Explore
... How are earthquakes distributed differently at each plate boundary type? Turn on the layer, New Zealand Quakes by depth 1930-2017. ? Do these earthquakes occur only at the boundary between plates? [No, they spread out - on one direction.] ? In what direction do the earthquakes become deeper? Comme ...
... How are earthquakes distributed differently at each plate boundary type? Turn on the layer, New Zealand Quakes by depth 1930-2017. ? Do these earthquakes occur only at the boundary between plates? [No, they spread out - on one direction.] ? In what direction do the earthquakes become deeper? Comme ...
The Earth`s Layers
... you measure the thickness of the Earth’s mantle on a continent, it would be between 35 and 75 kilometers thick. If measured from the deepest basins of the ocean, the mantle is only 5 to 10 kilometers thick. It is made up of brittle minerals like calcium and sodium. Because it is very cold compared t ...
... you measure the thickness of the Earth’s mantle on a continent, it would be between 35 and 75 kilometers thick. If measured from the deepest basins of the ocean, the mantle is only 5 to 10 kilometers thick. It is made up of brittle minerals like calcium and sodium. Because it is very cold compared t ...
class_intro
... • While at University of Marburg in 1911, Wegener was browsing in the library when he came across a paper that listed fossils of identical plants and animals found on opposite sides of the Atlantic (Brazil and Africa) • Intrigued, Wegener began to look for, and find, more cases of similar fossils se ...
... • While at University of Marburg in 1911, Wegener was browsing in the library when he came across a paper that listed fossils of identical plants and animals found on opposite sides of the Atlantic (Brazil and Africa) • Intrigued, Wegener began to look for, and find, more cases of similar fossils se ...
Homework Problem Set, Chapters 5 and 6, Week 3
... about 6 km thick, with the Upper Crust is made up of a 1 km thickness of extrusive (volcanic) basalts and upper feeder dikes, and the Lower Crust is a 5 km thick layer of lower dikes and gabbros (a frozen magma chamber). Calculate the total global production of oceanic crustal (including both upper ...
... about 6 km thick, with the Upper Crust is made up of a 1 km thickness of extrusive (volcanic) basalts and upper feeder dikes, and the Lower Crust is a 5 km thick layer of lower dikes and gabbros (a frozen magma chamber). Calculate the total global production of oceanic crustal (including both upper ...
File
... If there are a lot, the mineral will seem quite heavy compared to a less dense mineral which can seem light. Some lava rock is so light that it can float. This contributes to the ...
... If there are a lot, the mineral will seem quite heavy compared to a less dense mineral which can seem light. Some lava rock is so light that it can float. This contributes to the ...
Lab 2
... In the piedmont and mountain land regions of North Carolina, parent materials change when the rock type changes. Coastal Plain soils are formed from weathered and eroded rock particles that are moved by water and maybe alluvial or marine sediments. These sediments have similar minerals, so parent ma ...
... In the piedmont and mountain land regions of North Carolina, parent materials change when the rock type changes. Coastal Plain soils are formed from weathered and eroded rock particles that are moved by water and maybe alluvial or marine sediments. These sediments have similar minerals, so parent ma ...
Earth`s Physical Systems: Matter, Energy and
... geothermal heating gives rise to creative forces that shape our planet). Nine out of ten of the world’s earthquakes and over half of the world’s volcanoes occur on plate boundaries on the circum-Pacific belt, called “ring of ...
... geothermal heating gives rise to creative forces that shape our planet). Nine out of ten of the world’s earthquakes and over half of the world’s volcanoes occur on plate boundaries on the circum-Pacific belt, called “ring of ...
Science 7: Unit E – Topic 7 Notes: Mountains
... _________ – the downward or bottom part of the fold. _____________ – The upward or top part of the fold. Thrust Faulting and Fault Block Mountains ______ __________ – Sedimentary rock is broken into ...
... _________ – the downward or bottom part of the fold. _____________ – The upward or top part of the fold. Thrust Faulting and Fault Block Mountains ______ __________ – Sedimentary rock is broken into ...
Comparison of the Tectonic Conditions on Venus with Tectonic
... 2014) and defined by a friction coefficient (μ) within the range of 0.6–0.85 (Byerlee, 1978). It was shown earlier (Pilchin, 1986; Pilchin and Eppelbaum, 2002; Pilchin, 2005; Eppelbaum et al., 2014) that the serpentinization process takes part in every known obduction and every formation of ophiolit ...
... 2014) and defined by a friction coefficient (μ) within the range of 0.6–0.85 (Byerlee, 1978). It was shown earlier (Pilchin, 1986; Pilchin and Eppelbaum, 2002; Pilchin, 2005; Eppelbaum et al., 2014) that the serpentinization process takes part in every known obduction and every formation of ophiolit ...
