
Volcanoes & Earthquakes
... chimney) of his furnace was an island named Volcano… this was a simple attempt by people to try to understand the complex processes that cause volcanic activity ...
... chimney) of his furnace was an island named Volcano… this was a simple attempt by people to try to understand the complex processes that cause volcanic activity ...
View Sample - Popular Book Company
... of South America seems to fit nicely with the west coast of Africa, like two puzzle pieces? This can be explained by the theory of plate tectonics in which we believe that, millions of years ago, all the continents of the world were one big landmass called Pangaea. Pangaea began breaking up 180 mill ...
... of South America seems to fit nicely with the west coast of Africa, like two puzzle pieces? This can be explained by the theory of plate tectonics in which we believe that, millions of years ago, all the continents of the world were one big landmass called Pangaea. Pangaea began breaking up 180 mill ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... 1. broad volcano with gently sloping sides 2. long crack that forms as two tectonic plates move apart 3. magma that reaches Earth’s surface 4. point inside Earth where earthquake movement first occurs 5. small volcano formed from tephra 6. the surface of a break in a section of rock 8. steep-sided v ...
... 1. broad volcano with gently sloping sides 2. long crack that forms as two tectonic plates move apart 3. magma that reaches Earth’s surface 4. point inside Earth where earthquake movement first occurs 5. small volcano formed from tephra 6. the surface of a break in a section of rock 8. steep-sided v ...
Name: Period:______ Date: Earth Science in Action: Rocks Video
... 3) The word igneous comes from the Latin word “ignis” or _______________. Igneous rock starts out as _______________ inside the Earth. When it comes into contact with cooler surfaces it hardens into rock. ____________________ igneous rock is formed when magma exits the Earth in volcanoes, explosions ...
... 3) The word igneous comes from the Latin word “ignis” or _______________. Igneous rock starts out as _______________ inside the Earth. When it comes into contact with cooler surfaces it hardens into rock. ____________________ igneous rock is formed when magma exits the Earth in volcanoes, explosions ...
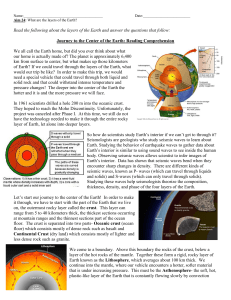
Read the following about the layers of the Earth and answer the
... less dense rock such as granite. We come to a boundary. Above this boundary the rocks of the crust, below a layer of the hot rocks of the mantle. Together these form a rigid, rocky layer of Earth known as the Lithosphere, which averages about 100 km thick. We continue into the mantle, where our vehi ...
... less dense rock such as granite. We come to a boundary. Above this boundary the rocks of the crust, below a layer of the hot rocks of the mantle. Together these form a rigid, rocky layer of Earth known as the Lithosphere, which averages about 100 km thick. We continue into the mantle, where our vehi ...
Chapters 1(review)
... What is a “marine magnetic anomaly?” In what ways do these anomalies help provide evidence to support plate tectonics? How can we use these anomalies to determine the velocity of a plate? **(see question 8 under “Questions for Review” on page 408.)** ...
... What is a “marine magnetic anomaly?” In what ways do these anomalies help provide evidence to support plate tectonics? How can we use these anomalies to determine the velocity of a plate? **(see question 8 under “Questions for Review” on page 408.)** ...
Notes on Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics states that the Earth`s crust
... The layer below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere. The lithosphere floats or moves around on the asthenosphere. Three ways the plates can move. 1. move apart 2. move together 3. move past each other Name of the three types of boundaries. 1. Divergent boundary 2. Convergent boundary 3. Transform f ...
... The layer below the lithosphere is the asthenosphere. The lithosphere floats or moves around on the asthenosphere. Three ways the plates can move. 1. move apart 2. move together 3. move past each other Name of the three types of boundaries. 1. Divergent boundary 2. Convergent boundary 3. Transform f ...
HS Earth Standard 3.3 Plate Tectonics
... transform boundary transform fault Suggested Activities/Strategies (District): 1. In the Phet Plate Tectonics Simulation, students explore how plates move on the surface of the earth and learn how to create new mountains, volcanoes, or oceans by changing temperature, composition, and thickness of pl ...
... transform boundary transform fault Suggested Activities/Strategies (District): 1. In the Phet Plate Tectonics Simulation, students explore how plates move on the surface of the earth and learn how to create new mountains, volcanoes, or oceans by changing temperature, composition, and thickness of pl ...
METAMORPHISM & METAMORPHIC ROCKS
... Deep-sea sediments, those found at depths greater than about 500 m, cover roughly two-thirds of the Earth. The predominant deep sediment is carbonate ooze, which covers nearly half the ocean floor ...
