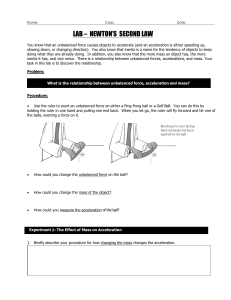
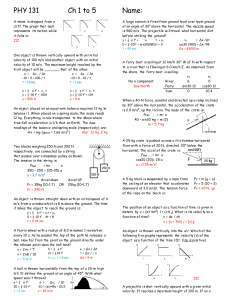
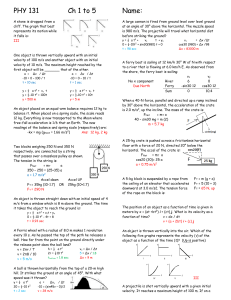
Newton`s Second Law.
... First of all, let us deal with a common mental mistake made by beginners. It is perhaps tempting to read Newton’s second law as a literal identification of force with mass times acceleration. This is not the way to think of it. Think of it as follows. You are in the lab. You have set up an experimen ...
... First of all, let us deal with a common mental mistake made by beginners. It is perhaps tempting to read Newton’s second law as a literal identification of force with mass times acceleration. This is not the way to think of it. Think of it as follows. You are in the lab. You have set up an experimen ...
Newton`s Laws and Forces
... What direction does the friction force act? A. Perpendicular to the surface in the same direction as the motion. B. Parallel to the surface in the same direction as the motion. C. Perpendicular to the surface in the opposite direction of the motion. D. Parallel to the surface in the opposite direct ...
... What direction does the friction force act? A. Perpendicular to the surface in the same direction as the motion. B. Parallel to the surface in the same direction as the motion. C. Perpendicular to the surface in the opposite direction of the motion. D. Parallel to the surface in the opposite direct ...
AP Physics - eLearning
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...
... 10. A skater extends her arms horizontally, holding a 5-kg mass in each hand. She is rotating about a vertical axis with an angular velocity of one revolution per second. If she drops her hands to her sides, what will the final angular velocity (in rev sec ) be if her moment of inertia remains appr ...
What is Force
... published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
... published them in his book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
Form B
... E) At the peak height all the rock's mechanical energy is in gravitational potential energy. F) The gravitational potential energy at the peak height is completely transferred to kinetic energy of the rock just before it hits the ground. G) The rock hits the ground and loses its kinetic energy to di ...
... E) At the peak height all the rock's mechanical energy is in gravitational potential energy. F) The gravitational potential energy at the peak height is completely transferred to kinetic energy of the rock just before it hits the ground. G) The rock hits the ground and loses its kinetic energy to di ...
AHSGE Review
... stretcher is 175 kg, and the lion’s upward acceleration is 0.657 m/s2. What is the unbalanced force necessary to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? ...
... stretcher is 175 kg, and the lion’s upward acceleration is 0.657 m/s2. What is the unbalanced force necessary to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? ...
PHY131 E1
... 12 kg. Everything is now transported to the Moon where free-fall acceleration is 1/6 that on Earth. The new readings of the balance and spring scale (respectively) are: -kx = mg (gmoon = 1.66 m/s2) Ans: 12 kg, 2 kg ...
... 12 kg. Everything is now transported to the Moon where free-fall acceleration is 1/6 that on Earth. The new readings of the balance and spring scale (respectively) are: -kx = mg (gmoon = 1.66 m/s2) Ans: 12 kg, 2 kg ...
Chapter 6 - Applying Newton`s Laws
... you should know something about the particle and it should be related directly to what you want to find ...
... you should know something about the particle and it should be related directly to what you want to find ...
Fall Final Study Guide Define a scalar quantity. A bicycle rider
... 15. 1 millimeter is equal to how many meters? 10-3 m. 16. 86.2 cm is equal to how many kilometers? 8.62x10-4 km 17. Tim has a problem to do involving time, distance, and velocity, but he has forgotten the formula. The question asks him for a measurement in seconds, and the numbers that are given hav ...
... 15. 1 millimeter is equal to how many meters? 10-3 m. 16. 86.2 cm is equal to how many kilometers? 8.62x10-4 km 17. Tim has a problem to do involving time, distance, and velocity, but he has forgotten the formula. The question asks him for a measurement in seconds, and the numbers that are given hav ...
CTWeek1 - University of Colorado Boulder
... Is there a discontinuity in f(x) or any of its derivatives at x = 0? A) f(x) is discontinuous at x = 0. B) f(x) is continuous, but df/dx is discontinuous at x = 0. C) f(x) and df/dx are continuous , but d2f/dx2 is discontinuous at x = 0. D) f(x), df/dx, and d2f/dx2 are all continuous, but d3f/dx3 is ...
... Is there a discontinuity in f(x) or any of its derivatives at x = 0? A) f(x) is discontinuous at x = 0. B) f(x) is continuous, but df/dx is discontinuous at x = 0. C) f(x) and df/dx are continuous , but d2f/dx2 is discontinuous at x = 0. D) f(x), df/dx, and d2f/dx2 are all continuous, but d3f/dx3 is ...
1 - ActiveClassroom!
... a. there are no forces acting on the system b. there are no external forces acting on the system c. there are no internal forces acting on the system d. the system is not moving e. the system has been moving long enough to gain momentum 39. An elephant is hit by a ping pong ball. The magnitude of th ...
... a. there are no forces acting on the system b. there are no external forces acting on the system c. there are no internal forces acting on the system d. the system is not moving e. the system has been moving long enough to gain momentum 39. An elephant is hit by a ping pong ball. The magnitude of th ...
Chapter 7 – Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... This expression is more general than the expression PE = mgy, which is valid for values of y that are small compared to earth’s radius. The above formula assumes that PE = 0 when r = . For finite separations the PE is negative. In applications we only worry about changes in PE, which can be positiv ...
... This expression is more general than the expression PE = mgy, which is valid for values of y that are small compared to earth’s radius. The above formula assumes that PE = 0 when r = . For finite separations the PE is negative. In applications we only worry about changes in PE, which can be positiv ...
Lecture 5 - HKU Physics
... The man rotates with the rotor and the centripetal force which acts on him is provided by the wall as normal force, N = ...
... The man rotates with the rotor and the centripetal force which acts on him is provided by the wall as normal force, N = ...