential energy at that height? GPE = mgh GPE = (0.06)(10)(2.9) GPE = 1.74J ...
... A 0.06 kg tennis ball starts to fall from a height of 2.9m. What was its gravitational potential energy at that height? GPE = mgh GPE = (0.06)(10)(2.9) GPE = 1.74J ...
Ch05 Energy
... Most forms of energy can be converted from one type to another. Law of the Conservation of Energy - states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It simply changes from one form into another Einstein’s theory of Relativity - E = mc2 a small amount of mass can be changed directly into a tremen ...
... Most forms of energy can be converted from one type to another. Law of the Conservation of Energy - states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It simply changes from one form into another Einstein’s theory of Relativity - E = mc2 a small amount of mass can be changed directly into a tremen ...
Unit 4 Notetakers
... ______________________ of the path the object takes between the 2 points. (The work done depends only on the initial and final positions.) ...
... ______________________ of the path the object takes between the 2 points. (The work done depends only on the initial and final positions.) ...
Potential Energy and Conservation of Mechanical Energy
... A force is conservative if the work done by it on a particle that moves between two points depends only on these points and not on the path followed. A force is nonconservative if the work done by it on a particle that moves between two points depends on the path taken between these two points. The ...
... A force is conservative if the work done by it on a particle that moves between two points depends only on these points and not on the path followed. A force is nonconservative if the work done by it on a particle that moves between two points depends on the path taken between these two points. The ...
Physical Science Chapter 5 Energy & Power 5.1 The Nature of Energy
... • Most forms of energy can be converted from one type to another. • Law of the Conservation of Energy - states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It simply changes from one form into another • Einstein’s theory of Relativity - E = mc2 • a small amount of mass can be changed directly into a ...
... • Most forms of energy can be converted from one type to another. • Law of the Conservation of Energy - states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It simply changes from one form into another • Einstein’s theory of Relativity - E = mc2 • a small amount of mass can be changed directly into a ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... The mechanical energy does not change because the loss in potential energy is simply transferred into kinetic energy. The energy in the system remains constant!! ...
... The mechanical energy does not change because the loss in potential energy is simply transferred into kinetic energy. The energy in the system remains constant!! ...
Chapter 7
... Work W is energy transferred to or from an object by means of a force acting on the object. If the object is accelerated by applying a force, its kinetic energy K increases. Energy transferred to the object is positive work +W. If you decelerate the object by applying a force, you decrease its ...
... Work W is energy transferred to or from an object by means of a force acting on the object. If the object is accelerated by applying a force, its kinetic energy K increases. Energy transferred to the object is positive work +W. If you decelerate the object by applying a force, you decrease its ...
Chapter 15 –Energy
... Force, mass, work 18. Energy and work are measured in the SI unit called the Newton, joule, watt 19. If the ? of an object doubles, its KE doubles Mass, speed, velocity 20. Energy that is stored due to position or shape is called KE, PE, thermal energy 21. When a pole-vaulter flexes the pole, the po ...
... Force, mass, work 18. Energy and work are measured in the SI unit called the Newton, joule, watt 19. If the ? of an object doubles, its KE doubles Mass, speed, velocity 20. Energy that is stored due to position or shape is called KE, PE, thermal energy 21. When a pole-vaulter flexes the pole, the po ...
1 - Eickman
... The energy in the ball is changed into thermal energy because of friction with the air and floor. It is also changed into sound. ...
... The energy in the ball is changed into thermal energy because of friction with the air and floor. It is also changed into sound. ...
springs
... in the front-wheel suspension. If it is compressed 0.17 m when she hit a bump, how much energy does the front spring now store? PE = ½ k (∆x)2 PE = ½ (64 N/m)(0.17 m)2 PE = 0.925 J ...
... in the front-wheel suspension. If it is compressed 0.17 m when she hit a bump, how much energy does the front spring now store? PE = ½ k (∆x)2 PE = ½ (64 N/m)(0.17 m)2 PE = 0.925 J ...