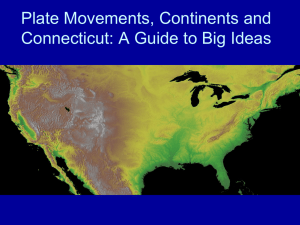
How do Earth`s plates move?
... Diagrams will vary. Arrows should show plates sliding past each other. Labels should show where boundaries stick and indicate it as a possible earthquake location. ...
... Diagrams will vary. Arrows should show plates sliding past each other. Labels should show where boundaries stick and indicate it as a possible earthquake location. ...
1. What is a mineral? 2. What are the special tests you can do to
... 11. What are the three types of sedimentary rocks? How are they different from each other? 12. What is a metamorphic rock? How is it formed? 13. What are the two different types of metamorphic rocks? 14. Why are metamorphic rocks considered “changing rocks”? 15. What two process cause metamorphi ...
... 11. What are the three types of sedimentary rocks? How are they different from each other? 12. What is a metamorphic rock? How is it formed? 13. What are the two different types of metamorphic rocks? 14. Why are metamorphic rocks considered “changing rocks”? 15. What two process cause metamorphi ...
Activity Matching - Miss Clark`s Website
... For each set of matching statements below place the letter that goes with the correct statement next to each item. Use your textbook and any notes to help you find the correct answer. _____ Rachel Carson _____ John Muir _____ Henry David Thoreau _____ Aldo Leopold _____ Ralph Waldo Emerson _____ Rob ...
... For each set of matching statements below place the letter that goes with the correct statement next to each item. Use your textbook and any notes to help you find the correct answer. _____ Rachel Carson _____ John Muir _____ Henry David Thoreau _____ Aldo Leopold _____ Ralph Waldo Emerson _____ Rob ...
Napoleon - Kawameeh Middle School
... These are the layers of the atmosphere and what can be found in each layer. ...
... These are the layers of the atmosphere and what can be found in each layer. ...
field project
... formed ~30 million years ago. The transform boundary that exists today was once a convergent boundary approximately 100 million years ago (Sloan, 2006, pg. 31). The force of compression was causing the Farallon Plate to subduct beneath the North American Plate, causing oceanic rocks from the Farallo ...
... formed ~30 million years ago. The transform boundary that exists today was once a convergent boundary approximately 100 million years ago (Sloan, 2006, pg. 31). The force of compression was causing the Farallon Plate to subduct beneath the North American Plate, causing oceanic rocks from the Farallo ...
RHV_Margins_Mini_Lesson.v8
... fluids contained in these materials, is carried beneath the lithosphere of the overriding plate. Some of this material can be accreted onto the overriding plate, and some fluids migrate upward as the crust is subducted to increasing depths. The rest is carried into the mantle. The whole cycle of inp ...
... fluids contained in these materials, is carried beneath the lithosphere of the overriding plate. Some of this material can be accreted onto the overriding plate, and some fluids migrate upward as the crust is subducted to increasing depths. The rest is carried into the mantle. The whole cycle of inp ...
Earth`s Interior
... • Layer of hot rock below the crust. • Temperature and pressure in the mantle increase with depth. • Lithosphere – Consists of the crust and the uppermost part of mantle. ...
... • Layer of hot rock below the crust. • Temperature and pressure in the mantle increase with depth. • Lithosphere – Consists of the crust and the uppermost part of mantle. ...
CHAPTER 3
... mountain ranges, deep trenches, vast plateaus, and enormous faults. Harry Hess, in the early 1960s, first proposed the existence of large convection cells in the mantle that act as conveyor belts for the overlying lithosphere. Where the lithosphere is cracked the hot mantle material is able to escap ...
... mountain ranges, deep trenches, vast plateaus, and enormous faults. Harry Hess, in the early 1960s, first proposed the existence of large convection cells in the mantle that act as conveyor belts for the overlying lithosphere. Where the lithosphere is cracked the hot mantle material is able to escap ...
Earth`s Landforms Study Guide
... c. the dune will erode more slowly and may even grow. d. the dune will erode more quickly. 27. How do volcanoes change Earth’s landforms? a. They release pressure that has built up under Earth’s crust. b. They blow ash and lava high into Earth’s atmosphere. c. They form over hot spots. d. They form ...
... c. the dune will erode more slowly and may even grow. d. the dune will erode more quickly. 27. How do volcanoes change Earth’s landforms? a. They release pressure that has built up under Earth’s crust. b. They blow ash and lava high into Earth’s atmosphere. c. They form over hot spots. d. They form ...
Ocean Floor
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
... Understand the processes that are continuously changing Earth’s surface as lithospheric plates move relative to one another. Identify the role of oceanic ridges, transform faults and deep-sea trenches in defining the edges of lithospheric plates. Understand the importance of asthenospheric thermal c ...
A Journey from the Inside Out
... true. If they are true, write them down Objective: I can as is. If they are false correct them understand important and write out the true statement. information about Earth’s layers 1. The rock cycle describes the natural processes that form, change, break down, Homework: and form rocks again. • 6. ...
