Layers of the Earth Study Guide
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
... 6. It is composed (means made of) minerals and rocks and is mostly made of granite and basalt. 7. The part of the crust where the continents are is known as continental crust. This is the thickest part of the crust. 8. The part of the crust beneath the ocean water is known as the oceanic crust, th ...
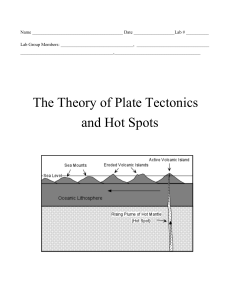
Hot Spot LAB 2017 - eat, sleep, breathe science
... was faster? Slower? Explain the reason for your answer by referring to specific ages on the graph. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... was faster? Slower? Explain the reason for your answer by referring to specific ages on the graph. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
The Plate Tectonic Model
... • Most divergent margins have oceanic crust on either side (oceanic ridges), but very young ones might involve a continent. These quickly evolve into oceanic ridges. • Transform margins form as a consequence of diverging plates. Therefore most are found crossing oceanic ridges. Occasionally a contin ...
... • Most divergent margins have oceanic crust on either side (oceanic ridges), but very young ones might involve a continent. These quickly evolve into oceanic ridges. • Transform margins form as a consequence of diverging plates. Therefore most are found crossing oceanic ridges. Occasionally a contin ...
Chapter 5 Earths Interior
... Less than 1% of Earth’s mass Minerals similar to granite, Less dense Average thickness 30 km ...
... Less than 1% of Earth’s mass Minerals similar to granite, Less dense Average thickness 30 km ...
Wegener—Continental Drift
... each other, forming volcanic cones. Continental crust sinking into the mantle and melting, coming back up as volcanoes. Oceanic crust subducting below continental crust, then melting and rising to the surface. Oceanic crust pushing against oceanic crust causing underwater volcanic peaks. ...
... each other, forming volcanic cones. Continental crust sinking into the mantle and melting, coming back up as volcanoes. Oceanic crust subducting below continental crust, then melting and rising to the surface. Oceanic crust pushing against oceanic crust causing underwater volcanic peaks. ...
Chapter 7.4 Notes Deformation of the Earth`s Crust *Deformation
... Volcanic Mountains: located at convergent boundaries where oceanic plates sink at subduction zones & under the sea to sometimes cause islands. ...
... Volcanic Mountains: located at convergent boundaries where oceanic plates sink at subduction zones & under the sea to sometimes cause islands. ...
Plate Tectonics presentation
... formed. Oceanic-oceanic plate convergence also results in the formation of undersea volcanoes. Over millions of years, however, the erupted lava and volcanic debris pile up on the ocean floor until a submarine volcano rises above sea level to form an island volcano. Such volcanoes are typically stru ...
... formed. Oceanic-oceanic plate convergence also results in the formation of undersea volcanoes. Over millions of years, however, the erupted lava and volcanic debris pile up on the ocean floor until a submarine volcano rises above sea level to form an island volcano. Such volcanoes are typically stru ...
Lithosphere - paulding.k12.ga.us
... formed. Oceanic-oceanic plate convergence also results in the formation of undersea volcanoes. Over millions of years, however, the erupted lava and volcanic debris pile up on the ocean floor until a submarine volcano rises above sea level to form an island volcano. Such volcanoes are typically stru ...
... formed. Oceanic-oceanic plate convergence also results in the formation of undersea volcanoes. Over millions of years, however, the erupted lava and volcanic debris pile up on the ocean floor until a submarine volcano rises above sea level to form an island volcano. Such volcanoes are typically stru ...
Changes in the Earth and its Atmosphere
... • One of these suggests that during the first billion years the atmosphere was mainly CO2 with little or no O2 (like Mars and Venus). There was probably also methane and ammonia. • What process could have created the oxygen? ...
... • One of these suggests that during the first billion years the atmosphere was mainly CO2 with little or no O2 (like Mars and Venus). There was probably also methane and ammonia. • What process could have created the oxygen? ...
