
Day - Hamelinck
... When a soccer player kicks a ball on the ground, the horizontal forces acting on the ball are the applied push force, friction with the ground and air resistance. As long as the applied push force is greater in magnitude than the sum of the forces of friction and air resistance acting on the ball, t ...
... When a soccer player kicks a ball on the ground, the horizontal forces acting on the ball are the applied push force, friction with the ground and air resistance. As long as the applied push force is greater in magnitude than the sum of the forces of friction and air resistance acting on the ball, t ...
a p course audit
... 5. Use of inertial balance to measure the mass of unknown object. Which graph will plot and how will you use it? 6. Push a car with bathroom scales and measure acceleration to find mass of car. Find the coefficient of static and kinetic friction. 7. Force table to use to derive the law of parallelog ...
... 5. Use of inertial balance to measure the mass of unknown object. Which graph will plot and how will you use it? 6. Push a car with bathroom scales and measure acceleration to find mass of car. Find the coefficient of static and kinetic friction. 7. Force table to use to derive the law of parallelog ...
A P COURSE AUDIT
... 5. Use of inertial balance to measure the mass of unknown object. Which graph will plot and how will you use it? 6. Push a car with bathroom scales and measure acceleration to find mass of car. Find the coefficient of static and kinetic friction. 7. Force table to use to derive the law of parallelog ...
... 5. Use of inertial balance to measure the mass of unknown object. Which graph will plot and how will you use it? 6. Push a car with bathroom scales and measure acceleration to find mass of car. Find the coefficient of static and kinetic friction. 7. Force table to use to derive the law of parallelog ...
Newton`s Second Law
... 12 The cart’s speed increases smoothly during the time interval while the flag passes through the photogate beam. At some instant during that time interval the cart’s instantaneous speed equals the average speed for the interval. That instant of time is shown in the “Time (s)” column next to its ass ...
... 12 The cart’s speed increases smoothly during the time interval while the flag passes through the photogate beam. At some instant during that time interval the cart’s instantaneous speed equals the average speed for the interval. That instant of time is shown in the “Time (s)” column next to its ass ...
Unit 3 Problems
... examples of each. Name the four (?) forces and give examples of each. If you drop a rock, the earth's gravity accelerates it down. According to Newton #3, what happens to the earth? Does it really? If you're traveling on the interstate at constant speed, why does your engine have to keep pushing? Do ...
... examples of each. Name the four (?) forces and give examples of each. If you drop a rock, the earth's gravity accelerates it down. According to Newton #3, what happens to the earth? Does it really? If you're traveling on the interstate at constant speed, why does your engine have to keep pushing? Do ...
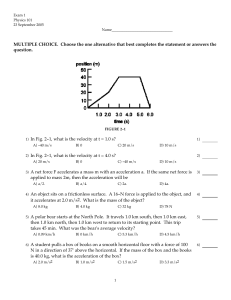
Exam 1
... A) Both its velocity and its acceleration are zero. B) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero. C) Neither its velocity nor its acceleration is zero. D) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero. ...
... A) Both its velocity and its acceleration are zero. B) Its velocity is zero and its acceleration is not zero. C) Neither its velocity nor its acceleration is zero. D) Its velocity is not zero and its acceleration is zero. ...
Grade 11 Physics – Homework 5 1. A skydiver of mass 80 kg falls
... A lamp of weight W is suspended by a wire fixed to the ceiling. With reference to Newton’s third law of motion, the force that is equal and opposite to W is the A. ...
... A lamp of weight W is suspended by a wire fixed to the ceiling. With reference to Newton’s third law of motion, the force that is equal and opposite to W is the A. ...
PHYSICS
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
Newton`s Laws Practice Problems
... the lunar plant match those being produced on the earth. Standard slotted masses are sent to the moon as well as a perfectly frictionless 10.0 kg block that can be slid along a horizontal table with zero frictional resistance. A stopwatch and a meter stick are sent as well. Lunar and earth laborator ...
... the lunar plant match those being produced on the earth. Standard slotted masses are sent to the moon as well as a perfectly frictionless 10.0 kg block that can be slid along a horizontal table with zero frictional resistance. A stopwatch and a meter stick are sent as well. Lunar and earth laborator ...
Newton`s Laws webquest
... 6. In your own words, explain a “Normal Force”… _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Provide 5 examples of “Normal Forces” in your school, classroom, home, etc. ____________________________________ ...
... 6. In your own words, explain a “Normal Force”… _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Provide 5 examples of “Normal Forces” in your school, classroom, home, etc. ____________________________________ ...
Forces
... An object will remain stationary or continue at constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force. i.e. if forces are balanced an object will remain stationary or move at constant velocity. ...
... An object will remain stationary or continue at constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force. i.e. if forces are balanced an object will remain stationary or move at constant velocity. ...
Wksht Momentum and Collisions
... 2. An ivory ball of mass 100 g is moving at a velocity of 20 cm/s to the right. It collides with a second ball with a mass of 200 g, which is moving at 10 cm/s to the right. After the collision, the first ball is slowed to 5 cm/s to the right, what is the final velocity of the second ball? 3. A 5 kg ...
... 2. An ivory ball of mass 100 g is moving at a velocity of 20 cm/s to the right. It collides with a second ball with a mass of 200 g, which is moving at 10 cm/s to the right. After the collision, the first ball is slowed to 5 cm/s to the right, what is the final velocity of the second ball? 3. A 5 kg ...
Forces and the Universe Unit Review: Weight [N] = 4.44 x Weight
... 1. What are mass and weight? How are they different? Mass is the amount of matter in something and is measured in [kg]. Weight is the force of gravity acting on something and is measured in [N]. 2. List three ways to accelerate. Speed up, slow down, and change direction. 3. List two ways not to acce ...
... 1. What are mass and weight? How are they different? Mass is the amount of matter in something and is measured in [kg]. Weight is the force of gravity acting on something and is measured in [N]. 2. List three ways to accelerate. Speed up, slow down, and change direction. 3. List two ways not to acce ...
Practice Test - Manhasset Public Schools
... 25. On the diagram, use a ruler and protractor to construct a vector representing the velocity of the river current. Use a scale of 1.0 centimeter = 0.50 meter per second. 26. Calculate or find graphically the magnitude of the resultant velocity of the boat. [Show all work, including the equation an ...
... 25. On the diagram, use a ruler and protractor to construct a vector representing the velocity of the river current. Use a scale of 1.0 centimeter = 0.50 meter per second. 26. Calculate or find graphically the magnitude of the resultant velocity of the boat. [Show all work, including the equation an ...
Slide 1
... • How do the motions of the flat sheet of paper and crumpled ball of paper compare? What forces do you think are acting on each sheet of paper? ...
... • How do the motions of the flat sheet of paper and crumpled ball of paper compare? What forces do you think are acting on each sheet of paper? ...



















![Forces and the Universe Unit Review: Weight [N] = 4.44 x Weight](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004111559_1-4b4665791c2c3caffe7377372b89110f-300x300.png)


