Density of Earth Materials Lab - Mercer Island School District
... its average composition is similar to the rock granite. Granite is a felsic rock (which means it has a high feldspar and silica content), composed of quartz, potassium-rich feldspar, and mica. Mafic rocks contain denser minerals and therefore, oceanic crust is denser than continental crust (the aver ...
... its average composition is similar to the rock granite. Granite is a felsic rock (which means it has a high feldspar and silica content), composed of quartz, potassium-rich feldspar, and mica. Mafic rocks contain denser minerals and therefore, oceanic crust is denser than continental crust (the aver ...
Physical Geology 101*Midterm 1
... rock. The pebbles have an isotopic age of 300 millions years. The rock is ________ the pebbles contained within it? A. younger than B. older than C. same age as D. none of the above 14. We suspect that life began at the end of the Archean Eon or the beginning of the Hadean Eon. 15. Magnetic anomalie ...
... rock. The pebbles have an isotopic age of 300 millions years. The rock is ________ the pebbles contained within it? A. younger than B. older than C. same age as D. none of the above 14. We suspect that life began at the end of the Archean Eon or the beginning of the Hadean Eon. 15. Magnetic anomalie ...
Seismic evidence for convection-driven motion of the North
... Theoretical studies indicate that plate motion is primarily controlled (,90%) by convective flow driven by density heterogeneities in the mantle, particularly those associated with sinking oceanic slabs1,7–9. The nature and strength of viscous coupling of tectonic plates to mantle convection remains ...
... Theoretical studies indicate that plate motion is primarily controlled (,90%) by convective flow driven by density heterogeneities in the mantle, particularly those associated with sinking oceanic slabs1,7–9. The nature and strength of viscous coupling of tectonic plates to mantle convection remains ...
Volcanism I
... Recall that for the geotherm rolls over when radiogenic isotopes are in the crust ...
... Recall that for the geotherm rolls over when radiogenic isotopes are in the crust ...
Unlocking the Secrets of the Rocky Planets
... asthenosphere. The red isosurface represents cold high viscosity plate material from the surface that is sinking into the deeper mantle. The grid for this case has 10,649,730 cells and a spatial resolution of about 50 km. ...
... asthenosphere. The red isosurface represents cold high viscosity plate material from the surface that is sinking into the deeper mantle. The grid for this case has 10,649,730 cells and a spatial resolution of about 50 km. ...
Volcanoes
... from a single vent that have been blow in into the air, cooled and fallen around the vent. • Composite are steep sided volcanoes composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high viscosity lava, ash, and rock debris • Shield volcanoes are shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle wi ...
... from a single vent that have been blow in into the air, cooled and fallen around the vent. • Composite are steep sided volcanoes composed of many layers of volcanic rocks, usually made from high viscosity lava, ash, and rock debris • Shield volcanoes are shaped like a bowl or shield in the middle wi ...
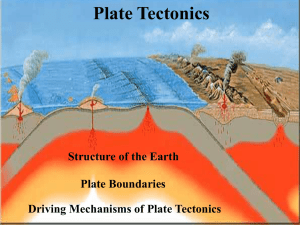
Plate Boundaries and Faults Notes
... – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, c. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the edges of the plates move side by side or back and forth to each other. The moving plates cause the crust to break creating friction that makes the rock melt and ro ...
... – the crust stretches but does not reach elastic limit and break, c. ocean ridges – from seafloor spreading. 3. Transform boundary – the edges of the plates move side by side or back and forth to each other. The moving plates cause the crust to break creating friction that makes the rock melt and ro ...
ZERNOLA: Irene Lopez, Leire Guerrico, Nagore Azkue
... and oceanic. The crust varies from 5 to 70km. Earth’s crust is a thin layer of dense rock about 5km thick. The continental crust is less dense, with lighter-colored rock that varies from 30 to 70 km thick. The continental crust is older. This photograph is the earth and there are all the layers. If ...
... and oceanic. The crust varies from 5 to 70km. Earth’s crust is a thin layer of dense rock about 5km thick. The continental crust is less dense, with lighter-colored rock that varies from 30 to 70 km thick. The continental crust is older. This photograph is the earth and there are all the layers. If ...
