Physics
... rockets. Deduce an expression for, (i) velocity at any instant and (ii) acceleration of the rocket. Q.3 (i) Define friction. (ii) Show that kinetic friction is less than the static friction. (iii) Establish that static friction is a self-adjustable force. (iv) Write the basic laws of static friction ...
... rockets. Deduce an expression for, (i) velocity at any instant and (ii) acceleration of the rocket. Q.3 (i) Define friction. (ii) Show that kinetic friction is less than the static friction. (iii) Establish that static friction is a self-adjustable force. (iv) Write the basic laws of static friction ...
Chapter 5-6
... 18. Walker3 6.P.066. [549531] Show Details A 2.0 kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at an angle of 65° above the horizontal. The upper end of the box is attached to a spring with a force constant of 16 N/m, as shown in Figure 6-38. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and the ...
... 18. Walker3 6.P.066. [549531] Show Details A 2.0 kg box rests on a plank that is inclined at an angle of 65° above the horizontal. The upper end of the box is attached to a spring with a force constant of 16 N/m, as shown in Figure 6-38. If the coefficient of static friction between the box and the ...
Newton`s Second Law
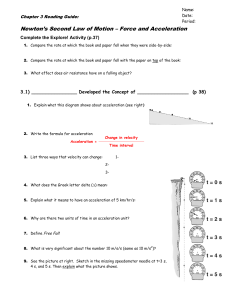
... doubling of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Similarly, comparing the values in rows 2 and 4 demonstrates that a halving of the net force results in a halving of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Acceleration is directly proportional to net force. Furthermore, the qualitative ...
... doubling of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Similarly, comparing the values in rows 2 and 4 demonstrates that a halving of the net force results in a halving of the acceleration (if mass is held constant). Acceleration is directly proportional to net force. Furthermore, the qualitative ...
- Fairview High School
... 10. Describe the acceleration experienced by a ball thrown upwards from the moment it leaves the throwers hand to the moment it impacts the ground. (A sketch can help): ...
... 10. Describe the acceleration experienced by a ball thrown upwards from the moment it leaves the throwers hand to the moment it impacts the ground. (A sketch can help): ...
Physics 20 Concept 20 Uniform Circular Motion I. Acceleration
... III. The Direction of Centripetal Acceleration Students often have difficulty in understanding how an acceleration can result in a change in direction without a change in speed. Consider the diagram to the right. An object is seen at r point A with velocity v i and then a very short time r r r late ...
... III. The Direction of Centripetal Acceleration Students often have difficulty in understanding how an acceleration can result in a change in direction without a change in speed. Consider the diagram to the right. An object is seen at r point A with velocity v i and then a very short time r r r late ...
Multiple Choice
... A box of mass m is released from rest at point A, the top of a long frictionless slide. Point A is at height H above the level points B and C. Although the slide is frictionless, the horizontal surface from point B to C is not. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and this surface is ...
... A box of mass m is released from rest at point A, the top of a long frictionless slide. Point A is at height H above the level points B and C. Although the slide is frictionless, the horizontal surface from point B to C is not. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and this surface is ...
19. Centripetal Force
... 1. The force that acts through a string is referred to as ____________. A ____________ sensor can measure the tension through a string in newtons. When an object rotates around a central point with a string, the tension in the string equals the ____________ force experienced by the object. An object ...
... 1. The force that acts through a string is referred to as ____________. A ____________ sensor can measure the tension through a string in newtons. When an object rotates around a central point with a string, the tension in the string equals the ____________ force experienced by the object. An object ...
13.42 Design Principles for Ocean Vehicles 1. Forces on Large Structures
... It is good here to note the important conditions on each component of the total potential. The incident potential is formulated from that of a free wave without consideration for the presence of the body. Therefore φI ( x, y, z, t ) satisfies only the free surface boundary conditions and the bottom ...
... It is good here to note the important conditions on each component of the total potential. The incident potential is formulated from that of a free wave without consideration for the presence of the body. Therefore φI ( x, y, z, t ) satisfies only the free surface boundary conditions and the bottom ...
Phys 111 Fall 2009
... Contact forces, Tension Newtons 2nd law example in 1D using tension and contact force Simple 2D example of forces Frictionless pulleys (acceleration and tension same on both sides) ...
... Contact forces, Tension Newtons 2nd law example in 1D using tension and contact force Simple 2D example of forces Frictionless pulleys (acceleration and tension same on both sides) ...