Problem: Average Velocity (1988)
... 65. A body moving in the positive x direction passes the origin at time t = 0. Between t = 0 and t = 1 second, the body has a constant speed of 24 meters per second. At t = 1 second, the body is given a constant acceleration of 6 meters per second squared in the negative x direction. The position x ...
... 65. A body moving in the positive x direction passes the origin at time t = 0. Between t = 0 and t = 1 second, the body has a constant speed of 24 meters per second. At t = 1 second, the body is given a constant acceleration of 6 meters per second squared in the negative x direction. The position x ...
4.1_simple_harmonic_motion_
... (a) when the springs are connected as in figure (a) calculate the period of oscillations when it is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released. (b) When the springs are connected instead as in figure (b) would the period change. 24. The graph in the figure shows the variation with tim ...
... (a) when the springs are connected as in figure (a) calculate the period of oscillations when it is displaced from its equilibrium position and then released. (b) When the springs are connected instead as in figure (b) would the period change. 24. The graph in the figure shows the variation with tim ...
Mechanics - Modeling Instruction Program
... tables propped up on one end. They make predictions as to which object will “win” the race down the table and then see if they are correct. At the end of the lab the teacher shows them four plastic disks and tells them the positions of the ball placed inside. (But they don’t know which disk has whic ...
... tables propped up on one end. They make predictions as to which object will “win” the race down the table and then see if they are correct. At the end of the lab the teacher shows them four plastic disks and tells them the positions of the ball placed inside. (But they don’t know which disk has whic ...
TEKS 5 - Pearson School
... the formula for Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent. Sample problem An automobile with a mass of 1000 kilograms accelerates when the traffic light turns green. If the net force on the car is 4000 newtons, what is the car’s acceleration? First, yo ...
... the formula for Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent. Sample problem An automobile with a mass of 1000 kilograms accelerates when the traffic light turns green. If the net force on the car is 4000 newtons, what is the car’s acceleration? First, yo ...
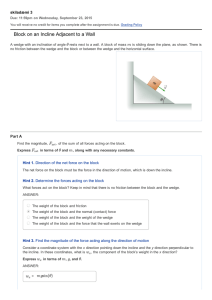
Block on an Incline Adjacent to a Wall
... that as θ gets very small or as θ approaches 90 degrees (π/2 radians), the contact force between the wall and the wedge goes to zero. This is what we should expect; in the first limit ( θ small), the block is accelerating very slowly, and all horizontal forces are small. In the second limit ( θ abou ...
... that as θ gets very small or as θ approaches 90 degrees (π/2 radians), the contact force between the wall and the wedge goes to zero. This is what we should expect; in the first limit ( θ small), the block is accelerating very slowly, and all horizontal forces are small. In the second limit ( θ abou ...
Exercises Lecture 15 Harmonic Oscillators
... Remark 15.4. The solution x(t) for an over-critically damped oscillator tends to zero as fast as possible without oscillating. What means “as fast as possible”? It means that a critically-damped oscillator slows down to its equilibrium position faster than any over-critically damped oscillator. With ...
... Remark 15.4. The solution x(t) for an over-critically damped oscillator tends to zero as fast as possible without oscillating. What means “as fast as possible”? It means that a critically-damped oscillator slows down to its equilibrium position faster than any over-critically damped oscillator. With ...
Review Sheet - Dynamics Test
... 18. Two boxes, A and B, are side by side on a table. The mass of box A is 3.20 kg, and the mass of box B is 2.10 kg. A horizontal force of 10.5 N is applied to box A, pushing it against box B. There is a frictional force of 2.00 N between box A and the table, and a force of friction of 1.00 N acting ...
... 18. Two boxes, A and B, are side by side on a table. The mass of box A is 3.20 kg, and the mass of box B is 2.10 kg. A horizontal force of 10.5 N is applied to box A, pushing it against box B. There is a frictional force of 2.00 N between box A and the table, and a force of friction of 1.00 N acting ...
Force = Mass x Acceleration - GZ @ Science Class Online
... on gravity. His law of universal gravitation states that objects with mass attract each other with a force that varies directly as the product of their masses and decreases as the distance between them increases. This gravitation force causes objects to accelerate towards the centre of the Earth (re ...
... on gravity. His law of universal gravitation states that objects with mass attract each other with a force that varies directly as the product of their masses and decreases as the distance between them increases. This gravitation force causes objects to accelerate towards the centre of the Earth (re ...
act04
... 7. Solving for acceleration: Use the relationships that you come up with in the step above to solve for the acceleration of the cart during the time that the hanging mass is falling. The acceleration expression should contain only the mass of the cart, the hanging mass and the constant of gravity o ...
... 7. Solving for acceleration: Use the relationships that you come up with in the step above to solve for the acceleration of the cart during the time that the hanging mass is falling. The acceleration expression should contain only the mass of the cart, the hanging mass and the constant of gravity o ...