... Deep-sea sediments, those found at depths greater than about 500 m, cover roughly two-thirds of the Earth. The predominant deep sediment is carbonate ooze, which covers nearly half the ocean floor ...
HOT SPOT ACTIVITY
... sea floor of the North Pacific Ocean: the Pacific Ocean is mostly floored by a single tectonic plate (known as the "Pacific Plate") that is moving over the layer in the Earth known as the asthenosphere. This movement takes it to the northwest compared to the layers below it at a rate of 5 to 10 cm/y ...
... sea floor of the North Pacific Ocean: the Pacific Ocean is mostly floored by a single tectonic plate (known as the "Pacific Plate") that is moving over the layer in the Earth known as the asthenosphere. This movement takes it to the northwest compared to the layers below it at a rate of 5 to 10 cm/y ...
Geobit 10.indd
... other phenomena has provided the evidence that shows us the “how” of continental drift. The explanation of this process is called the theory of plate tectonics, and it answers all of these questions. Hot rock, like water rising in a boiling pot, moves up, rising to the surface in some areas. Once co ...
... other phenomena has provided the evidence that shows us the “how” of continental drift. The explanation of this process is called the theory of plate tectonics, and it answers all of these questions. Hot rock, like water rising in a boiling pot, moves up, rising to the surface in some areas. Once co ...
bridge - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... A convergent boundary is also known as a destructive plate boundary because of subduction. It is an actively deforming region where two (or more) tectonic plates or fragments of lithosphere move toward one another and collide. As a result of pressure, friction, and plate material melting in the mant ...
... A convergent boundary is also known as a destructive plate boundary because of subduction. It is an actively deforming region where two (or more) tectonic plates or fragments of lithosphere move toward one another and collide. As a result of pressure, friction, and plate material melting in the mant ...
Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]
... not immediately cause a stampede, for they were new and uncertain and people doubted their reliability. Meanwhile, American scientists had been measuring the magnetism of rocks on the sea floor, partly out of curiosity, partly because the US Navy hoped these measurements might suggest new means to h ...
... not immediately cause a stampede, for they were new and uncertain and people doubted their reliability. Meanwhile, American scientists had been measuring the magnetism of rocks on the sea floor, partly out of curiosity, partly because the US Navy hoped these measurements might suggest new means to h ...
Virtual Lab Igneous Rock ID
... Terms to know prior to completing this lab: intrusive, extrusive, plutonic, volcanic, texture, composition, mafic, felsic, intermediate, aphanitic, phaneritic, vesicular, porphyritic, pegmatitic, glassy. These are the terms you needed to know for the pre-lab quiz. PART 1: Fill in the following table ...
... Terms to know prior to completing this lab: intrusive, extrusive, plutonic, volcanic, texture, composition, mafic, felsic, intermediate, aphanitic, phaneritic, vesicular, porphyritic, pegmatitic, glassy. These are the terms you needed to know for the pre-lab quiz. PART 1: Fill in the following table ...
Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: The Geosphere Read the
... If we consider the physical properties of each layer, instead of chemistry, the Earth can be divided into five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces cal ...
... If we consider the physical properties of each layer, instead of chemistry, the Earth can be divided into five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces cal ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics •The Earth`s ______ is
... The place where two plates meet is called a plate boundary. •Different landforms are created at plate boundaries depending on the direction plates are moving and the type of crust involved. Plate Types: -Oceanic crust = very dense; thin (basalt) -Continental crust = less dense; thick (granite) Types ...
... The place where two plates meet is called a plate boundary. •Different landforms are created at plate boundaries depending on the direction plates are moving and the type of crust involved. Plate Types: -Oceanic crust = very dense; thin (basalt) -Continental crust = less dense; thick (granite) Types ...
Oceanography Chapter 11
... When two oceanic plates collide, the denser plate will be subducted. Some of the material from the melting oceanic plate rises upward to form a volcanic island arc. ...
... When two oceanic plates collide, the denser plate will be subducted. Some of the material from the melting oceanic plate rises upward to form a volcanic island arc. ...
Created with Sketch. Tectonic sandwiches
... The Earth’s crust is made up of large separate plates or areas that fit together rather like a huge jigsaw puzzle. They float on the partially molten mantle. Where the plates meet – the boundaries – movement happens. The plates can move apart, they can move horizontally past each other or they can m ...
... The Earth’s crust is made up of large separate plates or areas that fit together rather like a huge jigsaw puzzle. They float on the partially molten mantle. Where the plates meet – the boundaries – movement happens. The plates can move apart, they can move horizontally past each other or they can m ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.

















![Plate Tectonics [ TCD IE ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000728998_1-eea64118f8dd5f3d44e4d2914cefeaa2-300x300.png)