C1 Topic 7 the earth revision Earth`s Structure (and rocks) 1. List the
... hydrogen for the earth’s early experiment? 23. Why does Miller and Urey’s experiment only provide weak ...
... hydrogen for the earth’s early experiment? 23. Why does Miller and Urey’s experiment only provide weak ...
Chapter 3 Vocabulary
... geosphere the mostly solid, rocky part of the Earth; extends from the center of the core to the surface of the crust greenhouse effect the warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of Earth that occurs when carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases in the air absorb and ...
... geosphere the mostly solid, rocky part of the Earth; extends from the center of the core to the surface of the crust greenhouse effect the warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of Earth that occurs when carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases in the air absorb and ...
ppt
... lighter materials rose to the top. Because of this, the crust is made of the lightest materials (rock- basalts and granites) and the core consists of heavy metals (nickel and iron). ...
... lighter materials rose to the top. Because of this, the crust is made of the lightest materials (rock- basalts and granites) and the core consists of heavy metals (nickel and iron). ...
Section 22.4 Plate Tectonics IPLS
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth’s plates move about quickly on top of the crust. 2. Circle the letters of the characteristics of Earth’s plates that the theory of plate tectonics explains. a. composition b. formation c. movement ...
... 1. Is the following sentence true or false? According to the theory of plate tectonics, Earth’s plates move about quickly on top of the crust. 2. Circle the letters of the characteristics of Earth’s plates that the theory of plate tectonics explains. a. composition b. formation c. movement ...
Structure of the Earth Study Guide with Answers
... RADIUS OF A CIRCLE AND DRAW CIRCLES AROUND ALL 3 STATIONS. WHERE THE CIRCLES INTERSECT IS THE WHERE THE EARTHQUAKE HAPPENED. ...
... RADIUS OF A CIRCLE AND DRAW CIRCLES AROUND ALL 3 STATIONS. WHERE THE CIRCLES INTERSECT IS THE WHERE THE EARTHQUAKE HAPPENED. ...
Unit 2: Plate Tectonics Test Review
... Where a dense plate dives under a less dense plate is a subduction zone. Rock can be “recycled” as it melts back into magma. Volcanoes may form & erupt here. ...
... Where a dense plate dives under a less dense plate is a subduction zone. Rock can be “recycled” as it melts back into magma. Volcanoes may form & erupt here. ...
Unit 2 Review
... Where a dense plate dives under a less dense plate is a subduction zone. Rock can be “recycled” as it melts back into magma. Volcanoes may form & erupt here. ...
... Where a dense plate dives under a less dense plate is a subduction zone. Rock can be “recycled” as it melts back into magma. Volcanoes may form & erupt here. ...
Plate Tectonics
... part of the mantle layer underneath. Together the crust and upper mantle are called the lithosphere and they extend about 80 km deep. The lithosphere is broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. These puzzle pieces move a little bit each year as they slide on top of a so ...
... part of the mantle layer underneath. Together the crust and upper mantle are called the lithosphere and they extend about 80 km deep. The lithosphere is broken into giant plates that fit around the globe like puzzle pieces. These puzzle pieces move a little bit each year as they slide on top of a so ...
contents - Less Stress More Success
... crust, the mantle and the core. The crust is broken into plates. These plates move. They separate, collide and slide past each other. The plates are carried about by convection currents in the mantle. ...
... crust, the mantle and the core. The crust is broken into plates. These plates move. They separate, collide and slide past each other. The plates are carried about by convection currents in the mantle. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
... were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
... were similar on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The ages of these rocks are also the same. ...
Science Review: Land Formations (Rocks, Minerals, Soil, etc
... ~roots of plants Erosion- moving sediment away (washing away) Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- t ...
... ~roots of plants Erosion- moving sediment away (washing away) Deposition- putting new sediments in place Forms: beaches Dunes Deltas Example: A friend lives on Marblehead Neck and has a private beach at the water line. After a storm, the sand is not there! It is all rocks! It has been washed away- t ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.