File
... Evidence for magnetic reversals has been primarily preserved in: A. metamorphic rocks near convergent plate boundaries B. limestone and shale accumulating in shallow ocean basins C. active dune fields in the arid regions of the world D. extrusive igneous rocks associated with mid-ocean ridges ...
... Evidence for magnetic reversals has been primarily preserved in: A. metamorphic rocks near convergent plate boundaries B. limestone and shale accumulating in shallow ocean basins C. active dune fields in the arid regions of the world D. extrusive igneous rocks associated with mid-ocean ridges ...
Crust - Spaulding Middle School
... Convection currents can cause the asthenosphere to flow slowly carrying with it the plates of the lithosphere. This movement of plates changes the sizes, shapes, and positions of Earth’s continents and oceans. Geologic Activities at Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary—where two plates are moving ...
... Convection currents can cause the asthenosphere to flow slowly carrying with it the plates of the lithosphere. This movement of plates changes the sizes, shapes, and positions of Earth’s continents and oceans. Geologic Activities at Plate Boundaries Divergent boundary—where two plates are moving ...
Chapter 1 Review answers
... Lithosphere can be divided into two layers, one under ocean basins (sima) and one making up continents (sial) Rocks of continents are also called crust Asthenosphere- upper 200-300km of upper layer of the mantle is called the asthenophere - is in a plastic state, sometimes acting like a liquid The s ...
... Lithosphere can be divided into two layers, one under ocean basins (sima) and one making up continents (sial) Rocks of continents are also called crust Asthenosphere- upper 200-300km of upper layer of the mantle is called the asthenophere - is in a plastic state, sometimes acting like a liquid The s ...
Name: Doe Date: May 13, 2015 Directions: 1. Read the following
... (all, the, changed) crust, the mantle and the core. (Let’s, Still, Billion) start with the layer you ...
... (all, the, changed) crust, the mantle and the core. (Let’s, Still, Billion) start with the layer you ...
FREE Sample Here
... 9. If the coastlines across the Atlantic Ocean are spreading apart, why isn’t the Atlantic Ocean deepest in its center? ANSWER: New ocean floor wells up and forms under the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. 10. What evidence confirmed seafloor spreading? ANSWER: Reversals of the Earth’s magnetic field are preserv ...
... 9. If the coastlines across the Atlantic Ocean are spreading apart, why isn’t the Atlantic Ocean deepest in its center? ANSWER: New ocean floor wells up and forms under the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. 10. What evidence confirmed seafloor spreading? ANSWER: Reversals of the Earth’s magnetic field are preserv ...
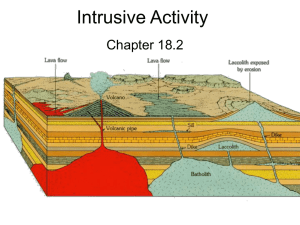
Intrusive Activity
... Intrusive Activity A. Magma can force the overlying rock apart and enter the newly formed fissures. B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
... Intrusive Activity A. Magma can force the overlying rock apart and enter the newly formed fissures. B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
Oreo Cookie Plate Tectonics
... The outer shell is the lithosphere from the Greek “lithos,” meaning hard rock. The plates, composed of Earth’s crust and uppermost mantle, ride on a warmer, softer layer of the mantle, is the asthenosphere. The Greek “asthenes” means ...
... The outer shell is the lithosphere from the Greek “lithos,” meaning hard rock. The plates, composed of Earth’s crust and uppermost mantle, ride on a warmer, softer layer of the mantle, is the asthenosphere. The Greek “asthenes” means ...
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY FINAL EXAM `PRACTICE TEST`
... b. point within the Earth where movement along the fault occurs. c. approximate center of a group of related earthquakes. d. point on the surface directly above a subterranean fault’s rupture point. 4. The troughs in a series of simple folds are called synclines. a. True b. False 5. The opposite of ...
... b. point within the Earth where movement along the fault occurs. c. approximate center of a group of related earthquakes. d. point on the surface directly above a subterranean fault’s rupture point. 4. The troughs in a series of simple folds are called synclines. a. True b. False 5. The opposite of ...
