physics powerpoint review 1st
... a horizontal force on the puck to keep it in motion. 5. Excluding the force due to air pressure, there is only one force acting on a book lying at rest on a tabletop. 6. If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle. 7. A quantity that has both ...
... a horizontal force on the puck to keep it in motion. 5. Excluding the force due to air pressure, there is only one force acting on a book lying at rest on a tabletop. 6. If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle. 7. A quantity that has both ...
Force and Newton` s Laws Study Guide
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
... 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the obj ...
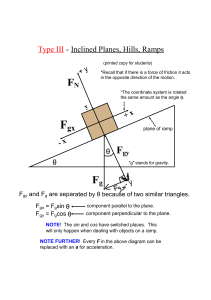
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
worksheet 4
... 3. Isaac Newton originated the idea of launching a satellite by blasting it vertically from a mountain top. 4. Most modern satellites are lifted to their desired orbiting heights by multistage rocket systems. 5. The speed necessary for a satellite to stay in a circular orbit is about 8 km/ s, or abo ...
... 3. Isaac Newton originated the idea of launching a satellite by blasting it vertically from a mountain top. 4. Most modern satellites are lifted to their desired orbiting heights by multistage rocket systems. 5. The speed necessary for a satellite to stay in a circular orbit is about 8 km/ s, or abo ...
Force and Motion {PowerPoint}
... • The learner will use equipment to measure time and distance so that the motion of the object can be determined. • The learner will use data collected to calculate the speed of an object. • The learner will explain the results of applying a force to an object. ...
... • The learner will use equipment to measure time and distance so that the motion of the object can be determined. • The learner will use data collected to calculate the speed of an object. • The learner will explain the results of applying a force to an object. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... A 10 kg object is subject to a net force of 25 N. What is the acceleration of the object in m/s2? The second law says a = F/m. Therefore a = 25 N /10 kg = 2.5 m/s2 If the object starts at rest, then how long will it be before its velocity is 25 m/s? You know that v = v0 + at and v0= 0. Rearranging g ...
... A 10 kg object is subject to a net force of 25 N. What is the acceleration of the object in m/s2? The second law says a = F/m. Therefore a = 25 N /10 kg = 2.5 m/s2 If the object starts at rest, then how long will it be before its velocity is 25 m/s? You know that v = v0 + at and v0= 0. Rearranging g ...
CCGPS Advanced Algebra
... object’s acceleration due to gravity (in feet per second per second), and h is the height of the object (in feet). On Earth, an object’s acceleration due to gravity is 32 ft/s2. From what height must a stone be dropped to reach a velocity of 128 ft/s at the moment it hits the ground? 2. The time it ...
... object’s acceleration due to gravity (in feet per second per second), and h is the height of the object (in feet). On Earth, an object’s acceleration due to gravity is 32 ft/s2. From what height must a stone be dropped to reach a velocity of 128 ft/s at the moment it hits the ground? 2. The time it ...
FY016_2012
... Sketch the vector force diagram, approximately to scale, clearly indicating the resultant force vector. (4 marks) ...
... Sketch the vector force diagram, approximately to scale, clearly indicating the resultant force vector. (4 marks) ...
Geophysical Methods: Refraction Seismology Critical and head
... migration clears this up so you can locate the fault properly ...
... migration clears this up so you can locate the fault properly ...
Practice test for final exam
... (practice and real ones). Understand all the formulas and concepts that were used in these exams. Re-use the three cheat cards you wrote, write three new ones or write your formulas on a 8x11.5 piece of paper. The final will probably consist of about 15 multiple choice and 15 longer questions. The m ...
... (practice and real ones). Understand all the formulas and concepts that were used in these exams. Re-use the three cheat cards you wrote, write three new ones or write your formulas on a 8x11.5 piece of paper. The final will probably consist of about 15 multiple choice and 15 longer questions. The m ...
An Alternative Analysis of the Probabilistic Seismic Hazard for Las Vegas Valley, Nevada 2014
... • 1400+ well logs • Sediment ranges from fine to coarse • Alluvial fans around basin • Interfingered grain sizes near LVVFS ...
... • 1400+ well logs • Sediment ranges from fine to coarse • Alluvial fans around basin • Interfingered grain sizes near LVVFS ...