THE AZORES
... autonomous region of Portugal, 850 miles to the west. The Azores lie at a triple junction between the Eurasian, North American and African Plate. The Archipelago is also bisected by the mid Atlantic ridge (the solid black line running N-S in figure 1) The islands are of varying compositions ge ...
... autonomous region of Portugal, 850 miles to the west. The Azores lie at a triple junction between the Eurasian, North American and African Plate. The Archipelago is also bisected by the mid Atlantic ridge (the solid black line running N-S in figure 1) The islands are of varying compositions ge ...
Transform boundaries
... Transform boundaries – The plates move past each other, but because of friction, they cannot just glide past each other so build up stress, which is released as an earthquake. Divergent boundaries – The plates slide apart from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crust fro ...
... Transform boundaries – The plates move past each other, but because of friction, they cannot just glide past each other so build up stress, which is released as an earthquake. Divergent boundaries – The plates slide apart from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crust fro ...
Science and Technology I Mid
... seismograph to detect and record earthquakes. • Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale, which ranges from 0-10 (10 is the worst possible earthquake). ...
... seismograph to detect and record earthquakes. • Earthquakes are measured on the Richter scale, which ranges from 0-10 (10 is the worst possible earthquake). ...
Earth`s Interior
... (b) Seismic and density data along with assumptions based on meteorite composition, point to a largely iron core (c) The presence of Earth’s magnetic field also suggests a metallic core. ...
... (b) Seismic and density data along with assumptions based on meteorite composition, point to a largely iron core (c) The presence of Earth’s magnetic field also suggests a metallic core. ...
Plate Margins
... Subduction zone: describes the whole area where subduction is taking place. Ocean Trench: is the deep valley formed in the ocean floor as the subducted plate bends. Benioff zone: zone of earthquakes set off by the solid lithospheric plate forcing it’s way through the mantle. Island Arc: An arc of is ...
... Subduction zone: describes the whole area where subduction is taking place. Ocean Trench: is the deep valley formed in the ocean floor as the subducted plate bends. Benioff zone: zone of earthquakes set off by the solid lithospheric plate forcing it’s way through the mantle. Island Arc: An arc of is ...
Sigmundsson pages
... the onset of voluminous volcanic eruptions3. But the new observations imply that many grabens and single faults, even at continental rifts, might reflect dyke-induced faulting4,5, and might form and evolve through repeated events such as those that occurred in Ethiopia in 2005. An intermediate stage ...
... the onset of voluminous volcanic eruptions3. But the new observations imply that many grabens and single faults, even at continental rifts, might reflect dyke-induced faulting4,5, and might form and evolve through repeated events such as those that occurred in Ethiopia in 2005. An intermediate stage ...
FIELD OCCURRENCE OF PLUTONIC IGNEOUS ROCKS I. Basic
... Flat-lying sediments below, domes sediments above. ...
... Flat-lying sediments below, domes sediments above. ...
Directions: For questions with multiple choices please highlight your
... beneath them. The results of their studies affect building codes governing construction materials and techniques. This has made newer buildings safer than older ones. Because of the dangers, the Japanese people understand the importance of being prepared for disasters. Schoolchildren participate in ...
... beneath them. The results of their studies affect building codes governing construction materials and techniques. This has made newer buildings safer than older ones. Because of the dangers, the Japanese people understand the importance of being prepared for disasters. Schoolchildren participate in ...
Volcano Worksheet
... 4. To what are the moving plates compared? __________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________ ...
... 4. To what are the moving plates compared? __________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________ ...
Geology 200, Questions for Test 1, 2009
... B. slow cooling of the magma C. rapid cooling of the magma D. two periods of cooling An igneous rock consisting of broken fragments of crystals, shards of glass, and rock fragments has a: A. pyroclastic texture B. phaneritic texture C. glassy texture D. porphyritic texture The two dominant minerals ...
... B. slow cooling of the magma C. rapid cooling of the magma D. two periods of cooling An igneous rock consisting of broken fragments of crystals, shards of glass, and rock fragments has a: A. pyroclastic texture B. phaneritic texture C. glassy texture D. porphyritic texture The two dominant minerals ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.