Mineral – Naturally formed solids that are not made from living
... Rock – Naturally occurring solid mixture of minerals. Classified by composition and texture Rock Cycle – Process by which new rocks formed from old rock material. Driven by heat, pressure, weathering, erosion, & deposition. Three basic types of rock are: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Magma ...
... Rock – Naturally occurring solid mixture of minerals. Classified by composition and texture Rock Cycle – Process by which new rocks formed from old rock material. Driven by heat, pressure, weathering, erosion, & deposition. Three basic types of rock are: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic. Magma ...
Warm-Up # 56 Seafloor spreading - East Hanover Township School
... B. Evidence that tectonic plates are being created at divergent boundaries is that younger _______ rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges and older ______________rocks are found further away. ...
... B. Evidence that tectonic plates are being created at divergent boundaries is that younger _______ rocks are found at the mid-ocean ridges and older ______________rocks are found further away. ...
Review Questions For Earth crust (answers)
... 10. Using the terms from question 9, where do earthquakes and volcanoes form and why do they form? Earthquakes often form where plates collide and where there are subduction zones. The frictions from the plates rubbing together cause earthquakes. The same thing can happen at fault zones where plates ...
... 10. Using the terms from question 9, where do earthquakes and volcanoes form and why do they form? Earthquakes often form where plates collide and where there are subduction zones. The frictions from the plates rubbing together cause earthquakes. The same thing can happen at fault zones where plates ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... Mountains of North America were exactly like the limestone in Scotland’s Highlands. ...
... Mountains of North America were exactly like the limestone in Scotland’s Highlands. ...
Section Quiz - TheVirtualNeal
... Folded mountain ranges form when two tectonic plates with continental crust collide. The crust is forced upward at the point of collision, which forms mountains over a long period of time. ...
... Folded mountain ranges form when two tectonic plates with continental crust collide. The crust is forced upward at the point of collision, which forms mountains over a long period of time. ...
ppt
... • Accretion of Earth and meteorites • Rocks from mantle including magmas • Their arguments can be run backwards once antineutrino data are in hand ...
... • Accretion of Earth and meteorites • Rocks from mantle including magmas • Their arguments can be run backwards once antineutrino data are in hand ...
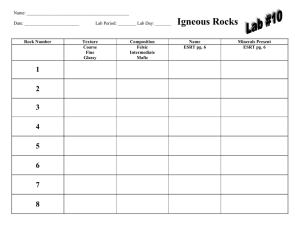
Igneous Rocks
... INTRODUCTION: Please read this as it contains information that will help you complete this lab successfully. Igneous rocks are rocks that form from the cooling of molten magma (under ground) or lava (above ground). The word igneous means "fireformed." Cooling can be immediate or over long periods of ...
... INTRODUCTION: Please read this as it contains information that will help you complete this lab successfully. Igneous rocks are rocks that form from the cooling of molten magma (under ground) or lava (above ground). The word igneous means "fireformed." Cooling can be immediate or over long periods of ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Formation: • Earth movements can push all types of rock deeper into the Earth. • These rocks are then subjected to massive temperatures and pressures, causing the crystalline structure and texture to change. • They do not become liquid, but become molten. ...
... Formation: • Earth movements can push all types of rock deeper into the Earth. • These rocks are then subjected to massive temperatures and pressures, causing the crystalline structure and texture to change. • They do not become liquid, but become molten. ...
EARTH`S FORMATION AND STRUCTURE The earth formed
... Eventually, bodies of several kilometers in diameter formed; these are known as planetesimals. The largest planetesimals grew fastest, at the expense of the smaller ones. This process continued until an earth-sized planet had formed. Early in its formation, the earth must have been completely molten ...
... Eventually, bodies of several kilometers in diameter formed; these are known as planetesimals. The largest planetesimals grew fastest, at the expense of the smaller ones. This process continued until an earth-sized planet had formed. Early in its formation, the earth must have been completely molten ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.