... true. If they are true, write them down Objective: I can as is. If they are false correct them understand important and write out the true statement. information about Earth’s layers 1. The rock cycle describes the natural processes that form, change, break down, Homework: and form rocks again. • 6. ...
Chapter 1 notes - Freedom Area School District
... Volcanism - happens on edges of the plates; the magma from the mantle pours onto the earth’s surface - lava Folding - plates move toward each other and fold up (i.e. App. Mtns.) Faulting - plates move apart or slide under one another ...
... Volcanism - happens on edges of the plates; the magma from the mantle pours onto the earth’s surface - lava Folding - plates move toward each other and fold up (i.e. App. Mtns.) Faulting - plates move apart or slide under one another ...
MB Chapter 02
... Plate Boundaries and Geologic Processes • The lithosphere is fragmented into fourteen major tectonic plates • Plates are moving across the Earth's surface in different directions and at different velocities. • Many geologic processes, such as plutonism, volcanism, and earthquakes result from the in ...
... Plate Boundaries and Geologic Processes • The lithosphere is fragmented into fourteen major tectonic plates • Plates are moving across the Earth's surface in different directions and at different velocities. • Many geologic processes, such as plutonism, volcanism, and earthquakes result from the in ...
First Hour Exam Answers
... this as justification for naming this new rock body the a. Colby Batholith c. Colby Stock b. Colby Xenolith d. Colby Lithostat 23. Porphyritic textures in igneous rocks is caused by a. rapid cooling of high-silica magmas. b. slow cooling of high-silica magmas. c. rapid cooling of low-silica magmas. ...
... this as justification for naming this new rock body the a. Colby Batholith c. Colby Stock b. Colby Xenolith d. Colby Lithostat 23. Porphyritic textures in igneous rocks is caused by a. rapid cooling of high-silica magmas. b. slow cooling of high-silica magmas. c. rapid cooling of low-silica magmas. ...
שקופית 1
... temperature. High temperatures, pressures and abundant pore fluids result in metamorphic rocks with large mineral grains ...
... temperature. High temperatures, pressures and abundant pore fluids result in metamorphic rocks with large mineral grains ...
Tectonic Plates
... The plate could be made of denser, ocean basin rock or of less dense, continental rock. The landforms and types of events that result depend on the direction of motion and the types of plates. 6 Divergent boundaries occur when two plates pull away from each other. When this happens, a rift or tear i ...
... The plate could be made of denser, ocean basin rock or of less dense, continental rock. The landforms and types of events that result depend on the direction of motion and the types of plates. 6 Divergent boundaries occur when two plates pull away from each other. When this happens, a rift or tear i ...
Baltica (proto
... Why is Connecticut so Amazing? • Connecticut shows evidence of various earth processes, such as continental collisions, rifting, and folding that have shaped its structure. ...
... Why is Connecticut so Amazing? • Connecticut shows evidence of various earth processes, such as continental collisions, rifting, and folding that have shaped its structure. ...
Investigating La Runion Hot Spot From Crust to Core
... address these challenges. Cutting- edge waveform tomography methods, which account for scattering of wave energy around narrow conduits, will be adapted to data from the seafloor and islands. Hemispheric- scale inversions will include all available regional data, including very deep diving waves tha ...
... address these challenges. Cutting- edge waveform tomography methods, which account for scattering of wave energy around narrow conduits, will be adapted to data from the seafloor and islands. Hemispheric- scale inversions will include all available regional data, including very deep diving waves tha ...
Homework Due Friday, January 15, 2016 The Plate Tectonic Theory
... discovered mountainous ridges along the bottom of the ocean. These ridges appear to be where two plates have started to move apart, allowing molten rock from the underlying mantle to ooze out and fill the space created by the plates’ movement. Plate tectonic theory has also helped scientists explain ...
... discovered mountainous ridges along the bottom of the ocean. These ridges appear to be where two plates have started to move apart, allowing molten rock from the underlying mantle to ooze out and fill the space created by the plates’ movement. Plate tectonic theory has also helped scientists explain ...
Earth`s Interior Information- Core-Innermost layer Inner Core
... Mantle-Is solid rock that behaves like plastic. It moves, has intense pressure at bottom layer, convection currents flow up towards the lithosphere Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe ...
... Mantle-Is solid rock that behaves like plastic. It moves, has intense pressure at bottom layer, convection currents flow up towards the lithosphere Asthenosphere-Not liquid, but there is melted rock, carries the lithosphere, moves slowly Lithosphere-broken into giant plates that fit around the globe ...
theme 5: the deeper earth
... is to link geochemical data with geological and geophysical observations. Many of the early geochemical models involved a layered mantle and the concept of geochemical reservoirs. Indeed, the two layer mantle model has been implicit in almost all geochemical literature and the provenance of OIB and ...
... is to link geochemical data with geological and geophysical observations. Many of the early geochemical models involved a layered mantle and the concept of geochemical reservoirs. Indeed, the two layer mantle model has been implicit in almost all geochemical literature and the provenance of OIB and ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.