7a earthquakes
... • About 8000 occur every day or one every 11 seconds • Caused by plates sliding beside each other (sliding/transform) • Tsunami - earthquake on the ocean floor: causing waves to become greater than 20 meters high ...
... • About 8000 occur every day or one every 11 seconds • Caused by plates sliding beside each other (sliding/transform) • Tsunami - earthquake on the ocean floor: causing waves to become greater than 20 meters high ...
Earth System Chapter 17 PowerPoint
... Continental Drift Evidence from Fossils – Similar fossils of several different animals and plants that once lived on land had been found on widely separated continents. – The ages of different fossils predated Wegener’s time frame for the breakup of Pangaea. – Fossils of Glossopteris, a seed fern th ...
... Continental Drift Evidence from Fossils – Similar fossils of several different animals and plants that once lived on land had been found on widely separated continents. – The ages of different fossils predated Wegener’s time frame for the breakup of Pangaea. – Fossils of Glossopteris, a seed fern th ...
Section 4: Sedimentary Rocks
... Ancient Egyptians used granite to build statues. Incas of Peru build fortresses from granite and other igneous rock. In the early 1900s, the U.S. used granite to build bridges and public buildings. Thin sheets of granite are used for curbstones and flooring. Basalt can be used for cobblestones or as ...
... Ancient Egyptians used granite to build statues. Incas of Peru build fortresses from granite and other igneous rock. In the early 1900s, the U.S. used granite to build bridges and public buildings. Thin sheets of granite are used for curbstones and flooring. Basalt can be used for cobblestones or as ...
SO YOU THINK YOU CAN DANCE SCIENCE?
... BOUNDARY IS WHEN TWO TECTONIC PLATES SEPARATE OR MOVE APART FROM EACH OTHER-MID-OCEAN RIDGE IS AN EXAMPLE OF THIS ...
... BOUNDARY IS WHEN TWO TECTONIC PLATES SEPARATE OR MOVE APART FROM EACH OTHER-MID-OCEAN RIDGE IS AN EXAMPLE OF THIS ...
Geologic Principles and Relative Dating
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
... a. ________________________________________________________ to the ages of other rock or events in the geological sequence b. Saying “ ________________________________________________” shows its age relative to a known. c. This means that geologists can say which layers are older than which and thus ...
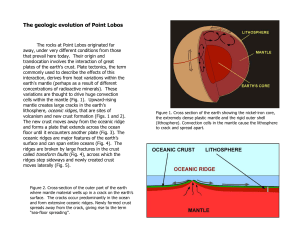
The geologic evolution of Point Lobos
... rest of the Carmelo Formation at Point Lobos, which is composed primarily of conglomerate and sandstone. Fossils are very scarce in this latter rock, but microfossils collected from mudstone at Hidden Beach indicate deep (600 to 2000 feet) marine deposition during the early Eocene (Fig. 14). Sedimen ...
... rest of the Carmelo Formation at Point Lobos, which is composed primarily of conglomerate and sandstone. Fossils are very scarce in this latter rock, but microfossils collected from mudstone at Hidden Beach indicate deep (600 to 2000 feet) marine deposition during the early Eocene (Fig. 14). Sedimen ...
Transitional I-S type characteristics in the Main Range Granite of
... Lachlan Fold Belt and consistent with the I-type features. Thus it is likely that the source rocks of the Main Range Granite were either mildly peraluminous or mildly metaluminous in character. Partial melting of these source rocks will give rise to a mildly peraluminous magma. It is however a part ...
... Lachlan Fold Belt and consistent with the I-type features. Thus it is likely that the source rocks of the Main Range Granite were either mildly peraluminous or mildly metaluminous in character. Partial melting of these source rocks will give rise to a mildly peraluminous magma. It is however a part ...
Section 20.1 - CPO Science
... 20.1 Measuring earthquakes The Moment Magnitude scale rates the total energy released by an earthquake. The numbers on this scale combine energy ratings and descriptions of rock movements. Seismologists tend to use the more ...
... 20.1 Measuring earthquakes The Moment Magnitude scale rates the total energy released by an earthquake. The numbers on this scale combine energy ratings and descriptions of rock movements. Seismologists tend to use the more ...
Bedrock Geology Glossary
... Shale: A deposit of clay, silt, or mud solidified into more or less a solid rock. Siltstone: A sedimentary rock made primarily of sand. ...
... Shale: A deposit of clay, silt, or mud solidified into more or less a solid rock. Siltstone: A sedimentary rock made primarily of sand. ...
Microsoft Word - Plate Tectonics Lab
... 2. What directions do the plates move relative to one another in a divergent plate boundary? ...
... 2. What directions do the plates move relative to one another in a divergent plate boundary? ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.