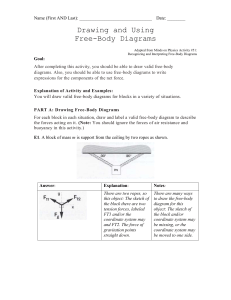
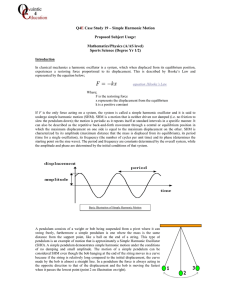
Chapter 15 Problems
... 84.4 s later? (b) What If? A hanging spring stretches by 35.5 cm when an object of mass 440 g is hung on it at rest. We define this new position as x = 0. This object is also pulled down an additional 18.0 cm and released from rest to oscillate without friction. Find its position 84.4 s later. (c) W ...
... 84.4 s later? (b) What If? A hanging spring stretches by 35.5 cm when an object of mass 440 g is hung on it at rest. We define this new position as x = 0. This object is also pulled down an additional 18.0 cm and released from rest to oscillate without friction. Find its position 84.4 s later. (c) W ...
Document
... Which type of wave causes the most destruction at Earth’s surface? A P-wave B S-wave C surface wave ...
... Which type of wave causes the most destruction at Earth’s surface? A P-wave B S-wave C surface wave ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - University of Mississippi
... Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the forc ...
... Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the forc ...
FORCE!
... F=mxa (Force equals mass times acceleration). Don’t worry about trying to understand the math or start working problems in your head. This Law is just a natural extension of the 1st Law. Here’s what it’s really saying: “It takes a certain amount of force to cause a certain amount of acceleration to ...
... F=mxa (Force equals mass times acceleration). Don’t worry about trying to understand the math or start working problems in your head. This Law is just a natural extension of the 1st Law. Here’s what it’s really saying: “It takes a certain amount of force to cause a certain amount of acceleration to ...
Chapter 09 - Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
... the center of mass comS for disk S is at the center of S, at x =-R. Similarly, the center of mass comC for composite plate C is at the center of C, at the origin. Assume that mass mS of disk S is concentrated in a particle at xS =-R, and mass mP is concentrated in a particle at xP. Next treat these ...
... the center of mass comS for disk S is at the center of S, at x =-R. Similarly, the center of mass comC for composite plate C is at the center of C, at the origin. Assume that mass mS of disk S is concentrated in a particle at xS =-R, and mass mP is concentrated in a particle at xP. Next treat these ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • There are generally two high tides per day, 12 hours apart Section 5.5 ...
... • There are generally two high tides per day, 12 hours apart Section 5.5 ...
Bio and Abstract
... interpretations. Specifically, we have a good quantitative understanding of how fold shapes and areas are related to fault geometries and displacements. Consequently we can combine forward modeling, structural restoration and related techniques such as area-depth analysis to constrain (1) fault shap ...
... interpretations. Specifically, we have a good quantitative understanding of how fold shapes and areas are related to fault geometries and displacements. Consequently we can combine forward modeling, structural restoration and related techniques such as area-depth analysis to constrain (1) fault shap ...
WEEKLIES ISSUE
... Friction is another everyday force for us. Without friction, things would be sliding everywhere, and it would be almost impossible to go anywhere. So what causes the force of friction? For things like mud or sandpaper, that is an easy question to answer. We know that the lumps in the mud and the san ...
... Friction is another everyday force for us. Without friction, things would be sliding everywhere, and it would be almost impossible to go anywhere. So what causes the force of friction? For things like mud or sandpaper, that is an easy question to answer. We know that the lumps in the mud and the san ...
Speed, Velocity and Acceleration
... upon any object that is attached to it for most springs, the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the amount of stretch or compression of the spring If both springs are the same size when not compressed, which spring will apply more force to the ball when released? Explain ...
... upon any object that is attached to it for most springs, the magnitude of the force is directly proportional to the amount of stretch or compression of the spring If both springs are the same size when not compressed, which spring will apply more force to the ball when released? Explain ...
Exam 1 - RIT
... _______ You twirl a ball on a string in a circle. Ignoring the effect of gravity, the force that causes the ball to move in a circle is (a) the tension force on the ball by the string (b) the tension force on the string by the ball (c) the tension force on the string by your hand (d) the tension for ...
... _______ You twirl a ball on a string in a circle. Ignoring the effect of gravity, the force that causes the ball to move in a circle is (a) the tension force on the ball by the string (b) the tension force on the string by the ball (c) the tension force on the string by your hand (d) the tension for ...
Chapter 05 Solutions
... 8. In accord with Newton’s first law, your body tends to remain in uniform motion. When the airplane accelerates, the seat pushes you forward. In accord with Newton’s third law, you simultaneously push backward against the seat. 9. When the ball exerts a force on the floor, the floor exerts an equal ...
... 8. In accord with Newton’s first law, your body tends to remain in uniform motion. When the airplane accelerates, the seat pushes you forward. In accord with Newton’s third law, you simultaneously push backward against the seat. 9. When the ball exerts a force on the floor, the floor exerts an equal ...
Document
... It is because Newtonian mechanics assumes that we can determine the velocity and position of the object at the same instant but actuall we cannot. 2) The velocity must not to be too large.(e.g. speed of light), otherwise special relativity have to be used. It is because the measured mass appears to ...
... It is because Newtonian mechanics assumes that we can determine the velocity and position of the object at the same instant but actuall we cannot. 2) The velocity must not to be too large.(e.g. speed of light), otherwise special relativity have to be used. It is because the measured mass appears to ...
Slide 1
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
P1710_MWF09
... Physics 1710 Chapter 5: Laws of Motion—II 1′ Lecture • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and ...
... Physics 1710 Chapter 5: Laws of Motion—II 1′ Lecture • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and ...
Intro Forces and Newton`s 3 Laws
... The relationship between mass and inertia: MASS IS A MEASURE OF INERTIA- the more massive the object, the more that object tends to resist changes in its state of motion. What would be easier to push a small car or a semi? ...
... The relationship between mass and inertia: MASS IS A MEASURE OF INERTIA- the more massive the object, the more that object tends to resist changes in its state of motion. What would be easier to push a small car or a semi? ...
Skating
... Why does a motionless skater tend to remain motionless? Why does a moving skater tend to continue moving? How can we describe the motion of a coasting skater? How does a skater start, stop, or turn? Why does a skater need ice or wheels in order to skate? ...
... Why does a motionless skater tend to remain motionless? Why does a moving skater tend to continue moving? How can we describe the motion of a coasting skater? How does a skater start, stop, or turn? Why does a skater need ice or wheels in order to skate? ...