Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
... and scalar quantities in italics (v) • You can distinguish between the two when you write them with an arrow above the symbol.( ) ...
... and scalar quantities in italics (v) • You can distinguish between the two when you write them with an arrow above the symbol.( ) ...
Forces and Motion
... Force = Mass X Acceleration • If the amount of force stays the same and the mass of the object increases, what will happen to the amount of acceleration? • If the amount of force stays the same and the mass of the object decreases what will happen to the amount of acceleration? ...
... Force = Mass X Acceleration • If the amount of force stays the same and the mass of the object increases, what will happen to the amount of acceleration? • If the amount of force stays the same and the mass of the object decreases what will happen to the amount of acceleration? ...
The Third Law:
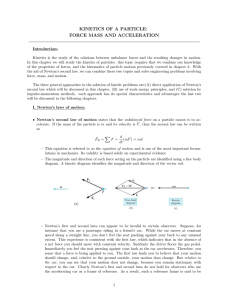
... earth, you end up with a pretty good acceleration – enough to make you move. What about the earth? It also had a force exerted on it – the one from your foot pushing on it. Does it also get accelerated? Well, yes, it has to. The same magnitude force is acting on it. Why then don’t you notice the ear ...
... earth, you end up with a pretty good acceleration – enough to make you move. What about the earth? It also had a force exerted on it – the one from your foot pushing on it. Does it also get accelerated? Well, yes, it has to. The same magnitude force is acting on it. Why then don’t you notice the ear ...
Lecture 7 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Two identical vertical springs are compressed by the same amount, one with a heavy ball and one with a light-weight ball. When released, which ball will reach more height? a) the heavy ball b) the light ball c) they will go up the same amount ...
... Two identical vertical springs are compressed by the same amount, one with a heavy ball and one with a light-weight ball. When released, which ball will reach more height? a) the heavy ball b) the light ball c) they will go up the same amount ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... friction must be applied to it. To keep the object in motion, a force at least as strong as friction must be applied continuously. Objects stop moving because friction or some other force acts on them. Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion. The greater the mass of an ob ...
... friction must be applied to it. To keep the object in motion, a force at least as strong as friction must be applied continuously. Objects stop moving because friction or some other force acts on them. Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change in motion. The greater the mass of an ob ...
on an object
... – Force of gravity pulling you toward the earth – F = ma becomes W = mg • W means weight • g means acceleration due to gravity ~10m/s2 ...
... – Force of gravity pulling you toward the earth – F = ma becomes W = mg • W means weight • g means acceleration due to gravity ~10m/s2 ...
Document
... transmit tension undiminished from one end to the other is NOT affected when the rope passes around a simple pulley (one end is stationary) ...
... transmit tension undiminished from one end to the other is NOT affected when the rope passes around a simple pulley (one end is stationary) ...
Chapter 8: Rotational motion
... If freely suspend an object from any point, the CM lies somewhere along the line vertically down from it. So, to determine exactly where, suspend it freely from some other point on the object, let it adjust, draw again the vertical line: the intersection of the two lines gives CM. ...
... If freely suspend an object from any point, the CM lies somewhere along the line vertically down from it. So, to determine exactly where, suspend it freely from some other point on the object, let it adjust, draw again the vertical line: the intersection of the two lines gives CM. ...
Document
... two cases? Are they different? How is the force diagram look like in two cases? What is the vertical component of acceleration (while the bullet is moving toward the ground)? ...
... two cases? Are they different? How is the force diagram look like in two cases? What is the vertical component of acceleration (while the bullet is moving toward the ground)? ...
Name Student ID
... Use the following scenario for the next four problems. A ball is fired from the level ground at an initial velocity of v0. The x- and y-component of v0 is v0x = -4.00 m/s, and v0y = 3.00 m/s, respectively, where the x-direction is defined to be horizontally to the right, and the y-direction is defin ...
... Use the following scenario for the next four problems. A ball is fired from the level ground at an initial velocity of v0. The x- and y-component of v0 is v0x = -4.00 m/s, and v0y = 3.00 m/s, respectively, where the x-direction is defined to be horizontally to the right, and the y-direction is defin ...
Answers - jpsaos
... MC A crate sits in the middle of the bed of a flatbed truck. The driver accelerates the truck gradually from rest to a normal speed, but then has to make a sudden stop to avoid hitting a car. If the crate slides as the truck stops, the frictional force would be (a) in the forward direction, (b) in t ...
... MC A crate sits in the middle of the bed of a flatbed truck. The driver accelerates the truck gradually from rest to a normal speed, but then has to make a sudden stop to avoid hitting a car. If the crate slides as the truck stops, the frictional force would be (a) in the forward direction, (b) in t ...